Canine parvovirus strain 2 (CPV-2)
Classification
Virus/Parvoviridae/Parvovirinae
Parvovirus feline panleukopenia virus (Canine parvovirus strain 2)
]
Description and Significance
Canine parvovirus strain 2 (CPV2) is the causative agent of "Parvo", an extremely virulent and contagious illness. CPV2 is the most significant viral infection of puppies in the United States. [2] Parvo is well controlled in the United States through the use of the parvovirus vaccine recommended for all dogs starting between the ages of 6-8 weeks and continued for the duration of their lives. CPV2 is almost identical to feline panleukopenia virus and only differs by two amino acids in the viral capsid and this small difference causes the virus to almost exclusively affect canines.
Structure, Metabolism, and Life Cycle
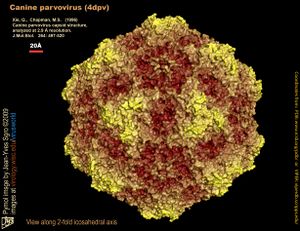
CPV2 is a non-enveloped, single-stranded DNA virusInteresting features of its structure; how it gains energy (how it replicates, if virus); what important molecules it produces (if any), does it have an interesting life cycle?
Ecology and Pathogenesis
Natural habitat (soil, water, commensal of humans or animals?)
If relevant, how does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, or plant hosts? Important virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.
References
[1] Prittie, Jennifer (September 2004). "Canine Parvoviral Enteritis: A Review of Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention". J Vet Emerg Crit Care. 14 (3): 167–176. doi:10.1111/j.1534-6935.2004.04020.x. [2] Kapil, S. (2007). "Canine Parvovirus Types 2c and 2b Circulating in North American Dogs in 2006 and 2007", Journal of clinical microbiology. 45(12), 4044-4047. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01300-07 [3] virology.wisc.edu/virusworld [4] Mitchell, K, ed. "Canine Parvovirus: Diseases of the Stomach and Intestines in Small Animals." The Merck Veterinary Manual. The Merck Veterinary Manual, n.d. Web. 22 Jul 2013. <http://www.merckmanuals.com/vet/digestive_system/diseases_of_the_stomach_and_intestines_in_small_animals/canine_parvovirus.html?qt=canine parvovirus&alt=sh
Author
Page authored by Brandon VanHee, student of Mandy Brosnahan, Instructor at the University of Minnesota-Twin Cities, MICB 3301/3303: Biology of Microorganisms.
