Infection Mechanism of Genus Ebolavirus: Difference between revisions
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Basler, C.F., Wang, X., Mühlberger, E., Volchkov, V., Paragas, J., Klenk, H.D., Garcia-Sastre, A. & Palese, P. (2000). The Ebola virus VP35 protein functions as a type I IFN antagonist. PNAS, 97, 12289-12294. | |||
Basler, C.F., Mikulasova, A., Martinez-Sobrido, L., Paragas, J., Mühlberger, E., Bray, M., Klenk, H.D., Palese, P. & García-Sastre, A. (2003). The Ebola Virus VP35 Protein Inhibits Activation of Interferon Regulatory Factor 3. Journal of Virology, 77(14), 7945-7956. | |||
Bavari, S., Bosio, C.M., Wiegand, E., Ruthel, G., Will, A.B., Geisbert, T.W., Hevey, M., Schmaljohn, C., Schmaljohn, A. & Aman, M.J. (2002). Lipid Raft Microdomains: A Gateway for Compartmentalized Trafficking of Ebola and Marburg Viruses. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 195(5), 593-602. | |||
Bhattacharyya, S., Warfield, K.L., Ruthel, G., Bavari, S., Aman, M.J. & Hope, T.J. (2010). Ebola virus uses clathrin-mediated endocytosis as an entry pathway. Virology, 401, 18-28. | |||
Borio, L., Inglesby, T., Peters, C.J., Schmaljohn, A.L., Hughes, J.M., Jahrling, P.B., Ksiazek, T., Johnson, K.M., Meyerhoff, A., O’Toole, T., Ascher, M.S., Bartlett, J., Breman, J.G., Eitzen, Jr., E.M., Hamburg, M., Hauer, J., Henderson, D.A., Johnson, R.T., Kwik, G., Layton, M., Lillibridge, S., Nabel, G.J., Osterholm, M.T., Perl, T.M., Russell, P. & Tonat, K. (2002). Hemorrhagic fever viruses as biological weapons: medical and public health management. Journal of the American Medical Association, 287, 2391-2405. | |||
CDC Special Pathogens Branch. (2010). Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever Case Count and Location List. Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever Information Packet. | |||
Cheng, P.C., Cherukuri, A., Dykstra, M., Malapati, S., Sproul, T., Chen, M.R. & Pierce, S.K. (2001). Floating the raft hypothesis: the roles of lipid rafts in B cell antigen receptor function. Semininars in Immunology, 13, 107-114. | |||
Crary, S.M., Towner, J.S., Honig, J.E., Shoemaker, T.R. & Nichol, S.T. (2003). Analysis of the role of predicted RNA secondary structures in Ebola virus replication. Virology, 306(2), 210-218. | |||
Emerson, S.U. (1982). Reconstitution studies detect a single polymerase entry site on the vesicular stomatitis virus genome. Cell, 31, 635-642. | |||
Empig, C.J. & Goldsmith, M.A. (2002). Association of the caveola vesicular system with cellular entry by filoviruses. Journal of Virology, 76, 5266-5270. | |||
Feldmann, H., Klenk, H.D. & Sanchez, A. (1993). Molecular biology and evolution of filoviruses. Archives of Virology, Supplementum, 7, 81-100. | |||
Hoenen, T., Groseth, A., Kolesnikova, L., Theriault, S., Ebihara, H., Hartlieb, B., Bamberg, S., Feldmann, H., Ströher, U. & Becker, S. (2006). Infection of Naïve Target Cells with Virus-Like Particles: Implications for the Function of Ebola Virus VP24. Journal of Virology, 80(14), 7260-7264. | |||
Huang, Y., Xu, L., Sun, Y. & Nabel, G.J. (2002). The assembly of Ebola virus nucleocapsid requires virion-associated proteins 35 and 24 and posttranslational modification of nucleoprotein. Molecular Cell, 10, 307-316. | |||
Iverson, L.E. & Rose, J.K. (1982). Sequential synthesis of 5’-proximal vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA sequences. Journal of Virology, 44, 356-365. | |||
Jasenosky, L.D., Neumann, G., Lukashevich, I. & Kawaoka, Y. (2001). Ebola Virus VP40-Induced Particle Formatin and Association with the Lipid BIlayer. Journal of Virology, 75(11), 5205-5214. | |||
John, S.P., Wang, T., Steffen, S., Longhi, S., Schmaljohn, C.S. & Jonsson, C.B. (2007). Ebola Virus VP30 Is an RNA Binding Protein. Journal of Virology, 81(17), 8967-8976. | |||
Johnson, K.M. & Breman, J.G. (1978) Ebola haemorrhagic fever in Zaire, 1976. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 56(2), 271-293. | |||
