Borrelia burgdorferi and Lyme Disease
History
The first case of the Lyme disease was in Lyme, Connecticut in 1975. The disease presented arthritic-like symptoms, and was therefore referred to as Lyme arthritis. The deer tick, Ixodes scapularis, was associated with the transmission of the disease in 1977, but the cause of the disease remained unknown until Willy Burgdorferi discovered Borrelia burgdorferi in 1981. The disease is caused by three species of bacteria all belonging to Borrelia-Borrelia burgdorferi, Borrelia afzelii, and Borrelia garinii. Borrelia burgdorferi is the main cause of Lyme disease in North America, where the other two species affect Europe.
Double brackets: [[
Filename: PHIL_1181_lores.jpg
Thumbnail status: |thumb|
Pixel size: |300px|
Placement on page: |right|
Legend/credit: Electron micrograph of the Ebola Zaire virus. This was the first photo ever taken of the virus, on 10/13/1976. By Dr. F.A. Murphy, now at U.C. Davis, then at the CDC.
Closed double brackets: ]]
Other examples:
Bold
Italic
Subscript: H2O
Superscript: Fe3+
Borrelia burgdorferi Description and Structure
Borrelia burgdorferi is a Gram-negative bacterium belonging to the class Spirochaetes. This bacterium is helical and has both an inner and outer membrane as well as a flexible cell wall. The cell is usually 1m wide, but can be up to 10-25 m long. Bacteria of the class spirochaetes have flagella located on the inside of the periplasm in between the inner and outer membranes. The flagellum along with the helical structure of the bacterium allows the bacterium to migrate through viscous fluids and burrow through various tissues. As a result, this cell is highly invasive. B. burgdorferi is also known for its outer surface proteins OspA and OspC have been studied extensively and have a role in transmission of the bacteria into the host cell.
The metabolism of this cell is limited, therefore; B. burgdorferi relies on their host for energy precursors. Its genome encodes transport proteins such as ABC transporters. B. burgdorferi also codes for enzymes and proteins that are used in the phosphotransferase system. The host serum as well as the environment are targets for these transport systems. The genome of this bacterium is distinctive. It consists of one linear chromosome of 910,725 base pairs long with at least 17 linear and circular plasmids that combine to a size of more than 533,000 base pairs. As a result of its large number of plasmids, the genetic organization of B. burgdorferi is specialized.
.
What is Lyme Disease?
Lyme disease is an infectious disease caused by the spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi that is carried in deer tick Ixodes scapularis. This disease is the most common vector borne disease in the United States, affecting far more individuals than West Nile virus. It has been estimates that there were nearly 40,000 cases of Lyme reported in 2009, a large underestimate. The Center for Disease Control estimates the true number of cases to be as much as 12 times higher, making the estimated total as high as 480,000. This estimate makes Lyme disease more prevalent than AIDS. Moreover, national surveillance began in 1982, which increased the number of cases reported nearly 25-fold.
Lyme disease is most commonly transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected tick as it bites. Without treatment, B. burgdorferi is able to migrate through the bloodstream and many connective tissues. In it’s early stages, Lyme disease affects the skin through skin rash and in later stages spreads to the joints, nervous system, and other organ systems in the later stages. If caught and treated early, Lyme disease is almost always cured. However, this disease has a high rate of progression and if it is not treated early, symptoms may last for months or even years. Unfortunately, thousands of patients go undiagnosed or misdiagnosed with doctors telling them their symptoms are in their head due to the difficulty in testing. Part of how this disease goes untreated and misdiagnosed is due to the characteristics of the burrowing bacterium, Borrelia burgdorferi. This bacterium has become an expert at hiding and surviving in human tissues, and its ability to take on different forms such as cysts, which allows the bacterium to escape the immune system, avoid antibiotics, and hide from detection by blood tests. The mechanism of transmission is poorly understood, but for many bacterial pathogens such as B. burgdorferi, the initial step in colonizing host tissues involves the expression of adhesive molecules that facilitate bacterial adherence to host cells or to the extracellular matrix.
Symptoms
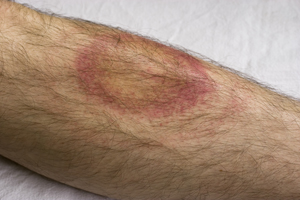
Lyme disease almost always first presents itself as a skin rash called erythema migrans. The rash most likely originates from the site of the tick bite and spreads. The rash can be a solid expanding red spot, or it can be a single red spot surrounded by lighter red skin resembling a bulls-eye. The skin rash is visible 1 to 2 weeks after the disease has been transmitted from the tick, and lasts for 3 to 5 weeks. Ticks are able to attach anywhere on the body, but-armpit, groin, back of the knee, nape-body creases are what is most common. Symptoms that can present themselves at the time of the rash include, joint pain, chills, fever, and fatigue. As the spirochete spreads throughout the body, more sever symptoms begin to surface. The more serious symptoms include tingling or numbness in the extremities, paralysis, severe fatigue and a stiff neck. Severe headaches, chronic arthritis, swelling of joints, cardiac abnormalities and mental disorders can appear weeks, months, and in some cases, years after being bitten.
Treatment
When Lyme disease is caught early, within the first few weeks of initial infection, the treatment is straightforward and it is highly likely that treatment will end in a cure. However, once it has been longer than three weeks since being infected, the likelihood of finding a cure decreases as long as the patient goes untreated. According to the American Lyme Disease Foundation, the most common antibiotics recommended for most symptoms of Lyme disease are Doxycycline, amoxicillin, and ceftin. Treatment for Lyme disease can be frustrating and be seen as inconclusive due to the sporadic progression of the disease. Some patients may experience symptoms of Lyme disease for years . The documentary, Under Our Skin, tells the story of several patients whose lives have been destroyed by this disease. After being misdiagnosed, undiagnosed, and untreated for so long, these patients experience extreme symptoms preventing them from walking and carrying out a normal lifestyle.
Adhesion Mechanisms
Future Work
Concluding Remarks
References
Edited by student of Joan Slonczewski for BIOL 238 Microbiology, 2009, Kenyon College.