The Interrelationship of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and the Gut Microbiome
Introduction
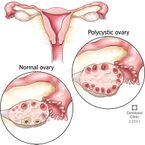
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS), alternatively referred to as polycystic ovary syndrome, is a hormonal disorder that occurs when ovaries create and secrete excessive androgen. PCOS has a variety of defining characteristics, including hormonal imbalance, ovarian cysts, infertility, and irregular menstrual cycles (Fig. 1).[1] These characteristics may be accompanied by complications such as obesity, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia or dysbiosis (an imbalance in the lipids or microbiome, respectively), impaired glucose metabolism, miscarriages, cardiovascular disease, sleep apnea, and cancer.[1][2] When left untreated, complications such as these are more likely to arise, causing a significant burden on many afflicted women and people assigned female at birth (AFAB).
PCOS affects an estimated 8–13% of women and people AFAB within reproductive age, accounting for 50%~70% of anovulatory infertility; in addition, an estimated 70% of PCOS cases are undiagnosed worldwide.[3][2][4] PCOS’s general symptoms usually arise during early to late puberty and can last through menopause; they include acne or oily skin, irregular periods, infertility, irregular hair growth/loss, and abdominal weight gain.[5] Just as there is no singular symptom for PCOS, there is no singular test to diagnose it; therefore, many different variables are taken into account to make a diagnosis. Most commonly, a PCOS diagnosis is made during the early reproductive years through a consideration of symptoms and blood tests, pelvic exams, and/or ultrasounds.[4]
Despite PCOS's widespread occurrence and impact, its precise etiology and pathology are still not fully understood. It is known that there is a significant genetic component to the acquisition of PCOS. It is currently considered to be a complex, polygenic, heterogenetic trait, as PCOS inheritance is believed to occur from multiple genes.[6] However, recent studies have begun to shed light on additional factors that impact the development and details of PCOS. For example, new research has begun to reveal a connection between PCOS and the human gut microbiome.
PCOS and Microbes: Research and Discovery
The human gastrointestinal tract hosts a robust and complex population of organisms: the gut microbiota.[7] This population assists in food digestion, nutrient absorption, metabolism, and immune regulation, which can influence the development of various diseases and disorders, including PCOS.[2] In fact, dysbiosis is a common characteristic of PCOS. A recent theory suggests that this dysbiosis activates the immune system, increasing serum insulin levels, thus interfering with insulin receptor function and normal follicular development, then increasing ovarian androgen deprivation.[7] To explore this, one study by BMC Microbiology transplanted fecal matter from PCOS patients and healthy controls into female mice. The results showed that mice with transplanted controls underwent no significant difference in biological profiles, whereas those with PCOS transplants underwent significant deviation, inducing dysbiosis in the mice.[7] Additionally, the mice with PCOS transplants were occasionally found to have damage to their gut barrier tissue as well as PCOS-like symptoms.[7] Therefore, it can be reasonably inferred that a correlation lies between the gut microbiome and PCOS.[5]
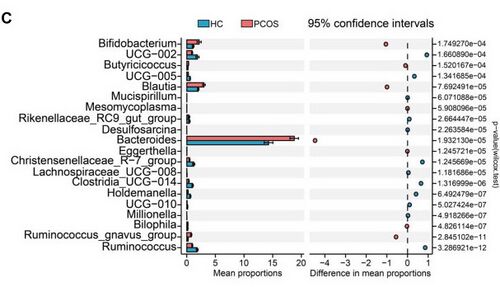
To further explore this theory, subsequent research has been conducted to compare human biological makeup in healthy vs. PCOS subjects. Various metrics and testing have been used to analyze these comparisons. Using Shannon and Chao1 diversity indices, it was determined that there is no statistically significant difference in alpha diversity between people with or without PCOS.[5] However, while there is no decrease in the amount of bacteria, the type of bacteria has been found to have varying significance. Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles (STAMP) and Wilcoxon non-parametric testing, both of which are used to analyze genera, found that the most significant differences were in the increased genera of Ruminococcus, UCG-002, Christensenellaceae_R-7_group, and Clostridia_UCG-014 and the decreased genera of Bifidobacterium, Blautia, and Bacteroides in individuals with PCOS (Fig. 2).[5]
Due to this difference in gut microbial diversity between PCOS patients and healthy individuals, the significance of the interrelationship between PCOS and the gut microbiome is beginning to be studied. Ideally, new treatments that could harness this connection will be thoroughly explored.