Klenk, H.-D. & Feldmann, H. (2004). Ebola and Marburg Viruses: Molecular and Cellular Biology. Wymondham: Horizon Bioscience. | |||
Martínez, M.J., Biedenkopf, N., Volchkova, V., Hartlieb, B., Alazard-Dany, N., Reynard, O., Becker, S. & Volchkov, V. (2008). Role of Ebola Virus VP30 in Transcription Reinitiation. Journal of Virology, 82(24), 12569-12573. | |||
Modrof, J., Becker, S. & Muhlberger, E. (2003). Ebola virus transcription activator VP30 is a zinc-binding protein. Journal of Virology, 77, 3334-3338. | |||
Moran, M. & Miceli, M.C. (1998). Engagement of GPI-linked CD48 contributes to TCR signals and cytoskeletal reorganization: a role for lipid rafts in T cell activation. Immunity, 9, 787-796. | |||
Mühlberger, E.,Weik, M., Volchkov, V.E., Klenk, H.D. & Becker, S. (1999). Comparison of the transcription and replication strategies of Marburg virus and Ebola virus by using artificial replication systems. Journal of Virology, 73, 2333-2342. | |||
Pratt, W.D., Wang, D., Nichols, D.K., Luo, M., Woraratanadharm, J., Dye, J.M., Holman, D.H. & Dong, J.Y. (2010). Protection of Nonhuman Primates against Two Species of Ebola Virus Infection with a Single Complex Adenovirus Vector. Clinical and Vaccine Immunology, 17(4), 572-581. | |||
Quinn, K., Brindley, M.A., Weller, M.L., Kaludov, N., Kondratowicz, A., Hunt, C.L., Sinn, P.L., McCray, P.B., Stein, C.S., Davidson, B.L., Flick, R., Mandell, R., Staplin, W., Maury, W. & Chiorini, J.A. (2009). Rho GTPases Modulate Entry of Ebola Virus and Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Pseudotyped Vectors. Journal of Virology, 83(19), 10176-10186. | |||
Reid, S.P., Leung, L.W., Hartman, A.L., Martinez, O., Shaw, M.L., Carbonnelle, C., Volchkov, V.E., Nichol, S.T. & Basler, C.F. (2006). Ebola Virus VP24 Binds Karyopherin α1 and Blocks STAT1 Nuclear Accumulation. Journal of Virology, 80(11), 5156-5167. | |||
Saeed, M.F., Kolokoltsov, A.A., Albrecht, T. & Davey, R.A. (2010). Cellular Entry of Ebola Virus Involves Uptake by a Macropinocytosis-Like Mechanism and Subsequent Trafficking through Early and Late Endosomes. PLOS Pathogens, 6(9). | |||
Saifuddin, M., Hedayati, T., Atkinson, J.P., Holguin, M.H., Parker, C.J. & Spear, G.T. (1997). Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 incorporates both glycosyl phosphatidylinositol-anchored CD55 and CD59 and integral membrane CD46 at levels that protect from complement-mediated destruction. Journal of General Virology, 78, 1907-1911. | |||
Sanchez, A., Kiley, M.P., Holloway, B.P. & Auperin, D.D. (1993). Sequence analysis of the Ebola virus genome: organization, genetic elements, and comparison with the genome of Marburg virus. Virus Research, 29, 215-240. | |||
Schümann, M., Gantke, T. & Mühlberger, E. (2009). Ebola Virus VP35 Antagonizes PKR Activity through Its C-Terminal Interferon Inhibitory Domain. Journal of Virology, 83(17), 8993-8997. | |||
Schornberg, K., Matsuyama, S., Kabsch, K., Delos, S., Bouton, A. & White, J. (2006). Role | |||
of endosomal cathepsins in entry mediated by the Ebola virus glycoprotein. Journal of Virology, 80(8), 4174-4178. | |||
Volchkov, V.E., Becker, S., Vochkova, V.A., Ternovoj, V.A., Kotov, A.N., Netesov, S.V. & Klenk, H.D. (1995). GP mRNA of Ebola virus is edited by the Ebola virus polymerase and by T7 and vaccinia virus polymerases. Virology, 214, 421-430. | |||
Watanabe, S., Noda, T., Halfmann, P., Jasenosky, L. & Kawaoka, Y. (2007). Ebola Virus (EBOV) VP24 Inhibits Transcription and Replication of the EBOV Genome. The Journal of Infectious Diseases, 196, S284-290. | |||
Weik, M., Modrof, J., Klenk, H.D., Becker, S. & Mühlberger, E. (2002). Ebola Virus VP30-Mediated Transcription Is Regulated by RNA Secondary Structure Formation. Journal of Virology, 76(17), 8532-8539. | |||
World Health Organization. (2010). Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever. Epidemic and Pandemic Alert and Response (EPR). | |||
