Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis - The Link Between Climate Change and Amphibians
Introduction
By Scott Upton
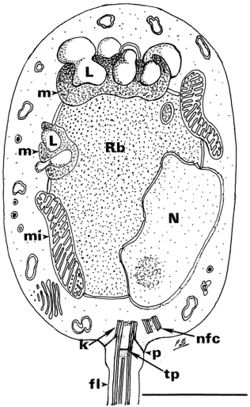
Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis is a pathogen primarily found in amphibians, and it’s presence can have devastating effects on amphibian populations. Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis is responsible for causing Chytridiomycosis, or chytrid, in amphibians all across the world in response to rising global temperatures. (Fig 1).Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag
[2]
A citation code consists of a hyperlinked reference within "ref" begin and end codes.
To repeat the citation for other statements, the reference needs to have a names: "<ref name=aa>"
The repeated citation works like this, with a back slash.[3]
Section 1
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Every point of information REQUIRES CITATION using the citation tool shown above.
Section 2
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Section 3
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Section 4
Conclusion
References
- ↑ Berger et al. 2005. Life cycle stages of the amphibian chytrid Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis. Inter-Research. 68:52-63
- ↑ Bartlett et al.: Oncolytic viruses as therapeutic cancer vaccines. Molecular Cancer 2013 12:103.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedaa
Authored for BIOL 238 Microbiology, taught by Joan Slonczewski, 2021, Kenyon College.
