Nanoarchaeum: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Discovered as being tiny dots on another organism, ''Nanoarchaeum'' was published as being an organism in need of a new phylum among the Archaea. They have not been able to grown on their own and while a parasitic lifestyle cannot be excluded at present, there have been several observations that promote a symbiotic mode of life. Since the original publication, there have been nanoarchaeotal 16 S rDNA sequences found in high temperature biotopes all over the world that are related to Nanoarchaeum but need to be classified in different families. < | {| | ||
| height="69" bgcolor="#FFDF95" | | |||
'''NCBI:<br />[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&id=193568&lvl=3&lin=f&keep=1&srchmode=1&unlock Taxonomy]<br />[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/framik.cgi?db=Genome&gi=376 Genome] ''' | |||
|} | |||
[[Image:nanoarchaeum_1.JPG|thumb|300px|right|''Ignicoccus'' sp. with four ''Nanoarchaeum'' cells attached. Scale bar = 1.0um. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=retrieve&db=pubmed&list_uids=11986665&dopt=Abstract Courtesy of Huber et al. (2002).]]] | |||
==Classification== | |||
===Higher order taxa:=== | |||
Archaea; Nanoarchaeota | |||
===Species:=== | |||
''Nanoarchaeum equitans'' | |||
==Description and Significance== | |||
[[Image:nanoarchaeum_3.JPG|frame|200px|right|Five ''N. equitans'' cells attacted to ''Ignicoccus'' cell. bar = 1um. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=12706504&dopt=Citation Image courtesy of Huber et al.]]] | |||
Discovered as being tiny dots on another organism, ''Nanoarchaeum'' was published as being an organism in need of a new phylum among the Archaea. They have not been able to grown on their own and while a parasitic lifestyle cannot be excluded at present, there have been several observations that promote a symbiotic mode of life. Since the original publication, there have been nanoarchaeotal 16 S rDNA sequences found in high temperature biotopes all over the world that are related to ''Nanoarchaeum'' but need to be classified in different families. | |||
==Genome Structure== | |||
''Nanoarchaeum'' has a tiny genome with only 490 kb, which represents the smallest archaeal genome to date. Comparing ss rRNA sequences, it was noted that sequence identities were more like archaeon than bacterial species. There was no difference, however, in the sequence identity to the Crenarchaeota, Euryarchaeota, and 'Korarchaeota', indicating it represents a new archaeal phylum. | |||
It is very common for parasitic and symbiotic bacteria to have small genomes. They can develop these by the elimination of unneeded genes and the acquisition of new genes by lateral gene transfer. It is possible that ''N''. ''equitans'' had a size reduction during adaptation to ''Ignicoccus'' or it could be an ancient genome since it is assumed that the genomes of the first microorganisms were small. | |||
Recently, the genome of ''[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/framik.cgi?db=Genome&gi=376 Nanoarchaeum equitans Kin4-M]'' was sequenced. | |||
==Cell Structure and Metabolism== | |||
[[Image:nanoarchaeum_2.JPG|thumb|250px|right|''N. equitans'' attached to the outer membrane of ''Ignicoccus''. Scale bar = 1.0um. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=retrieve&db=pubmed&list_uids=11986665&dopt=Abstract Courtesy of Huber et al. (2002)]]] | |||
These coccus cells are only 400 nm in diameter and are covered by an S-layer. They require cell-cell contact with an actively growing ''Ignicoccus'' cell in order to grow. No negative effects have been observed on ''Ignicoccus'' cells with the addition of ''Nanoarchaeum'', hinting at a possible non-parasitic lifestyle. This new ''Ignicoccus'' species that has been found as a ''Nanoarchaeum'' host, is an autotrophic sulfur-reducing thermophile. | |||
==Ecology== | |||
