Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth
Overview
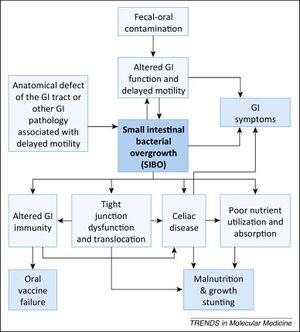
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) is defined as the abnormal increase in the overall bacterial population in the small intestine. [1] [2] Common symptoms of SIBO include diarrhea, flatulence, abdominal pain and bloating. [3] [4]Currently there is no single valid test for SIBO, but common ways of screening for SIBO include small-bowel aspiration and quantitative culture and breath testing. [5]
SIBO was first suggested by Barker and Hummel in their 1939 publication “Macrocytic anemia in association with intestinal strictures and anastomoses.”, providing key findings for both the study of Macrocytic anemia and the study of SIBO. [6]
At right is a sample image insertion. It works for any image uploaded anywhere to MicrobeWiki. The insertion code consists of:
Double brackets: [[
Filename: PHIL_1181_lores.jpg
Thumbnail status: |thumb|
Pixel size: |300px|
Placement on page: |right|
Legend/credit: Electron micrograph of the Ebola Zaire virus. This was the first photo ever taken of the virus, on 10/13/1976. By Dr. F.A. Murphy, now at U.C. Davis, then at the CDC.
Closed double brackets: ]]
Other examples:
Bold
Italic
Subscript: H2O
Superscript: Fe3+
Testing for SIBO
Medical Management of SIBO
Unfortunately, the current management of SIBO is unclear. [7] Common management strategies include using antibiotics
Research also proposes dietary changes to help relieve the functional gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms. [8] Reduce intake of FODMAPs (fermentable oligo-, di-, and mono-saccharides and polyols)—poorly absorbed short-chain carbohydrates can effectively reduce bloating and other functional gastrointestinal symptoms. [8] Although the effectiveness of this strategy—previously used only to treat IBS and other GI conditions—for treating SIBO-related symptoms is still unclear. [2] Other food sources of functional gastrointestinal symptoms including gluten and natural and added food chemicals such as amines and glutamates and the benefit of dietary strategies that reduce the intake of these chemicals are still being researched. [8]
Interactions Between SIBO and Other Systemic Conditions
Although the prevalence and role in the pathogenesis of other diseases remain uncertain, reviews and case studies still show potential connections between SIBO and other systemic conditions such as IBS, or Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. [9] Other conditions that are hypothesized to be associated with SIBO include [INSERT A LIST OF CONDITIONS] [10]
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome is a group of rare disorders caused by collagen synthesis defects. Delayed gastric emptying, which is a risk factor for SIBO, is common among EDS patients. [11] Studies show that SIBO diagnosis is common among EDS patients. [11]
Conclusion
Overall text length (all text sections) should be at least 1,000 words (before counting references), with at least 2 images.
Include at least 5 references under References section.
References
- ↑ “Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO).” Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 6 Jan. 2022, https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/small-intestinal-bacterial-overgrowth/symptoms-causes/syc-20370168.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Adike, Abimbola, and John K. DiBaise. “Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth.” Gastroenterology Clinics of North America, vol. 47, no. 1, 2018, pp. 193–208., https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gtc.2017.09.008.
- ↑ Sachdev, Amit H, and Mark Pimentel. “Gastrointestinal bacterial overgrowth: pathogenesis and clinical significance.” Therapeutic advances in chronic disease vol. 4,5 (2013): 223-31. doi:10.1177/2040622313496126
- ↑ Bohm, Matthew, et al. “Diagnosis and Management of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth.” Nutrition in Clinical Practice, vol. 28, no. 3, 2013, pp. 289–299., https://doi.org/10.1177/0884533613485882.
- ↑ Saad, Richard J., and William D. Chey. “Breath Testing for Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: Maximizing Test Accuracy.” Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, vol. 12, no. 12, 2014, pp. 1964–1972., https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2013.09.055.
- ↑ Barker, W. H., and L. E. Hummel. "Macrocytic anemia in association with intestinal strictures and anastomoses." Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp 64.2 (1939): 15.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs named“Bohm” - ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Gibson, Peter R, and Susan J Shepherd. “Food Choice as a Key Management Strategy for Functional Gastrointestinal Symptoms.” American Journal of Gastroenterology, vol. 107, no. 5, 2012, pp. 657–666., https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2012.49.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs named“Adike” - ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs named“” - ↑ 11.0 11.1 Xiong, Tingting, et al. “1182 Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) Is Common in Patients with Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS).” American Journal of Gastroenterology, vol. 114, no. 1, 2019, https://doi.org/10.14309/01.ajg.0000594256.00026.1d.
Edited by Yufan Lu, student of Joan Slonczewski for BIOL 116 Information in Living Systems, 2022, Kenyon College.