Yonezawa, A., Cavrois, M. & Greene, W.C. (2005). Studies of Ebola Virus Glycoprotein-Mediated Entry and Fusion by Using Pseudotyped Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Virions: Involvement of Cytoskeletal Proteins and Enhancement by Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha. Journal of Virology, 79(2), 918-926. | |||
Revision as of 19:20, 2 November 2010
A Viral Biorealm page on the family Infection Mechanism of Genus Ebolavirus
Ebola hemorrhagic fever is a severe, often fatal, disease in humans and non-human primates caused by Ebolavirus. Even though the virus first appeared in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (formerly Zaire) in the summer of 1976 and has only sporadically reemerged, it has still managed to capture the attention of the world due to death rates that can be as high as 90% as well as the visceral manner in which it kills (CDC 2010, Johnson & Breman 1978). Few viruses have the ability to turn internal organs into a soup that promptly flows out of the body, so those that do tend to capture the public eye.
Despite the low incidence of infections, the lethality and potential airborne transmission of Ebolavirus makes it a severe biological threat. This is compounded by the possibility of the virus being obtained from the wild for use as a biological weapon (Borio et al. 2002). As of present, there are no licensed vaccines or specific antiviral treatments available for Ebolavirus infections, with significant progress only made in the development of vaccines for nonhuman primates (Pratt et al. 2010). Therefore, the elucidation of the viral replication cycle as well as complete understanding of viral proteins is necessary for the production of human vaccines.
Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever
One of the reasons that Ebola is so dangerous is that its symptoms are varied and appear quickly, yet are close enough to those of other viruses that Ebola is not rapidly recognized. Initial symptoms include high fever, severe headache, severe weakness, exhaustion, sore throat, nausea, dizziness and muscle, joint or abdominal pain. The unfortunate thing about these symptoms is that they are easily mistaken for malaria, typhoid fever, dysentery, influenza or various bacterial infections, all of which are far more common in regions where Ebola is prevent, but also less fatal (CDC 2010).
After this period, the fever often progresses to cause more serious symptoms: diarrhea, dark or bloody feces, vomiting blood, red eyes due to distention and hemorrhage of sclerotic arterioles, petechia, maculopapular rash and purpura. There is often gastrointestinal bleeding from the mouth and rectum, sometimes leading to the sloughing of the gut and venting from the anus. Internal and external hemorrhage from orifices, such as the nose and mouth, may also occur. As the virus progresses, bleeding in the brain can lead to severe depression, seizures and delirium (CDC 2010).
The span of time from onset of symptoms to death is usually between 7 and 14 days. By the second week of the infection, the patient will either experience a full recovery or undergo systemic multi-organ failure. Mortality rates are generally high, ranging from 50-90% depending on the specific strain. The cause of death is normally due to hypovolemic shock or organ failure (WHO 2010).
Description and Significance
Infection by FPTHV has been associated with fibropapillomatosis (FP), a neoplastic disease of marine turtles [14]. This condition manifests itself through the presence of epithelial fibropapillomas, tumors consisting of the epidermal and dermal skin layers, as well as internal fibromas, benign tumors composed of fibrous or connective tissue [10]. Although the tumors are considered benign, the disease can be life-threatening; large external fibropapillomas interfere with vision and feeding, while visceral fibromas can interfere with organ function [13].
