Blood Glucose Regulation
Introduction
Blood glucose regulation involves maintaining blood glucose levels at constant levels in the face of dynamic glucose intake and energy use by the body. On average this target range is 60-100 mg/dL for an adult although people can be asymptomatic at much more varied levels. In order to maintain this range there are two main hormones that control blood glucose levels: insulin and glucagon. Insulin is released when there are high amounts of glucose in the blood stream. Glucagon is released when there are low levels of glucose in the blood stream. There are other hormones that effect glucose regulation and are mainly controlled by the sympathetic nervous system. Blood glucose regulation is very important to the maintenance of the human body. The brain doesn’t have any energy storage of its own and as a result needs a constant flow of glucose, using about 120 grams of glucose daily or about 60% of total glucose used by the body at resting state. (Berg,2002) With out proper blood glucose regulation the brain and other organs could starve leading to death.
Introduce the topic of your paper. State your health service question, and explain the biomedical issues.
Hormones
Insulin
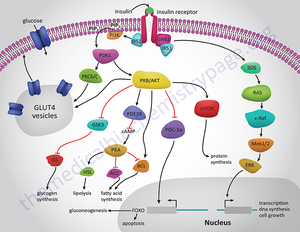
A key regulatory pathway to control blood glucose levels is the hormone insulin. Insulin is released from the beta cells in the islets of Langerhans found in the pancreas. Insulin is released when there is a high concentration of glucose in the blood stream. The beta cells know to release insulin through the fallowing pathway. Glucose enters the cell and ATP is produce in the mitochondria through the Krebs cycle and electron transport chain. This increase in ATP causes channels to closes. These channels allow potassium cations to flow into the cell. With these channels closed the inside of the cell becomes more negative causing calcium channels to open allowing calcium cations to flow into the cell. Calcium cation ions flow into the cell due to a concentration and elector chemical gradient that favors the influx of calcium cations. Calcium ions are key in the vesicle excretion processes. A protein on the vesicle called the v-SNARE protein becomes entangled with a t-SNARE protein on the beta cell surface. With calcium facilitating the interaction amongst the SNARE proteins the vesicle is forced to merge with the cell membrane and insulin is excreted into the blood stream.
Insulin travels through the blood stream to muscle, brain or adipose tissue. Once there, the insulin binds to a dimeric transmembrane receptor. This receptor autophosphorylates and causes many downstream pathways relating to glucose regulation, energy storage and DNA transcription. For the glucose regulation pathway the receptor autophosphorylates then causes insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) to be phosphorated. IRS-1 then phosphorylates Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K). PI3K cleaves Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) leaving diacyl glycerol (DAG) in the cell membrane and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) in the cytosol. IP3 travels to the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) and cause calcium channels to open in the SER, releasing cations into the cytosol. DAG activates a kinase named protein kinase C which also opens calcium channels in the SER. This ambient increase in calcium facilitates the binding of vesicles to the membrane. These vesicles have Glut4 proteins imbedded in the membrane. Glut4 proteins are channel proteins that allow glucose into the cell. Once these vesicles bind with the cell membrane glucose flows through the Glut4 protein and into the cell, reducing blood glucose levels. The process by which insulin is degraded and metabolized is poorly understood. However it is known that the liver is responsible for the majority of insulin break down. Since the liver is so important to proper insulin levels when the liver is damaged perhaps by alcohol the regulatory system can be interfered with. Alcohol effects on the regulation of blood glucose will be addressed later in this article. The kidney is also key in the break down of insulin. Peripheral tissue is thought to hold on to insulin perhaps reversibly binding to membrane receptors. (Duckworth, 1981) These means it is possible for insulin to be removed from the blood stream with out being broken down. Insulin clearance rates are shown to decrease in those who are obese or have diabetes. This may create insensitivity to insulin. (Duckworth, 1998)
Glucagon
