Nosema ceranae: Difference between revisions
Laceyberry (talk | contribs) |
Laceyberry (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
[4]Hernandez, R., Meana,A., Palencia,P., Marín, P., Botías,C., Bailon, E., Barrios, L. and Higes, M., 2009. Effect of Temperature on the Biotic Potential of Honeybee Microsporidia. Applied and Enviromental Microbiology 75(8):2554. | [4]Hernandez, R., Meana,A., Palencia,P., Marín, P., Botías,C., Bailon, E., Barrios, L. and Higes, M., 2009. Effect of Temperature on the Biotic Potential of Honeybee Microsporidia. Applied and Enviromental Microbiology 75(8):2554. | ||
[5]Higes, M., Garcia-Palencia, P., Martin-Hernandez, R. and Meana, A. 2006. Experimental infection of Apis mellifera honeybees with Nosema ceranae (Microsporidia). Journal of Invertbrate Pathology 94: 211-217. | |||
Revision as of 16:27, 5 December 2011
WIKI IN PROGRESS
Ex. [[]]
Characteristics of the symbiont/pathogen
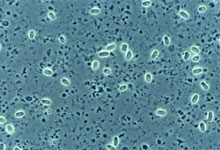
Nosema ceranae, a microsporidium fungi, is part a member of the Nosematidae family. N. ceranae is a spore forming, rod or oval shaped microbe that measures approximately 3.9-5.3 µm in length and 2.0-2.5 µm in width. Nosema ceranae has three developmental stages: Meronts, which is the earliest stage, and during this stage the plasma membrane of the microbe makes direct contact with the cytoplasm of the host. During sporont stage the microbe becomes elongated and oval and consists of a dense cytoplasm, yet there is no distinct internal structures. The third stage is the Sporoblast stage, the microbe is smaller during this stage than the sporont stage, and has a distinct cell wall as well as two nuclei [2]. A complete sequencing of N. ceranae's genome, it was shown to consists of 7.86 MB and a strong AT bias [3].
Characteristics of the host
The symbiont relationship with N. ceranae and the honey bee originated in the Asian honey bee Apis cerana, but has since then switched host to infect the European honey bee Apis mellifera. Nosema ceranae infects most of the honey bees found in Europe and North America [3].
Host-Symbiont Interaction
N. ceranae and the honeybee have a obligate parasitic relationship, meaning that the N. ceranae benefits while the honey bee is harmed throughout the process. N. ceranae forms spores which are then ingested by the honey bee through water or food. These spores then invade the gut epithelium immediately [3]. However, it is not until day 6 or 7 that symptoms are visible and usually by day ten mortality has occurred in those infected by N. ceranae []. The spores rapidly multiply in the gut and then are excreted and the spores are transferred to the other honeybees that live in the same colony through the cleaning and feeding activities [2]. Nosema ceranae decrease the ability of the honey bee to obtain nutrients from the environment which ultimately shortens their lifespan. Nosema ceranae can effect the overall colony growth and hinder winter survival [3].
Molecular Insights into the Symbiosis
Describe molecular/genetic studies on the symbiosis.
Ecological and Evolutionary Aspects
This symbiont relationship between Nosema ceranae and Apis mellifera is a recent discovery, and new studies are continually done to uncover more about this parasitic relationship. Originally Nosema ceranae infected the Asian honey bee (Apis cerana), but has since then swtiched to the European honey bee (Apis mellifera). It is unknown when and how this switch occurred, and researchers are unsure if the predominant parasite of honey bees in Europe and North America still remains N. apis or N. ceranae has taken over [3]. The biological cycle of Nosema ceranae relies on the temperature. Nosema ceranae effects more cells when kept at a constant temperature, but is a better adapter to conditions the other species such as "Nosema apis. N. ceranae unlike N. apis can infect their host in all four seasons, while N. apis usually only infects their host in the milder seasons such as spring and autumn [4]. This may be because N. ceranae has been found as a more generalized infection, meaning it is able to grow and multiply in other tissues other then just the gut [].
Recent Discoveries
In past studies it was though that N. ceranae was becoming the more prevalent parasite to the Honey bee, however recent studies have shown otherwise. N. apis in a 5 year study showed to grow in greater quantity then N. ceranae except in one colony. However it was also found that N. ceranae is a more general infection, which has displayed the ability to grow in other tissues then just the gut. In this five year study N. ceranae was observed to grow in not only the gut, but the hypopharyneal glands, salivary glands, malpighian tubes and fat bodies, and the brain. This could account for the hypothesis that N. ceranae causes more deaths then N. apis. It was also found that N. ceranae during the germination process when exposed to low temperature decreased to less the 10 percent. The remaining spores that where able to germinate were unusually short and most likely did not complete the true germination process.
References
[Sample reference] [[2] Seemanapalli SV, Xu Q, McShan K, Liang FT. 2010. Outer surface protein C is a dissemination-facilitating factor of Borrelia burgdorferi during mammalian infection. PLoS One 5:e15830.]
[1] http://www.diark.org/img/species_pict/Nosema_ceranae_BRL01
[2]Chen,Y., Evans,J., Murphy,C., Gutell,R., Zuker,M., Gundensen-Rindal,D and Pettis,J. 2009. Morphological, molecular, and phylogenetic characterization of Nosema ceranae, a microsporidian parasite isolated from the European honey bee, Apis mellifera. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology 56: 142-147.
[3]Cornman, R., Chen, Y., Schatz,M., Street,C., Zhao,Y., Desany, B., Egholm, M., Hutchison, S., Pettis, J., Lipkin and W., Eva, J. 2009. Genomic Analyses of the Microsporidian Nosema ceranae, an Emergent Pathogen of Honey Bees. PLoS Pathogens 5(6): e1000466.
[4]Hernandez, R., Meana,A., Palencia,P., Marín, P., Botías,C., Bailon, E., Barrios, L. and Higes, M., 2009. Effect of Temperature on the Biotic Potential of Honeybee Microsporidia. Applied and Enviromental Microbiology 75(8):2554.
[5]Higes, M., Garcia-Palencia, P., Martin-Hernandez, R. and Meana, A. 2006. Experimental infection of Apis mellifera honeybees with Nosema ceranae (Microsporidia). Journal of Invertbrate Pathology 94: 211-217.
Edited by [Lacey Berry], student of Grace Lim-Fong