SARS-CoV nsp7 and nsp8
Introduction
The outbreak of SARS in Hong Kong almost caused and pandemic and created a worldwide panic. From late 2002 to July 2003, there were about 8,273 cases and 775 deaths. People who are infected often have muscle pain, headache, fever as well as respiratory symptoms such as cough and pneumonia. The disease is known to infect older people with mortality rate the highest for those over 50 years old. Also known as severe acute respiratory syndrome, SARS has not been eradicated and can return to infect the human population. Since no antibiotics, antivirals, steroids, and therapies are known to be effective against this viral disease, it has become a top priority for the government and public health scientists around the world to identify and develop vaccines and medicine to prevent another outbreak.
Severe acute respiratory syndrome is caused by a SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV). SARS-CoV is a positive strand RNA virus that causes respiratory and enteric disease. Viral replication of the coronavirus genome replication takes place in the cytoplasm. Infection by the coronavirus can alter cell cycle, transcription and translation pattern as well as induce apoptosis and inflammation. SARS-CoV was identified by a number of laboratories to be the main cause of SARS. In April 2003, Michael Smith Genome Sciences Centre, located in Vancouver, became the first lab in the world to sequence the coronavirus that causes SARS using samples from infected patients in Toronto. The mapping of the SARS-CoV is a step forward to fighting SARS. With this sequence, scientists can began to understand more about the coronavirus structure, function and genome replication as well as began antiviral research against SARS coronavirus.
The discovery of the SARS-CoV has propelled extensive studies on its viral replication. Non-structural proteins 7 and 8 (nsp(7+8)) have been identified to be involved in the coronavirus replication and transcription. Furthermore, the interaction between nsp(7+8) is important for RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) activities of the SARs-coronavirus genome. By understanding the structures of these non-structural proteins, scientists are one step closer to decipher the mechanism of SARS-CoV genome replication and may even use them to develop new strategies for the prevention or treatment of SARS in animals and humans.
Structures and interactions of nsp 7 and nsp 8
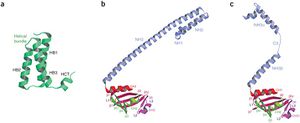
The transcription and replication machinery of SARS-CoV can be understood from its structure. Yujia Zhai et al., was able to present the crystal structure of the hexadecameric nsp7-nsp8 supercomplex of SARS-CoV at 2.4-A resolution. This structure is considered to be the first to show interactions between coronavirus replication proteins as well as the architecture of the coronavirus replication and transcription machinery.
The structure of the supercomplex resembles a hollow cylinder with a central channel that has two handles protruding from opposite sides. It is assembled from eight copies of nsp8 and bound tightly together by eight copies of nsp7. Nsp7 is an alpha helical protein of about 10kDA. It has single domain with a novel fold that consists of five helical secondary structures. The interhelical side-chain interactions that stabilize and hold the helices together have residues that are predominantly hydrophobic. Nsp7 localizes to cytoplasmic membrane structures that are also known to be the sites of viral replication in infected cells. SARS-CoV nsp7 dimerizes and interact with other protein such as nsp5, nsp8, nsp9 and nsp13. Nsp7 central core consists of an N-terminal helical bundle (HB) that contains helices HB1, HB2, and HB3. Its HB region is conserved and is known to interact with nsp8. Nsp8 has a molecular mass of about 22kDa and is unique for coronaviruses. The four monomers of nsp8 has two different conformations: nsp8I and nsp8II. Nsp8I is described as a “golf-club” like structure composed of an N-terminal “shaft” domain that contains three helices (NH1-3) and a C-terminal “head” domain while nsp8II 2 has a similar “head” domain, but its shaft helix NH3 bends into two shorter helices.
RdRp activities driven b nsp(7+8) complex
There are two RdRp activities that are believed to be involved in replication of SARS-CoV genome. The first activity involves the 106-kDa nsp12 while the second polymerase involves the 22-kDa nsp8. Nsp8 is unique for CoVs and is the only protein reported to be capable of de novo RNA synthesis. De novo synthesis is the synthesis of complex molecules from simple molecules.