PCOS Treatment: Lifestyle, Medication, and Microbial Options
Currently, there is no cure for PCOS. However, treatments are available through which symptoms may be managed and outgrown. Because PCOS has a wide variety of symptoms, there is a broad range of treatment options. The two most common options are lifestyle changes and medications.[8] Often, a healthy diet and consistent exercise can reduce symptoms and result in weight loss, possibly assisting in improved insulin regulation, lowered blood glucose levels, and restored ovulation.[8] Pharmaceutical remedy, on the other hand, is arguably more complex, consisting of many different treatment paths. If a patient is aiming to restore fertility, they will likely use an ovulation induction agent, such as Clomiphene.[9] However, it must be noted that ovulation inducers can pose risks, such as hyperstimulation (overproduction of hormones) and higher rates of multiple births (twins, triplets, etc.).[8] If a patient is not attempting to become pregnant, other pharmaceutical options are commonly taken. Metformin (an insulin-sensitizing agent) and various oral contraceptives are a frequently prescribed choice.[9] If a patient attempts to resolve specific symptoms, such as hirsutism (the growth of excessive male-patterned hair), other more specific medications, such as Eflornithine (also known as Vaniqa), may be used.[9]
While these paths are the most common treatments, research regarding PCOS and the gut microbiome has unveiled new possible remedies. While there is no current microbial treatment, fecal microbiota transplants (FMTs), prebiotics, and probiotics are all being explored as future PCOS remedies.[10] The first of these possibilities, FMT, is the transplantation of feces from a healthy donor into a patient's small intestine.[11] While there have been some promising results from studies involving rats and mice (including the one previously described), the applicability and safety with humans are unknown.[10] Currently, FMT is only FDA-approved for C. difficile colonization.[10] Prebiotics and probiotics, meanwhile, have been found to help relieve symptoms of PCOS; unfortunately, clinically, these treatment options are not well understood in a clinical setting, specifically in the details of ideal dosages and types.[10]
There is fascinating research surrounding this connection between PCOS and the gut microbiome; however, more studies are needed to turn experiments into applicable solutions.
Conclusion: PCOS and Health Research Disparity

Despite the prevalence, pain, and dangers of PCOS, it is essential to note that research regarding the disorder can feel disturbingly lacking. A large portion of this relates to the medical disparities and inequities between men and women, sometimes referred to as the Women’s Health Gap. Women’s research is often misunderstood, under-researched, and underfunded; as a result, female patients are more likely to face obstacles to treatment, including dismissiveness, diagnostic delays, and suboptimal treatment (Fig. 3).[12] Therefore, when considering PCOS’s broad symptoms, highly variable treatments, and arguably underexplored research, one has to consider if enough is being done to fully understand and aid in decreasing the pervasiveness of PCOS. By further researching and understanding PCOS, including within the microbial world, millions of women and people AFAB could benefit worldwide.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Cleveland Clinic. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) & treatment [Internet. Cleveland Clinic. 2023.]
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Sun Y, Gao S, Ye C, Zhao W. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in polycystic ovary syndrome: Mechanisms of progression and clinical applications. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology. 2023 Feb 24;13.
- ↑ Thursby E, Juge N. Introduction to the Human Gut Microbiota. Biochemical Journal [Internet. 2017 May 16;474(11):1823–36.]
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 WHO. Polycystic ovary syndrome [Internet. World Health Organization. 2023.]
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Yang Y, Cheng J, Liu C, Zhang X, Ma N, Zhou Z, et al. Gut microbiota in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: an individual based analysis of publicly available data. EClinicalMedicine [Internet. 2024 Oct 18;77:102884–4.]
- ↑ Khan MJ, Ullah A, Basit S. Genetic basis of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): Current perspectives. The Application of Clinical Genetics [Internet. 2019 Dec;Volume 12(12):249–60.]
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Huang F, Deng Y, Zhou M, Tang R, Zhang P, Chen R. Fecal microbiota transplantation from patients with polycystic ovary syndrome induces metabolic disorders and ovarian dysfunction in germ-free mice. BMC Microbiology. 2024 Sep 28;24(1).
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 John Hopkins Medicine. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) [Internet. John Hopkins Medicine. 2019.]
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Radosh L. Drug Treatments for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. American Family Physician [Internet. 2009 Apr 15;79(8):671–6.]
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 Corrie L, Awasthi A, Kaur J, Vishwas S, Gulati M, Kaur IP, et al. Interplay of Gut Microbiota in Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome: Role of Gut Microbiota, Mechanistic Pathways and Potential Treatment Strategies. Pharmaceuticals. 2023 Jan 28;16(2):197.
- ↑ Barron M. Fecal Microbiota Transplants (FMT): Past, Present and Future [Internet. ASM.org. 2024.]
- ↑ Balch B. Why we know so little about women’s health [Internet. Association of American Medical Colleges. Association of American Medical Colleges; 2024.]
Edited by Lauren Karg, student of Joan Slonczewski for BIOL 116, 2024, Kenyon College.
