Lipothrixviridae
Baltimore Classification
Higher order taxa
Viruses; dsDNA viruses, no RNA stage; Lipothrixviridae
Genera
Alphalipothrixvirus, Betalipothrixvirus, Gammalipothrixvirus
Description and Significance
Lipothrixviridae is a family crenarchaeal viruses. It is by far the most diverse family of crenarchaeal viruses, with six isolates divided into three genera: Alphalipothrixvirus, Betalipothrixvirus, and Gammalipothrixvirus. Alphalipothrixvirus contains TTV1, TTV2, and TTV3, isolated from acidic hot springs Iceland. Betalipothrixvirus contains SIFV, also isolated in Iceland. Finally, Gammalipothrixvirus is represented by AFV1, isolated from Yellowstone National Park. (sources: Häring et al., Ortmann et al.)
Genome Structure
The genome of Lipothrixviridae is not segmented and contains a single molecule of linear double-stranded DNA. The complete genome is 16000 nucleotides long. (source: ICTVdB)
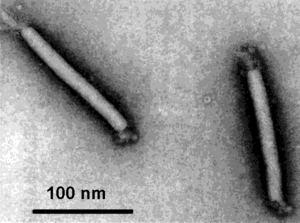
Virion Structure of a Lipothrixviridae
The virions of Lipothrixviridae consist of an envelope and a nucleocapsid. The virus capsid is enveloped and the virions are rod-shaped, rigid and have protrusions extending from the core through the envelope that arise asymmetrically from both ends. The virions measure 38 nm in diameter and are 410 nm long with a tight fitting membrane. The envelope has no surface projections. The capsid is elongated and exhibits helical symmetry and the core is helical. (source: ICTVdB)
Reproductive Cycle of a Lipothrixviridae in a Host Cell
Viral Ecology & Pathology
The Lipothrixviridae infect both acidophilic thermophiles (such as Sulfolobus and Acidianus species) as well as thermophiles from more neutral environments (such as Thermoproteus tenax). Like most crenarchaeal viruses, the Lipothrixviridae set up chronic infections rather than lytic infections (i.e., the host cell is not lysed). (source: Ortmann et al.)
References
ICTVdB - The Universal Virus Database, version 3. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ICTVdb/ICTVdB/
Ortmann et al. "Hot crenarchaeal viruses reveal deep evolutionary connections." Nature Reviews Microbiology 4 (2006): 520-528.
