EHEC: Difference between revisions
From MicrobeWiki, the student-edited microbiology resource
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Uncurated}} | {{Uncurated}} | ||
[[Image:9995_lores.jpg|thumb|200px|right|''Escherichia coli'' O157:H7 showing flagella. From [http://www.microbeworld.org/component/jlibrary/?view=article&id=6731]]] | [[Image:9995_lores.jpg|thumb|200px|right|''Escherichia coli'' O157:H7 showing flagella. From: Microbeworld.org [http://www.microbeworld.org/component/jlibrary/?view=article&id=6731]]] | ||
===Etiology/Bacteriology=== | ===Etiology/Bacteriology=== | ||
====Taxonomy==== | ====Taxonomy==== | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
|} | |} | ||
====Description==== | ====Description==== | ||
''Escherichia coli'' O157:H7 is an emerging pathogen that causes hemorrhagic colitis. | ''Escherichia coli'' O157:H7 is an emerging pathogen that causes hemorrhagic colitis. ''E. coli'' is a Gram negative rod, facultative anaerobe, motile by means of peritrichous flagella, and found in the GI tract of mammals. ''E. coli'' O157:H7 was first reported by the [[CDC]] in 1982. | ||
===Pathogenesis=== | ===Pathogenesis=== | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
===Host Immune Response=== | ===Host Immune Response=== | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
[Sample reference] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6817062 Centers for Disease Control (CDC). Isolation of E. coli O157:H7 from sporadic cases of hemorrhagic colitis - United States. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1982 Nov 5;31(43):580, 585. PubMed PMID: 6817062.] | [Sample reference] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6817062 Centers for Disease Control (CDC). Isolation of E. coli O157:H7 from sporadic cases of hemorrhagic colitis - United States. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1982 Nov 5;31(43):580, 585. PubMed PMID: 6817062.] | ||
Created by Tyrrell Conway at the University of Oklahoma. | Created by Tyrrell Conway at the University of Oklahoma. | ||
Revision as of 20:48, 10 June 2013
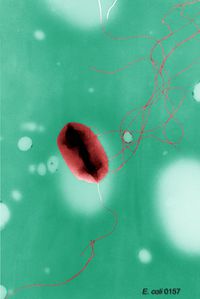
Escherichia coli O157:H7 showing flagella. From: Microbeworld.org [1]
Etiology/Bacteriology
Taxonomy
| Domain = Bacteria | Phylum = Proteobacteria | Class = Gammaproteobacteria | Order = Enterobacteriales | Family = Enterobacteriaceae | Genus = Escherichia | species = E. coli | subspecies = O157:H7 | prototype strain = EDL933 |
|
NCBI: Taxonomy Genome: Escherichia coli O157:H7 str. EDL933 |
Description
Escherichia coli O157:H7 is an emerging pathogen that causes hemorrhagic colitis. E. coli is a Gram negative rod, facultative anaerobe, motile by means of peritrichous flagella, and found in the GI tract of mammals. E. coli O157:H7 was first reported by the CDC in 1982.
Pathogenesis
Clinical features
Diagnosis
Treatment
Prevention
Host Immune Response
References
Created by Tyrrell Conway at the University of Oklahoma.
