HIV Treatment: Difference between revisions
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
As of 2019, there are an estimate 38 million people currently living with HIV world-wide. Among the HIV-positive population, approximately 81% have received a diagnosis for HIV and 26 million HIV-positive people receive anti-retroviral therapy. Today, the burden of disease is primarily concentrated in sub-Saharan African (Figure 1). HIV accounts for 1.7% of deaths globally, but HIV mortality varies considerably throughout the world. In Europe, HIV accounts for 0.1% of deaths, in the United States it accounts for 0.26% of deaths, and in Brazil it accounts for 1.14% of deaths. In South Africa and Botswana, HIV accounts for approximately 28% of deaths, in Kenya it accounts for 17% of deaths, and in Nigeria it accounts for 10.74% of deaths. In sub-Saharan African, women account for the majority of new HIV diagnoses, while in the rest of the world, men account for most of the new recorded cases. | As of 2019, there are an estimate 38 million people currently living with HIV world-wide. Among the HIV-positive population, approximately 81% have received a diagnosis for HIV and 26 million HIV-positive people receive anti-retroviral therapy. Today, the burden of disease is primarily concentrated in sub-Saharan African (Figure 1). HIV accounts for 1.7% of deaths globally, but HIV mortality varies considerably throughout the world. In Europe, HIV accounts for 0.1% of deaths, in the United States it accounts for 0.26% of deaths, and in Brazil it accounts for 1.14% of deaths. In South Africa and Botswana, HIV accounts for approximately 28% of deaths, in Kenya it accounts for 17% of deaths, and in Nigeria it accounts for 10.74% of deaths. In sub-Saharan African, women account for the majority of new HIV diagnoses, while in the rest of the world, men account for most of the new recorded cases. | ||
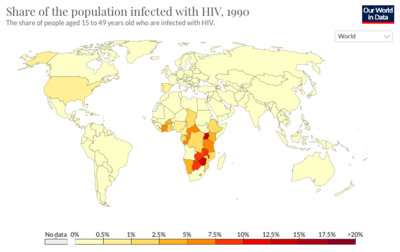
[[Image:Screen_Shot_2021-03-29_at_10.34.27_AM.png |thumb|400px| | [[Image:Screen_Shot_2021-03-29_at_10.34.27_AM.png |thumb|400px|center|<b>Figure 1:</b> Global prevalence of HIV Infections in 1990. [https://ourworldindata.org/hiv-aids].]] | ||
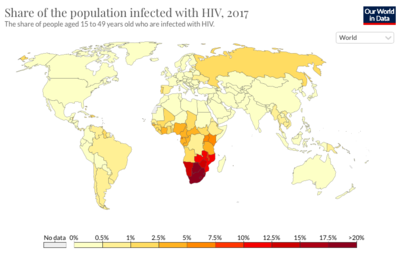
[[Image:Screen_Shot_2021-03-29_at_10.34.39_AM.png |thumb|400px| | [[Image:Screen_Shot_2021-03-29_at_10.34.39_AM.png |thumb|400px|center|<b>Figure 2:</b> Global prevalence of HIV Infections in 2017. [https://ourworldindata.org/hiv-aids].]] | ||
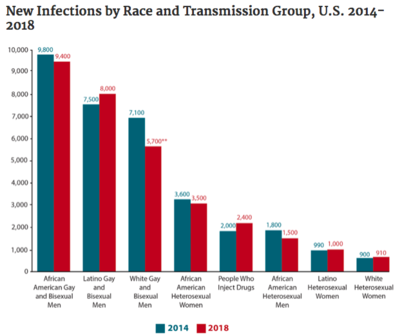
In the United States, there are currently about 1.2 million people who are positive for HIV (approximately 14% of whom are unaware of their status). The majority (69%) of new cases occur in men who have sex with men (MSM). HIV disproportionately affects Black/African American and Hispanic/Latinx communities (Figure 4), accounting for 42% and 27% of new HIV diagnoses, respectively. | In the United States, there are currently about 1.2 million people who are positive for HIV (approximately 14% of whom are unaware of their status). The majority (69%) of new cases occur in men who have sex with men (MSM). HIV disproportionately affects Black/African American and Hispanic/Latinx communities (Figure 4), accounting for 42% and 27% of new HIV diagnoses, respectively. | ||
Revision as of 15:06, 29 March 2021
Introduction
By Alice Tillman
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is an RNA retrovirus which attacks the immune system of the infected individual. There are two main strains of HIV: HIV-1 and HIV-2. HIV-1 is more prevalent and pathogenic. HIV belongs to a type of retroviruses which are called lentiviruses. Lentiviruses infect their hosts over a very long period of time and it can take years for symptoms to manifest. Over time, HIV can progress into Acquired Immunodeficiency syndrome or AIDS. HIV/AIDS is characterized by a decline in the number of CD4+ T-cells and an increased susceptibility to other infections.
