Oophila amblystomatis
Classification
Domain: Eukaryota, Kingdom: Plantae, Division: Chlorophyta, Class: Chlorophyceae, Order: Chlorococcales, Family: Chlorococcaceae, Genus: Oophila, Species: O. amblystomatis
Description and Significance
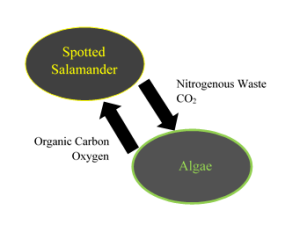
Oophila amblystomatis is a single celled green algae. The only place in nature where it is found is in the eggs of the salamander, Ambystoma maculatum. The salamanders eggs are typically laid in temporary, small, woodland ponds where decaying leaves and other detritus are present and therefore these are the areas where Oophila amblystomatis can be found. These environments are typically low in oxygen concentration. By producing oxygen as the byproduct of photosynthesis, the green algae increases oxygen concentrations within the eggs they inhabit conferring fitness benefits to the salamander embryo hosts. A study found that salamander eggs inhabited by the green algae exhibit lower mortality, earlier hatching time and faster growth. The green algae benefit by metabolising the nitrogenous waste produced by the embryos as well as utilizing the CO2 produced by the respiration of the salamander embryos. Experiments of the green algae in the presence and absence of an embryo found that the green algae grew more vigorously when embryos were present. Because both the green algae and the salamander embryos in eggs benefit this is an example of a mutualistic relationship.
Genome Structure
Describe the size and content of the genome. How many chromosomes? Circular or linear? Other interesting features? What is known about its sequence?
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
O. amblystomatis is classified as a plant cell, which means that it contains not only the all the organelles of a eukaryotic cell, but also chloroplasts, pyreniods, and starch. These cells also have flagella, which help the cell travel through the water to enter the eggs of the spotted salamander (Ambystoma maculatum).
Ecology
Oophila amblystomatis is a single-celled green algae that can only be found inside of the spotted salamander (Ambystoma maculatum) eggs. It is not present anywhere else in nature. The algae grows alongside the salamander within the enclosed egg and provides the green color that is present. The algae more specifically, in the presence of light, uses the process of photosynthesis and provides higher oxygen concentrations to the egg. However, in the absence of light, the oxygen levels are extremely low within the egg. The spotted salamander egg provides nitrogenous waste CO2 to the algae, and the algae in return provides the salamander organic carbon and oxygen. This creates the mutualistic relationship between the two.
References
Bachmann, Marilyn D., Burkholder, JoAnn M., Carlton, Richard G., & Wetzel, Robert G.(1986).Symbiosis between salamander eggs and green algae: microelectrode measurements inside eggs demonstrate effect of photosynthesis on oxygen concentration. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 64(7): 1586-1588.
Gilbert, P. W., 1944. The alga-egg relationship in Ambystoma maculatum, a case of symbiosis. Ecol., 25: 366-369
Gilbert, P. W. (1942). Observations on the eggs of Ambystoma maculatum with especial reference to the green algae found within the egg envelopes. Ecology. 23 (2): 215–227.
Hutchison, V. H., & Hammen, C. S. (1958). Oxygen utilization in the symbiosis of embryos of the salamander, Ambystoma maculatum and the alga, Oophila amblystomatis. The Biological Bulletin, 115(3), 483-489
Author
Page authored by Avery Quinlan, Max Zaret, & Jessica Zellinger students of Prof. Jay Lennon at IndianaUniversity.