HIV-Derived Lentiviral Vectors and Their Use as Gene Therapy Agents Against Human Immunodeficiency Virus
Introduction
What is gene therapy?
Gene therapy is a method of treating genetic disorders in which an individual’s genes are modified to correct or prevent a disease. Depending on the genetic disease, the subject’s cells can be treated by replacement of a mutant gene with a healthy gene, deactivation of a disease gene, or introduction of a gene to fight a disease. Unlike pharmaceutical drugs, gene therapy often offers a permanent cure for individuals who have inherited diseased genes, rather than treatment to manage symptoms. One mechanism of cell transformation for gene therapy involves the use of modified viral agents to introduce or remove genes from host cells.
Why use viral agents? Viruses are naturally occurring obligate intra-cellular infectious agents that require host cell machinery in order to replicate [12]. During replication, the virus transfects the host cell with its own DNA. Researchers have taken advantage of the efficiency of viral transformation by modifying the viral genome to carry a therapeutic gene in place of a non-essential viral gene [12]. To date, viral vectors have been used to induce pluripotent stem cells, silence genes, induce transgene expression, and confer immunization [10].
What are Lentiviruses? For some viral genera, replication involves the insertion of the viral genome into that of the host cell. Once integrated, the viral genes are replicated and passed on to daughter cells as though a part of the original host cell. One such genera is the Lentivirus genera of the Retroviridae family, who use a reverse transcriptase enzyme to produce a DNA copy of its RNA genome before inserting its DNA genome into that of the host [8]. Lentiviruses are appealing as gene therapy agents because of this permanency of transformation. Lentivuses were first proposed in 1996 as gene therapy vectors because of this ability to integrate their genome into host DNA, as well as their ability to target different cell types and infect both dividing and non-dividing cells [10]. One species of lentivirus, HIV-1, the primary cause of HIV and AIDS in humans, has been developed as a vector because of its specificity of integration at localized hotspots within the human genome, making it less likely to insert randomly and interfere with critical genes than other viral vectors, such as the murine leukemia virus [7].
Using Lentiviral Vectors to fight HIV:
One of the most encouraging advances in the use of the HIV-1 virus as a vector has actually been to fight HIV itself. Recent studies have shown that lentiviruses can be used to target key virus or host genes to confer resistance to the HIV-1 virus. This can be achieved by either targeting essential viral genes, such as replication machinery, or targeting host genes that are involved in allowing viral entry into the cell. One promising example of using HIV-1 to fight HIV involves a vector that contains three anti-HIV transgenes. Anderson et al (2009) have shown that transforming CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells with CCR5 short hairpin RNA gene, a TRIM5α gene, and a transactivation response element gene, each which operate at different stages of the viral life cycle, successfully block HIV infection [1].
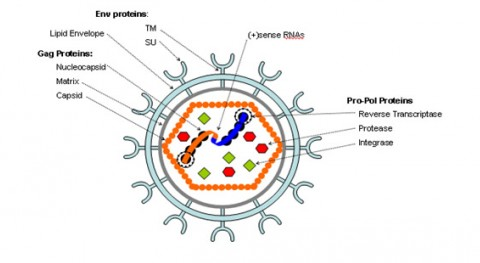
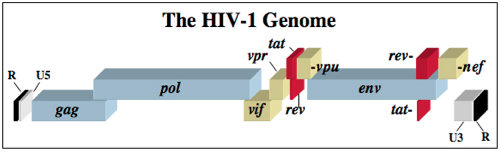
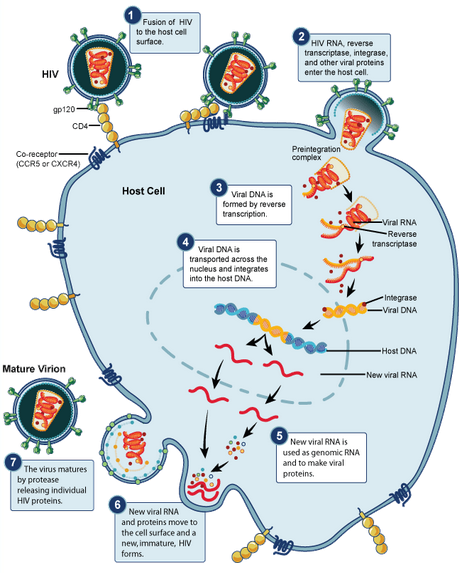
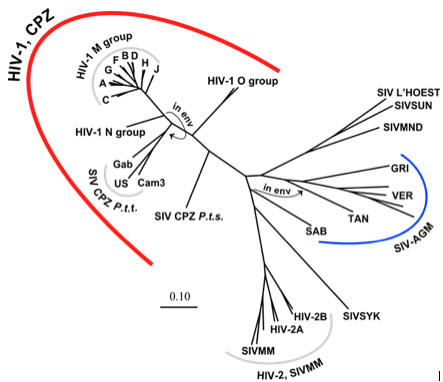

At right is a sample image insertion. It works for any image uploaded anywhere to MicrobeWiki. The insertion code consists of:
Double brackets: [[
Filename: PHIL_1181_lores.jpg
Thumbnail status: |thumb|
Pixel size: |300px|
Placement on page: |right|
Legend/credit: Electron micrograph of the Ebola Zaire virus. This was the first photo ever taken of the virus, on 10/13/1976. By Dr. F.A. Murphy, now at U.C. Davis, then at the CDC.
Closed double brackets: ]]
Other examples:
Bold
Italic
Subscript: H2O
Superscript: Fe3+
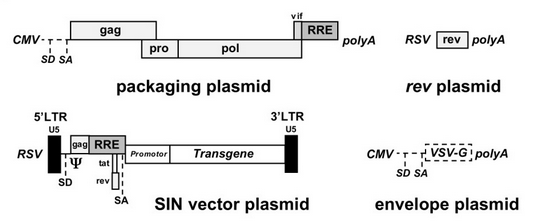
Overview of Lentiviral Vectors
Section 2
Include some current research in each topic, with at least one figure showing data.
Section 3
Include some current research in each topic, with at least one figure showing data.
Conclusion
Overall paper length should be 3,000 words, with at least 3 figures.
References
Edited by student of Joan Slonczewski for BIOL 238 Microbiology, 2009, Kenyon College.