When blood glucose levels are low, glucagon is released which inhibits the break down of glucose, glycolysis and activates the formation of glucose, gluconeogenesis. Gluconeogenesis creates glucose from such molecules as pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, and glucogenic amino acids. Glucagon is released from the alpha cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. Glucose is brought into the cell through SLC2A1 channel proteins. The glucose is then used to generate ATP. This increase in ATP opens potassium channels unlike in beta cells where they are inhibited. This increase in intercellular potassium causes calcium channels to open which facilitates the binding of vesicles contain glucagon. Glucagon is then released into the blood stream. Glucagon primarily operates on the liver. Once the hormone has made it through the blood stream to the liver it binds to a transmembrane protein called a G protein coupled receptor(GPCR). The associated G protein is phosphorylated with GTP and the alpha unit of the G protein moves to activate adenylate cyclase (AC). AC converts ATP into cyclic AMP (cAMP). Cyclic AMP activates protein kinase A (PKA). PKA phosphorylates phosphofructo kinase-2 (PFK-2) and fructose bisphosphatase- 2(FBPase-2). Due to the addition of the phosphate PFK-2 becomes less active. This in turn reduces the amount of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate (F-2,6-BP) being produce. High levels of F-2,6-BP cause glycolysis or the break down of glucose. So less active PFK-2 decreases the amount of F-2,6-BP. In addition FBPase-2 is activated which breaks downs F-2,6-BP which also decreases the amount of F-2,6-BP. Low levels of F-2,6-BP cause the activation of FBPase-1 which increase gluconeogenesis. In addition there is no activation of PFK-1, which is involved in glycolysis both of witch increase the amount of blood glucose.
Epinephrine
During extreme stimuli the sympathetic nervous system kicks into action. This is colloquially known as the fight or flight response. The brain sends signals throughout the body to increase heart rate, cause bronchial dilation and haptic glucose release. The brain also sends signals to the adrenal glands. Epinephrine is released from the adrenal glands. This hormone is key to the prolonged sympathetic response. Epinephrine produces similar results as the initial neuronal signal however it is longer lasting. Epinephrine travels through the blood stream and causes the liver to release glucose thus increasing blood glucose levels in order to be ready for the threat. The pathway by which this occurs is outlined here. Epinephrine binds to a transmembrane receptor on the liver known as the beta-adrenergic receptor protein. The receptor activates a G protein which then activates. The G protein activates by swapping out at GDP for a GTP. Once activated the G protein diffuses along the membrane. The G protein then binds with and activates adenylyl cyclase. Adenylyl cyclase causes ATP to become cyclic AMP (cAMP).The molecule cAMP binds with protein kinase-A which phosporalayts specific proteins. In this step phosphorylase is phosphorylated. Phosphorylase then cuts glucogen creating a glucose-1-phosphate. This is further refined into glucose-6-phosphate by phosphoglucomutase. Glucose-6-phosphate can then be used for energy requirements necessary in the sympathetic nervous system response. This allows for more ATP in the muscle and brain. This hormone pathway is reversed when the parasympathetic nervous system takes priority.This system is sometimes referred to as the “rest and digest”.
Diabetes Mellitus
When there is a issue with the ability of the human body to use glucose due to a problem with the insulin pathway diabetes mellitus (diabetes mellitus) may be at fault. There are a few types of diabetes mellitus with the most common being: type 1 diabetes mellitus, type 2 Diabetes mellitus and gestational Diabetes mellitus.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin or not enough insulin is made. People who are obese have a high risk for contracting type 2 Diabetes mellitus. Although there is no cure for type 2 careful monitoring of exercise and nutrition can help. Other effects of the body are in increased rate of stroke and heart issues. Also damage to small blood vessels can occur. This happens particularly in the eyes (diabetic retinopathy) and kidneys (renalopathy). Also due to increased amounts of sugar in the blood stream a diabetic is at a higher risk of infection and wounds will take longer to heal.
Section 3
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Conclusion
References
Authored for BIOL 291.00 Health Service and Biomedical Analysis, taught by Joan Slonczewski, 2016, Kenyon College.