B. Cereus Cudmore-Lewis
Classification
Domain: Bacteria
Phylum: Firmicutes
Class: Bacilli
Order: Bacillales
Family: Bacillaceae
Species
|
NCBI: Taxonomy |
Bacillus cereus
Habitat Information
Location:
Lat:30.002092
Long:-97.883009
Soil: Castephen Clay Loam/ 3-5% slopes, eroded
Description: New housing development, empty lot
Precipitation:Not within 48 hours
Temperature:70, few clouds
Depth: 1.25 inches
Visibility: 10 miles
Humidity: 59%
Wind: S 10 mph
Sea Level: 1011.8
Date & Time: September 8, 2016, 18:53
Description and Significance
Description:
Color: Yellow (mustard-like color)
Form: Circular
Margin: Entire
Consistency: Semi-mucoid
Texture: Smooth
Elevation: Raised
A standard Gram stain was performed on the sample to observe cellular morphology.
Gram reaction: positive
Cellular morphology: very small, clustered rods
Antibiotics
Antibacterial Activity: None
Antibiotic Resistance: Nafcillin
Significance
B. cereus can be considered significant in food manufacturing, livestock health, human disease, and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Genome Structure
Describe the size and content of the genome. How many chromosomes? Circular or linear? Other interesting features? What is known about its sequence?
S Ribosomal sequences obtained from PCR:
GACNGANCAACGCCGCGTGAGTGATGAAGGCTNTCCCNTCNNAAAACTCTGTTGTTAGGGAAGAACAAGTGCTAGTTGAATAAGCTGGCACCTTGACGGTACCTAACCAGAAAGCCACGGCTAACTACGTGCCAGCAGCCGCGGTAATACGTANGTGGCAAGCGTTATCCGGAATTATTGGGCGTAAAGCGCGCGCAGGTGGNTTCTTAAGTCTGATGTGAAAGCCCACGGCTCANCCGTGGAGGGTCATTGGAAACTGGGAGACTTGAGTGCAGAAGAGGAAAGTGGAATTCCATGTGTAGCGGTGAAATGCGTAGAGATATGGAGGAACACCAGTGGCGAAGGCGACTTTCTGGTCTGTAACTGACACTGAGGCGCGAAAGCGTGGGGAGCAAACAGGATTAGATACCCTGGTAGTCCACGCCGTAAACGATGAGTGCTAAGTGTTAGAGGGTTTCCGCCCTTTAGTGCTGAAGTTAACGCATTAAGCACTCCGCCTGGGGAGTACGGCCGCAAGGCTGAAACTCAAAGGAATTGACGGGGGCCCGCACAAGCGGTGGAGCATGTGGTTTAATTCGAAGCAACGCGAANAACCTTACCAGNTCTTGACATCCTCTGACAACCCTANAGATAGGGCTTCTCCTTCGGGAGCAGAGTGACAGGTGGGTGCATGGTTGTCGTCAGCTCGTGNCCNTNNNATGTCNTANCTGTTTCCNGNANNTNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
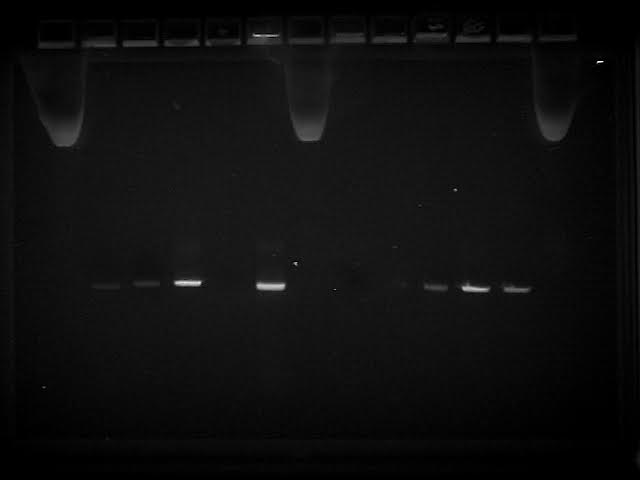
Gel Electrophoresis results from Microbiology class. Well 4 is B. cereus sample collected by Lewis and Cudmore.
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Interesting features of cell structure; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces.
Other stain results:
Capsule stain: negative
Endospore stain: negative
Physiology and Pathogenesis
The pathogenicity of B. cereus, whether intestinal or non-intestinal, is intimately associated with the production of tissue-destructive exoenzymes.Among these secreted toxins are four hemolysins, three distinct phospholipases, an emesis-inducing toxin, and proteases. (1)
B. cereus has been known to cause food-borne illness (most notably "fried-rice syndrome"), as well as skin infections (most commonly keratitis) in humans.
In some animals, B. cereus can be used as a probiotic.
B. cereus was found to be the most common contaminant in pharmaceutical manufacturing. (2)
References
1. Bottone, Edward J. “Bacillus Cereus, a Volatile Human Pathogen.” Clinical Microbiology Reviews 23.2 (2010): 382–398. PMC. Web. 7 Dec. 2016.
2. Sandle, Tim (28 November 2014). "The Risk of Bacillus cereus to Pharmaceutical Manufacturing". American Pharmaceutical Review (Paper). 17 (6): 56.
Author
Page authored by Carley Cudmore and Jennifer Lewis, students of Prof. Kristine Hollingsworth at Austin Community College.