The supercomplex of nsp7 and nsp8 is known to be a unique RNA polymerase. Although nsp8 is capable of RdRp activities on its own, it is known to co-crystallize and form a unique hexadecameric ring-structure with nsp7. Aartijan J.W. te Velthuis et al., studied the relationship of nsp7 and nsp8 complex to RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) activities for the RNA virus, SARS-CoV. They found that exposure of nsp8’s natural N-terminal residue was important for its ability to associate with nsp7 as well also boosting its RdRp activity
To examine whether nsp7 improve nsp8’s function and capability to bind to RNA, measurement of dsRNA was measured using fixed concentration of nsp7 with either wild-type or mutant nsp8. Without the presence of nsp9, no RNA binding was observed. However, the presence of the formation of the nsp7+8 complex created an increase in the number of bound dsRNA. Furthermore, increase in the bindng affinity for RNA was also observed for nsp8 RNA-binding mutant K58A and D52A. These results show that the addition of nsp7 must have evolved to enhance RNA binding by nsp8.
Primer extension activity is also found in the nsp 7+8 complex. To verify that the activity was nsp(7+8) derived and to identify the most critical residues for activity in the complex, a set of mutations were designed. The study found that mutation of the conserved N-terminal D/ExD/E motif, with D50 and D52 in SARS-CoV, stopped RdRp activity. Mutation of the C-terminal motif, with SARS-CoV residues D161 and D163, did not stop the polymerase activity
Further experiment shows the importance of nsp7 to nsp8 and its primer extension activity. The nsp7 is shown to directly increase the primer extension activity that is driven by the nsp8. The comparison of two enzyme complexes found that the primer extension activity of nsp8 alone was less than 2-fold lower than when nsp7 and nsp8 were present at equal molarity.
Interaction of the nsp7 and nsp 8 with double stranded (ds)RNA
The structure and interaction of the nsp7-nsp8 supercomplex covey that its role is to bind nucleic acids The inner channel of the complex has positive potential while the outer surface is covered by negative potential. This charge distribution allows the phosphate backbone of nucleic acids to pass through the channel without electrostatic repulsion. The hollow cylindrical structure of the supercomplex also helps to facilitate coronavirus replication. Replication of the coronavirus occurs in the cytoplasm of infected cells and double (ds) RNA intermediate is required for this replication during RNA synthesis. The hollow cylindrical of the supercomplex encircles and stabilize dsRNA, holding the nascent and template strands together for transcription and replication. Furthermore, the high conservation of nsp7 and nsp8 in coronaviruses indicates that they are a general component for all coronaviruses. The discovery that dsRNA and the supercomplex is a natural binding partner can be useful for antiviral research for SARS. Peptides compounds can be designed to mimic the interaction between nsp7 and nsp8 to block supercomplex formation and prevent virus replication. The structure of the supercomplex can also be used to design drugs to treat SARS.
Conclusion
Recent studies on the structures of nsp 7 and nsp 8 have provided important insight on SARS-CoV. Scientists discovered that nsp 7 and nsp 8 do not only interact with each other, but that nsp 8 is dependent upon nsp 7. This interaction and dependency is important for SARS-CoV genome replication. Furthermore, the hollow cylindrical structure of the supercomplex of nsp 7 and nsp 8 are important for the facilitation of the coronavirus replication. Without these structures, the RdRp activities are limited
Although discovery of these non-structural proteins have allowed scientists to better understand the replication of SARS-CoV, more experiments are needed in order to better understand the function of nsp 7 and nsp 8. For example, there are two RdRp activities, with either nsp 12 or nsp(7+8), that are involved in the replication of SARS-CoV genome. However, not much is know whether these two polymerase activities are within the same enzyme complex or whether they can influence each other's activity.
Since nsp 7 and nsp 8 are known to be important to the replication of SARS-CoV, it is also important for future research to study how they can be used to treat diseases that are caused by this virus. It is crucial to began intensive antiviral research using nsp 7 and nsp8 as models to develop drugs and vaccines since SARS has not been eradicated and a potential outbreak may occur in the future.
References
Edited by (Amy Tran), a student of Nora Sullivan in BIOL187S (Microbial Life) in The Keck Science Department of the Claremont Colleges Spring 2013.