This new microorganism was first identified from hot rocks taken at Kolbeinsey ridge, north of Iceland. This hydrothermal system is located at the subpolar Mid-Atlantic Ridge at a depth estimated at 106m. ''N. equitans'' can grow in the same temperature range as its host, which is 70-98<font size="-1"><sup>o</sup></font>C, a pH around 6.0, and salt concentrations of about 2% NaCl. They grow on ''Ignicoccus'' cells in what is either a symbiotic or parasitic relationship. | |||
Other nanoarchaeotal 16S rRNA genes have been obtained from the East Pacific Rise (pH 6.5), the Obsidian Pool in Yellowstone National Park (80<font size="-1"><sup>o</sup></font>C, pH 6.0), and Caldera Uzon in Kamchatka, Russia (85<font size="-1"><sup>o</sup></font>C, pH 5.5). | |||
==References== | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=retrieve&db=pubmed&list_uids=11986665&dopt=Abstract Huber et al. 2002. A new phylum of Archaea represented by a nanosized hyperthermophilic symbiont. Nature 417: 63-67.] | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=12706504&dopt=Citation Huber et al. 2003. The phylum Nanoarchaeota: Present knowledge and future perspectives of a unique form of life. Research in Microbiology 154: 165-171]. | |||
Revision as of 20:25, 20 June 2006
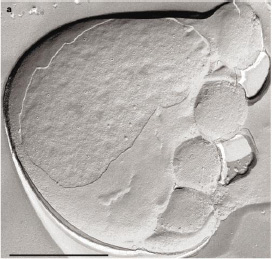
Classification
Higher order taxa:
Archaea; Nanoarchaeota
Species:
Nanoarchaeum equitans
Description and Significance
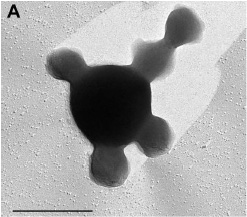
Discovered as being tiny dots on another organism, Nanoarchaeum was published as being an organism in need of a new phylum among the Archaea. They have not been able to grown on their own and while a parasitic lifestyle cannot be excluded at present, there have been several observations that promote a symbiotic mode of life. Since the original publication, there have been nanoarchaeotal 16 S rDNA sequences found in high temperature biotopes all over the world that are related to Nanoarchaeum but need to be classified in different families.
Genome Structure
Nanoarchaeum has a tiny genome with only 490 kb, which represents the smallest archaeal genome to date. Comparing ss rRNA sequences, it was noted that sequence identities were more like archaeon than bacterial species. There was no difference, however, in the sequence identity to the Crenarchaeota, Euryarchaeota, and 'Korarchaeota', indicating it represents a new archaeal phylum.
It is very common for parasitic and symbiotic bacteria to have small genomes. They can develop these by the elimination of unneeded genes and the acquisition of new genes by lateral gene transfer. It is possible that N. equitans had a size reduction during adaptation to Ignicoccus or it could be an ancient genome since it is assumed that the genomes of the first microorganisms were small.
Recently, the genome of Nanoarchaeum equitans Kin4-M was sequenced.
Cell Structure and Metabolism

These coccus cells are only 400 nm in diameter and are covered by an S-layer. They require cell-cell contact with an actively growing Ignicoccus cell in order to grow. No negative effects have been observed on Ignicoccus cells with the addition of Nanoarchaeum, hinting at a possible non-parasitic lifestyle. This new Ignicoccus species that has been found as a Nanoarchaeum host, is an autotrophic sulfur-reducing thermophile.
Ecology
This new microorganism was first identified from hot rocks taken at Kolbeinsey ridge, north of Iceland. This hydrothermal system is located at the subpolar Mid-Atlantic Ridge at a depth estimated at 106m. N. equitans can grow in the same temperature range as its host, which is 70-98oC, a pH around 6.0, and salt concentrations of about 2% NaCl. They grow on Ignicoccus cells in what is either a symbiotic or parasitic relationship.
Other nanoarchaeotal 16S rRNA genes have been obtained from the East Pacific Rise (pH 6.5), the Obsidian Pool in Yellowstone National Park (80oC, pH 6.0), and Caldera Uzon in Kamchatka, Russia (85oC, pH 5.5).
