SungTimon2.2
Classification
Kingdom- Bacteria; Phylum- Firmicutes; Class- Bacilli; Order- Bacillales; Family- Bacillaceae; Genus- Bacillus; Species- Bacillus Megaterium
Our Blast results were inconclusive. Bacillus Megaterium is the "best guess" narrowed down from our biochemical results and cellular and colonial characteristics in the lab**
Species
Genus species
Bacillus Megaterium
(Our second choice was Bacillus Cereus)
Habitat Information
The soil organism was isolated from a partially shaded front yard, underneath an oak tree, in Austin, TX on XXX. The air temperature was X, humidity X%, pressure X, solar radiation UV X. The grid coordinates from NRCS are XX. Spores are known to occur in soil, dust, water and plants.
Description and Significance
This organism is a gram positive, endospore forming, rod shaped bacteria. The colonial morphology is circular, smooth in the center, 'grainy' on the outside,umbonate elevation, and opaque with a golden appearance.
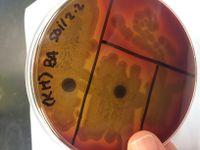
Kirby Bauer Antimicrobial results:
Strong Zone of Inhibition for linezolid, cefamandole, azlocillin, vancomycin, sufisozazole.
Weak Zone of Inhibition for oxacillin.
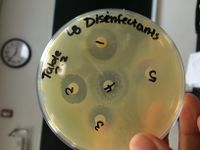
Disinfectant Sensitivity Results:
Strong Zone of Inhibition for clove, 10% lysol.
Weak Zone of Inhibition for tea tree oil, 100% bleach, and lavender.
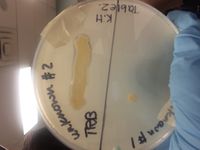
Anti-microbial activity was observed on an S. aureus test patch plate.
B. megaterium is a significant organism because it can be used industrially as a commercial strain and expression host [1]. Some strains are capable of nitrogen fixation [2]. B. megaterium has important uses in glucose dehydrogenase, penicillin aminidase, vitamin B12, oxetanocin, and P450 cytochromes, bioremediation.
Genome Structure
Describe the size and content of the genome. How many chromosomes? Circular or linear? Other interesting features? What is known about its sequence? Include S Ribosomal sequence that you obtained from PCR and sequencing here.
The size and content of the genome are undetermined due to inconclusive Blast results. PCR and DNA sequencing did not yield an adequate sequence for organism identification. Therefore, our genome information is based off of a 'best guess' of what organism might be based on biochemical tests and staining results.
Literature research indicates that B. megaterium has a genome XX.
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Interesting features of cell structure
The vegetative surface of B. megaterium consists of a capsule, proteinaceous surface layer, and peptidiglycan. The function of the proteinaceous surface layer, made of crystalline glycoprotein subunits, is unknown. It may be involved in bacterial metal interactions [3]
B. megaterium utilizes aerobic metabolism but has been known to survive anaerobic conditions.
what important molecules it produces.
Physiology and Pathogenesis
enzymes made, other characteristics that may be used to identify the organism; contributions to environment (if any).
B. megaterium is a common bacteria found in soil, does not produce endotoxins, and is non-pathogenic.
Biochemical characteristics:
NEGATIVE RESULTS INCLUDE: Starch Hydrolysis, Gelatin Hydrolysis, Methyl Red-Voges Proskauer, Citrate test, SIM (negative for sulfur reduction, indole production, nonmotile organism), nitrate reduction, Urea hydrolysis, Eosin methylene blue (no coliforms, lactose fermenters, no growth: meaning possible gram +), Hektoen Enteric (presumptive ID for Gram +), MacConkey Agar (Gram + evidence), Decarboxylation Test, Phenylalanine deaminase, and catalase.
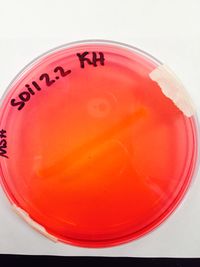
POSITIVE RESULTS INCLUDE: Casein hydrolysis, DNA hydrolysis, Lipid hydrolysis, Triple sugar iron, oxidase, blood agar (beta- complete lysis of RBC), mannitol salt agar (weak positive), phenylethal alcohol, and bile esculin.
Interpretation of Results: Our bacteria is a gram positive organism that possesses the enzymes casease,DNase, ligase, fermentable enzymes, and cytochrome C oxidase. This organism can completely lyse red blood cells, and can weakly ferment mannitol.
References
http://www.eol.org/pages/974186/overview http://www.tgw1916.net/Bacillus/megaterium.html
[3] http://textbookofbacteriology.net/Bacillus_2.html
Author
Page authored by Hsiang-Yuan Sung and Kaleen Timon, student of Prof. Kristine Hollingsworth at Austin Community College.