The HIV genome consists of single-stranded, positive-sense mRNA, with three main open reading frames (gag, pol, and env). The viral capsid of HIV includes its genetic material, as well as reverse transcriptase, protease, and integrase. CD4 is the primary receptor targeted by HIV. CD4 is commonly found on helper T-lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, and monocytes. The virus also has to bind a co-receptor, CCR5, on the target cell in order to gain entry the cell. Once inside the cell, HIV uses its own reverse transcriptase to convert its mRNA into DNA and then inserts itself into the host genome, where it takes over the cell machinery to direct its own replication.
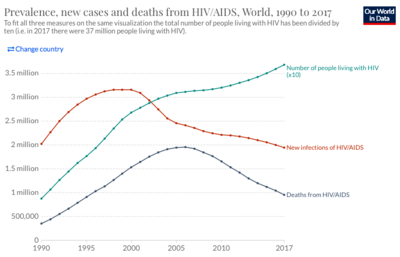
As of 2019, there are an estimate 38 million people currently living with HIV world-wide. Among the HIV-positive population, approximately 81% have received a diagnosis for HIV and 26 million HIV-positive people receive anti-retroviral therapy. Today, the burden of disease is primarily concentrated in sub-Saharan African (Figure 1). HIV accounts for 1.7% of deaths globally, but HIV mortality varies considerably throughout the world. In Europe, HIV accounts for 0.1% of deaths, in the United States it accounts for 0.26% of deaths, and in Brazil it accounts for 1.14% of deaths. In South Africa and Botswana, HIV accounts for approximately 28% of deaths, in Kenya it accounts for 17% of deaths, and in Nigeria it accounts for 10.74% of deaths. In sub-Saharan African, women account for the majority of new HIV diagnoses, while in the rest of the world, men account for most of the new recorded cases.
In the United States, there are currently about 1.2 million people who are positive for HIV (approximately 14% of whom are unaware of their status). The majority (69%) of new cases occur in men who have sex with men (MSM). HIV disproportionately affects Black/African American and Hispanic/Latinx communities (Figure 4), accounting for 42% and 27% of new HIV diagnoses, respectively.
Although HIV remains an enormous challenge to public health, significant improvements have been made in both preventing the spread of HIV and treating the infection. Over the last two decades, the rate new infections have declined by 39% and deaths by 51%, but the overall number of people with HIV has continued to grow. Improved outcomes for people with HIV, are due, in large part, to the creation of drugs known as anti-retroviral therapy (ART). ART consists of a combination of three drugs, which each target different components of the HIV life-cycle. Because HIV has such a HIV mutation rate, it is necessary to use a combination of different medications to ensure protection of a patient. Despite tremendous efforts, there still does not exist a vaccine for HIV. Currently, efforts are underway to develop a number of different types of vaccines for HIV.
The insertion code consists of:
Double brackets: [[
Filename: PHIL_1181_lores.jpg
Thumbnail status: |thumb|
Pixel size: |300px|
Placement on page: |right|
Legend/credit: Electron micrograph of the Ebola Zaire virus. This was the first photo ever taken of the virus, on 10/13/1976. By Dr. F.A. Murphy, now at U.C. Davis, then at the CDC. Every image requires a link to the source.
Closed double brackets: ]]
Other examples:
Bold
Italic
Subscript: H2O
Superscript: Fe3+
Sample citations: [1]
[2]
A citation code consists of a hyperlinked reference within "ref" begin and end codes.
To repeat the citation for other statements, the reference needs to have a names: "<ref name=aa>"
The repeated citation works like this, with a back slash.[1]
Section 1
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Every point of information REQUIRES CITATION using the citation tool shown above.
Section 2
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Section 3
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
