Oleispira antarctica: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
[https://enviromicro-journals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/1462-2920.14956 Gregson BH, Metodieva G, Metodiev MV, Golyshin PN, McKew BA. 2020. Protein expression in the obligate hydrocarbon‐degrading psychrophile oleispira antarctica RB‐8 during alkane degradation and cold tolerance. Environmental Microbiology 22:1870–1883.] | [https://enviromicro-journals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/1462-2920.14956 Gregson BH, Metodieva G, Metodiev MV, Golyshin PN, McKew BA. 2020. Protein expression in the obligate hydrocarbon‐degrading psychrophile oleispira antarctica RB‐8 during alkane degradation and cold tolerance. Environmental Microbiology 22:1870–1883.] | ||
[https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms3156 Kube M, Chernikova TN, Al-Ramahi Y, Beloqui A, Lopez-Cortez N, Guazzaroni M-E, Heipieper HJ, Klages S, Kotsyurbenko OR, Langer I, Nechitaylo TY, Lünsdorf H, Fernández M, Juárez S, Ciordia S, Singer A, Kagan O, Egorova O, Alain Petit P, Stogios P, Kim Y, Tchigvintsev A, Flick R, Denaro R, Genovese M, Albar JP, Reva ON, Martínez-Gomariz M, Tran H, Ferrer M, Savchenko A, Yakunin AF, Yakimov MM, Golyshina OV, Reinhardt R, Golyshin PN. 2013. Genome sequence and functional genomic analysis of the oil-degrading bacterium oleispira antarctica. Nature Communications 4.] | |||
[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/genome/GCF_000967895.1/ Planck M. 2013. Oleispira Antarctica RB-8 genome assembly ASM96789v1 - NCBI - NLM. National Center for Biotechnology Information. U.S. National Library of Medicine.] | |||
[https://academic.oup.com/femsec/article/49/3/419/584773 Yakimov MM, Gentile G, Bruni V, Cappello S, D’Auria G, Golyshin PN, Giuliano L. 2004. Crude oil-induced structural shift of coastal bacterial communities of Rod Bay (terra nova bay, Ross Sea, Antarctica) and characterization of cultured cold-adapted hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 49:419–432.] | [https://academic.oup.com/femsec/article/49/3/419/584773 Yakimov MM, Gentile G, Bruni V, Cappello S, D’Auria G, Golyshin PN, Giuliano L. 2004. Crude oil-induced structural shift of coastal bacterial communities of Rod Bay (terra nova bay, Ross Sea, Antarctica) and characterization of cultured cold-adapted hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 49:419–432.] | ||
[https://www.microbiologyresearch.org/content/journal/ijsem/10.1099/ijs.0.02366-0 Yakimov MM, Giuliano L, Gentile G, Crisafi E, Chernikova TN, Abraham W-R, Lünsdorf H, Timmis KN, Golyshin PN. 2003. Oleispira Antarctica gen. Nov., sp. nov., a novel hydrocarbonoclastic marine bacterium isolated from Antarctic Coastal Sea Water. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 53:779–785.] | [https://www.microbiologyresearch.org/content/journal/ijsem/10.1099/ijs.0.02366-0 Yakimov MM, Giuliano L, Gentile G, Crisafi E, Chernikova TN, Abraham W-R, Lünsdorf H, Timmis KN, Golyshin PN. 2003. Oleispira Antarctica gen. Nov., sp. nov., a novel hydrocarbonoclastic marine bacterium isolated from Antarctic Coastal Sea Water. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 53:779–785.] | ||
[https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/aem.01896-22 Zhang W, Liu Y, Zheng K, Xing J, Li Q, Gu C, Wang Z, Shao H, Guo C, He H, Wang H, Sung YY, Mok WJ, Wong LL, Liang Y, McMinn A, Wang M. 2023. Discovery of an abundant viral genus in polar regions through the isolation and genomic characterization of a new virus againstoceanospirillaceae. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 89.] | |||
==Author== | ==Author== | ||
Revision as of 16:50, 2 December 2024
Classification
cellular organisms; Bacteria; Pseudomonadati; Pseudomonadota; Gammaproteobacteria; Oceanospirillales; Oceanospirillaceae
Species
|
NCBI: [1] |
Oleispira O. antarctica
Genus species
Description and Significance
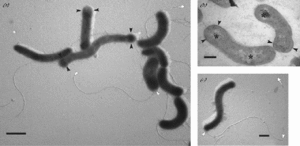
Oleispira antarctica is a gram-negative bacterium. The size of O. antarctica can vary from 2-5 μm long and 0.4-0.8 μm wide. They tend to be wider towards the ends and thinner in the middle. O. antarctica have a singular, polar flagella that aids in movement.
Oleispira antarctica is found in cold, shallow sea water in Rod Bay, in the Ross Sea, Southern Antarctica. They experience optimum growth between 1°C and 15°C and a salinity of 0.25 M and 1 M.
Oleispira antarctica plays an important role cold marine water environments. Being a cold-adapted bacteria allows them to function and survive in frigid waters. O. antarctica has the ability to break down petroleum hydrocarbons, which is useful in cleaning up harmful oil spills in the oceans surrounding Antarctica.
Genome Structure
Oleispira is classified as a psychrophile. The size of Oleispira antarctica’s genome is around 4.4 Mb According to the ncbi.nih.nih database and contains around 3,557 protein-coding genes. Oleispira antarctica has a singular circular chromosome. This bacterium is a member of the Gammaproteobacterial class and has adapted to thrive in low-temperature environments by using hydrocarbons as a primary energy source. The genome has genes that support cold adaptation, membrane fluidity and specialized metabolic pathways for breaking down alkanes and other hydrocarbons in the waters/oceans. Oleispira antarctica’s unique genetic features and energy requirements allow it to be utilized in oil spill clean-up. The bacterium genome highlights its importance in polar marine ecology and its potential application in environmental biotechnology.
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Oleispira antarctica are gram-negative bacteria that are vibrioid or spirillus shaped but can change based on environmental conditions. The morphology can change between cocci, bacillus, and spirillus shapes. The cells are around 2-5μm with more recent studies finding smaller cells on average with lengths of around 1.2μm (Gentile et al., 2020). They are motile cells with one polar flagellum. O. antarctica is a species of aerobic bacteria that are chemoorganoheterotrophs that grow in aliphatic alkanes which are hydrocarbons made up of single covalent bonds (Gregson et al., 2020). They are able to degrade hydrocarbons such as Deisel for energy and produce fatty acids and alcohols in the process (Gentile et al., 2016).
Ecology and Pathogenesis
Habitat; symbiosis; biogeochemical significance; contributions to environment.
If relevant, how does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.
References
Author
Page authored by Trinity O'Neal, Kaliany Vazquez, Savion Powell, & Dylan Price, students of Prof. Bradley Tolar at UNC Wilmington.