Thiomargarita namibiensis food storage
Introduction
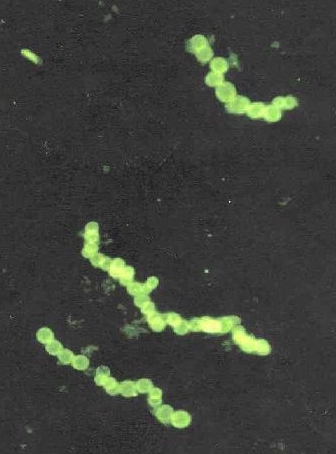
The Thiomargarita namibiensis was discovered in 1997 by Heidi N. Schulz off of the coast of Walvis Bay, Namibia, Africa. The Thiomargarita namibiensis is a sulfide eating bacteria and although it mainly consumes sulfides, the Thiomargarita namibiensis also consumes some amounts of nitrates. The Thiomargarita namibiensis is currently the largest found bacteria (up to 0.3 mm in diameter). A separate strand of the Thiomargarita namibiensis was also found off the coast of the Gulf of Mexico in 2005 but this strand does not does not divide along a single axis and because of that, it is unable to form large chains. The Thiomargarita namibiensis is closely related to a much smaller bacteria called the Thioploca which live in vertical sheaths and have to move up and down in order to get the nutrients that they need. Furthermore, the Thiomargarita namibiensis does not need to do that in order to become completely satiated.
Metabolism
The Thiomargarita namibiensis is capable of using nitrogen as the terminal electron acceptor during the Electron Transport Chain. Throughout this process, it oxidizes hydrogen sulfide (H2S) into elemental sulfur (S2).
Sample citations: [1]
[2]
A citation code consists of a hyperlinked reference within "ref" begin and end codes.
Section 2 Microbiome
Include some current research, with a second image.
Conclusion
Overall text length should be at least 1,000 words (before counting references), with at least 2 images. Include at least 5 references under Reference section.
References
Edited by [Author Name], student of Joan Slonczewski for BIOL 116 Information in Living Systems, 2020, Kenyon College.
