File:Coxsackievirus Type B Proteases.png: Difference between revisions
(Figure: Direct myocardial damage induced by virus-encoded proteinases. A, Dystrophin is an important component of the dystrophin–glycoprotein complex that links the cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix. coxsackievirus B3–encoded proteinase 2A c...) |
(No difference)
|
Latest revision as of 19:08, 9 December 2017
Figure: Direct myocardial damage induced by virus-encoded proteinases. A, Dystrophin is an important component of the dystrophin–glycoprotein complex that links the cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix. coxsackievirus B3–encoded proteinase 2A cleaves dystrophin, contributing to myocardial dysfunction by increasing cell permeability and decreasing force transmission. B, Dysferlin is a transmembrane protein highly expressed in skeletal and cardiac muscles. It is localized to the sarcolemma and cytoplasmic vesicles and plays a key role in Ca2+-dependent membrane repair. Proteolytic processing of dysferlin by proteinase 2A contributes to impaired cardiac function, likely via disrupting membrane repair function. C, Virus-encoded proteinase 2A and 3C can produce direct cytotoxicity in the heart through inducing apoptosis by direct cleavage of caspases and inhibiting host protein translation through processing eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4γ (eIF4G) and poly A-binding protein (PABP). D, Serum response factor (SRF) is a muscle-enriched transcription factor that regulates the expression of many cardiac contractile and regulatory proteins by binding to serum response element (SRE) in the promoter region of target genes. SRF cleavage mediated by proteinase 2A results in cardiac dysfunction by eliminating SRF-mediated gene expression. E, Misfolded protein aggregates are frequently detected in common heart diseases and are thought to be highly toxic to cardiomyocytes. Autophagic adaptor proteins p62 and neighbor of BRCA1 (NBR1), as well as RNA-binding protein transactive response DNA-binding protein-43 (TDP-43) are cleaved by proteinase 2A and 3C, contributing to impaired autophagy and increased accumulation of protein aggregates (Illustration Credit: Ben Smith). Taken from Fung G., Luo H., Qiu Y., Yang D. and McManus B. 2016, with permission (59).
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 19:08, 9 December 2017 | 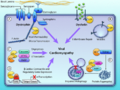 | 440 × 329 (100 KB) | Bjardin (talk | contribs) | Figure: Direct myocardial damage induced by virus-encoded proteinases. A, Dystrophin is an important component of the dystrophin–glycoprotein complex that links the cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix. coxsackievirus B3–encoded proteinase 2A c... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file:
