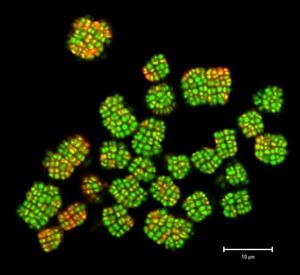
Kineococcus radiotolerans
Classification
Bacteria (Domain); Actinobacteria (Phylum); Actinobacteria (Class); Actinomycetales (Order); Kineosporiaceae (Family); Kineococcus (Genus)
Species
|
NCBI: Taxonomy |
Kineococcus radiotolerans
Description and Significance
K. radiotolerans was first recognized at the Savannah River Site in South Carolina where scientists were studying decades-old, high level nuclear waste inside tanks. Colonies are orange and round with rough edges while individual cells are coccus shaped, about 1.5 µm in diameter. This pigment color is a result of a carotenoid with absorption peaks at approximately 444, 471 and 501 nm. Kineococcus radiotolerans is a catalase-positive, oxidase-negative, urease-negative organism that normally grows in clusters but on average 1% of the cells are motile due to flagella. Each one of these cells is surrounded by a thick extra-cellular polymer shell. Growth is most abundant with temperatures ranging between 11º and 41º C and with a pH level between 5 and 9.
This bacterium thrives in normally deadly radiation and has incredible survival characteristics in terms of DNA. It has the ability to reassemble its own DNA within five to six hours after being blasted into several little pieces. This is a process that cannot be endured in humans and most other organisms. With this information, hopefully further research will lead to clues that could aid in medical research and cancer studies.
Genome Structure
K. radiotolerans’ genome was first sequenced at the Joint Genome Institute (JGI). This genome consists of three contigs: a linear chromosome along with two plasmids, one circular and one linear. Its chromosomal DNA has been completely sequenced. The length of the chromosome is approximately 4.8 Mbp with a 74% GC content. The linear plasmid has a length of 182,572 base pairs while the circular plasmid only has a length of 12,917 base pairs. The genome codes for roughly 4,700 genes and has a unique mechanism that protects the telomeres of the chromosomes. The completed genome sequence achieves an average of 14-fold sequence coverage per base with an error rate less than 1 in 100,000.
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Interesting features of cell structure; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces.
Ecology and Pathogenesis
Habitat; symbiosis; biogeochemical significance; contributions to environment.
If relevant, how does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.
References
1. Bagwell, Christopher E., Swapna Bhat, Gary M. Hawkins, Bryan W. Smith, Tapan Biswas, Timothy R. Hoover, Elizabeth Saunders, Cliff S. Han, Oleg V. Tsodikov, and Lawrence J. Shimkets. "Survival in Nuclear Waste, Extreme Resistance, and Potential Applications Gleaned from the Genome Sequence of Kineococcus radiotolerans SRS30216." PLoS ONE 3 (2008). PLos ONE. 5 Dec. 2008. PubMed Central. Apr. 2009 <http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pubmed&pubmedid=19057647>.
2. "Genome Project Result." NCBI HomePage. 17 Apr. 2009 <http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=genomeprj&cmd=Retrieve&dopt=Overview&list_uids=10689>.
3. Pavey, Rob. "Organism found at SRS amazes scientific world." The Augusta Chronicle 30 Apr. 2007. Apr. 2009 <http://chronicle.augusta.com/stories/latest/lat_126668.shtml>.
4. Phillips, Robert W., Juergen Wiegel, Christopher J. Berry, Carl Fliermans, Aaron D. Peacock, David C. White, and Lawrence J. Shimkets. "Kineococcus radiotolerans sp. nov., a radiationresistant, Gram-positive bacterium." International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology (2002): 933-38. PubMed. NCBI. Apr. 2009 <http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12054260>.
Author
Page authored by Kelsey Skodak and Whitney Soltau, students of Prof. Jay Lennon at Michigan State University.