Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae: Difference between revisions
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
==Genome Structure== | ==Genome Structure== | ||
The approximate size of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae's genome is 1,787,941 base pairs. However, the size can depend on the strain of the bacteria. It has one chromosome and it is circular. Another interesting feature of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae is that it produces H2S, which can allow the bacteria to thrive once inside a host. It can be easily differentiated by the fact that it has little to no mobility. What we know about the sequence is that the bacteria has virulence genes. Virulence genes help the bacteria to invade the host more successfully. It also had metabolic genes that let the bacteria change and adapt to fit whatever environment it enters. Strains Sy1027 and Fujisawa have been entirely sequenced which helps us understand more about the bacteria. | |||
==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ||
Revision as of 01:47, 27 November 2024
Classification
Bacteria; Bacillota; Erysipelotrichia; Erysipelotrichales; Erysipelotrichaceae; Erysipelothrix.
Species
|
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae: [1] |
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
Description and Significance
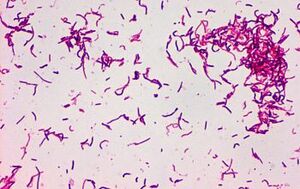
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae is a gram-positive bacteria, and is also in the shape of a rod. It is found predominantly in soil and water that has been infected by an animal containing the bacteria. One of the primary animals susceptible to it are pigs. This bacteria has a longer lifespan and can live for weeks in soil or animal matter. This is all important to not only protect animals from it, but humans as well. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae is zootonic which means it can jump from animals to humans. Being able to safely manage this bacteria is important for the health of humans.
Genome Structure
The approximate size of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae's genome is 1,787,941 base pairs. However, the size can depend on the strain of the bacteria. It has one chromosome and it is circular. Another interesting feature of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae is that it produces H2S, which can allow the bacteria to thrive once inside a host. It can be easily differentiated by the fact that it has little to no mobility. What we know about the sequence is that the bacteria has virulence genes. Virulence genes help the bacteria to invade the host more successfully. It also had metabolic genes that let the bacteria change and adapt to fit whatever environment it enters. Strains Sy1027 and Fujisawa have been entirely sequenced which helps us understand more about the bacteria.
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Interesting features of cell structure; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces.
Ecology and Pathogenesis
Habitat; symbiosis; biogeochemical significance; contributions to environment.
If relevant, how does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.
References
Microbe Canvas. "Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae." Dept. Medical Microbiology and Infectious diseases.
Author
Page authored by Isabelle Oberdorf, Makayla Watson, Keanna Teodoro, & Jacqui Olsen, students of Prof. Bradley Tolar at UNC Wilmington.