Shock chlorination
Introduction
From swimming pools to wells, chlorine is a common chemical used to disinfect water sources.
Due to safety concerns, hypochlorite (bleach) is the most commonly used compound to conduct shock chlorination1. Hypochlorite is used in one of three forms: commercial bleach (approx. 3.5-5% concentration), calcium hypochlorite (Ca(OCl)2; 65-70% concentrated), or sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl; about 12% concentration)2. These forms of hypochlorite are not as pure as chlorine gas, and will degrade in strength when in storage. However, like chlorine gas, they also react with water to form a disinfectant, hypochlorous acid (HOCl).
Microbial agents
Frequently, microbial factors infiltrate water sources through fecal matter. Many types of bacterial pathogens can initiate waterborne illnesses, including enteric bacteria, protozoa, or viruses3.
Helicobacter pylori
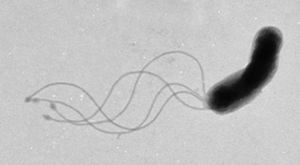
Helicobacter pylori is known to cause gastritis and peptic ulcers.
Studies done in Peru4 and Japan5 have shown the presence of the bacteria in public water sources, proving its possibility as a waterborne microbe.
Cryptosporidium
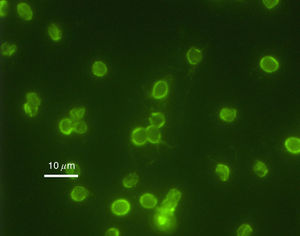
Cryptosporidium parvum is a type of parasite capable of causing gastrointestinal illness. Unlike Helicobacter pylori, however, Cryptosporidium has been proven to be unresponsive to chlorination6.
Methods
Commercial
Domestic
Success rates
Alternative methods
Scientists are not content with shock chlorination. As technology advances, methods to improve both testing and disinfection are created.
References
Edited by Erika Jensen, student of Joan Slonczewski for BIOL 116 Information in Living Systems, 2013, Kenyon College.
