Fuselloviridae
Baltimore Classification
Higher order taxa
Viruses; dsDNA viruses, no RNA stage; Fuselloviridae
Genera
Fusellovirus
Description and Significance
Fuselloviridae infect the archaeon Sulfolobus, which inhabits high-temperature (>70°C), acidic (pH of <4.0) environments. Members of this family have been found in acidic hotsprings in Japan and Iceland. The Fuselloviridae family currently consists of only one virus, Sulfolobus spindle-shaped virus 1 (SSV1), and three tentative members (SSV2, SSV3, and the staaelite virus pSSVx, which stands for plasmid SSV x). SSV1, the type virus for the family, was the first high-temperature virus to be characterized. (sources: Wiedenheft et al., Rice et al.)
Genome Structure
The genome of a fuselloviridae is non-segmented and contains a single molecule of circular, double-stranded DNA. The DNA is positively supercoiled. The complete genome is 15500 nucleotides in length. (source: ICTVdB)
Virion Structure of a Fuselloviridae
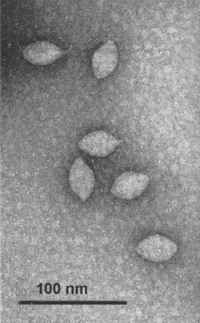
Fuselloviridae virions consist of an envelope and a nucleocapsid. The capsid is enveloped. Virions are spindle-shaped, flexible, and have protrusions that extend through the envelope. One pole has short tail-like fibers attached to it. The virions are 100 nm in length and 60 nm in diameter. (sources: ICTVdB, Wiedenheft et al.)
Reproduction Cycle of a Fuselloviridae in a Host Cell
Viral Ecology & Pathology
As mentioned above, viruses in the Fuselloviridae family infect the archaeon Sulfolobus.
References
ICTVdB - The Universal Virus Database, version 3. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ICTVdb/ICTVdB/
