Desulfobacter
A Microbial Biorealm page on the genus Desulfobacter
[[Image:.jpg|thumb|350px|right|
Classification
Higher order taxa:
Bacteria; Proteobacteria; delta/epsilon subdivisions; Deltaproteobacteria; Desulfobacterales; Desulfobacteraceae
Species:
|
NCBI: Taxonomy Genome |
Description and Significance
Genome Structure
Cell Structure and Metabolism
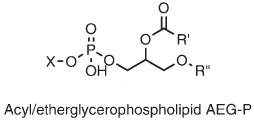
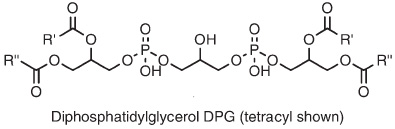
D. variabilis contains significant quantities of AEG-P (top), and almost 20% of the alkyl-glycerol bond is present as DPG lipids, also known as "cardiolipin" (bottom). Note that the DPGs contain either ether or ester linkages in the core lipids.Sturt et al |
| Sulfate reducers have a wide range of cellular morphologies, including rods, vibrios, ovals, spheres and even tear-dropped or onion shaped cells. Some are motile, others are not. Most sulfate-reducing bacteria are mesophilic, but a few thermophiles are known. Desulfosarcina variabilis is mesophilic, and contains bacterial core lipids (see images on left). The dominant phospholipid headgroups in D. variabilis are Phosphoethanolamine PE (48%) and Phosphoglycerol PG (33%). One study has found that Desulfosarcina variabilis solely contained n-hexadecyl ether side chains. For more information on tetraether lipids found in Archaea, click here. |
Ecology
Although sulfate reduction is thought to be an anaerobic process, sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) are also important in aerobic environments if they can proliferate in anaerobic zones. For example, in marine sediments and in aerobic wastewater treatment systems, sulfate reduction accounts for up to 50% of the mineralization of organic matter. Furthermore, sulfate reduction strongly stimulates microbially enhanced corrosion of metals.