Even though first reports of infection were only in green turtles (Chelonia mydas), cases have recently been confirmed in both loggerhead (Caretta caretta) and olive ridley (Lepidochely olivacea) species [26]. In the 1990s, it was believed that FP would be responsible for the extinction of marine turtles. However, recent studies have shown that wild turtles can, and will, recover from the disease [3]. Despite this fact, the incidence of FP has gradually increased in recent times, providing an additional ecological stress on magnificent creatures whose long-term survival is already in doubt.
Genome Structure
The genome of FPTHV consists of linear, dsDNA with unpaired, complementary nucleotides at each terminus. While the entire genome has not yet been sequenced, it is expected to be between 124 and 241 kbp, based on the size of fully sequenced alphaherpesviruses [9]. Overall, the sequence resembles that of another alphaherpesvirus, herpes simplex virus, which can be responsible for genital herpes [1]. Thus, FPTHV most likely contains at least 74 genes arranged in two unique regions, the long unique region (UL) and the short unique region (US), flanked by inverted repeats [16,24].
Protein coding genes are transcribed by host RNA polymerase II [2]. The first genes to be expressed during infection, immediate early genes, encode enzymes involved in nucleotide metabolism, DNA replication and for glycoproteins of the viral envelope. In contrast, late genes code for proteins of the viral capsid [12].
Virion Structure
The exact structure of the FPTHV virion has not been specifically determined. However, much insight can be gained by examining other alphaherpesviruses since the genomes show great homology [9].
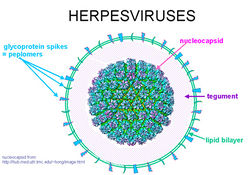
Alphaherpesvirus virions are composed of a large, dsDNA genome enclosed in an icosahedral capsid. This is coated first in a layer of tegument proteins and then in an envelope composed of roughly a dozen viral proteins and glycoproteins. The capsid is 125 nm in diameter and consists of four main structural proteins, VP5, VP19C, VP23 and VP26, along with a number of minor capsid proteins. A number of these minor subunits are required for the packing of replicated viral DNA into new capsid shells [25]. The viral envelope is derived from vesicles of the trans-Golgi network, and contains several virus-encoded glycoproteins that are absolutely essential for viral entry, including gB, gH and gL [23].
Reproductive Cycle
Again, very little is known about the specific reproductive cycle of FPTHV, though generalizations can be made after studying similar alphaherpesviruses. These virions make initial contact with host cells through the interactions of envelope glycoproteins gB and/or gC with the surface glycosaminoglycan heparan sulfate. While this binding is not essential for infection, it can increase entry efficiency by concentrating the virus on the cell surface so viral ligand gD can find cell receptors [21].
Viral glycoproteins gB, gD, gH and gL then act together to induce fusion of the envelope with the cell membrane following association with one of three classes of entry receptors: herpesvirus entry mediator, a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family; nectin-1 and nectin-2, members of the immunoglobulin family; and specific sites in heparin sulfate [22]. The virion moves to the nucleus and attaches to a nuclear entry pore, then inserts its DNA through the capsid portal. Each icosahedral virion contains one ring-shaped capsid portal, which is formed by twelve copies of the portal protein UL6 [4].
In the nucleus, the DNA circularizes and uses host enzymes to code for its “early genes.” The mRNA migrates to the cytoplasm and codes for proteins that then must return to the nucleus in order to help with further transcription. Late genes then code for capsid subunits, as well as for proteins that are incorporated into the nuclear cell membrane to become part of the primary viral envelope. In the meantime, the viral DNA continues to replicate in a rolling-circle mechanism that rapidly produces end-to-end copies called concatemers that must be cut into individual genomes as they are packaged into capsids [15].
The first step in nuclear egress of alphaherpesviruses is a budding process at the inner leaflet of the nuclear membrane in which capsids acquire a primary envelope [17]. The UL31 and UL34 proteins are necessary for efficient exit, with the UL34 protein inducing protein kinase C to soften the nuclear lamina via phosphorylation [20]. Following this, the primary envelope fuses with the outer leaflet of the nuclear membrane and releases the viral capsid, sans primary envelope and primary tegument, into the cytoplasm [6].
Once there, the final tegument is formed. These proteins help link capsid subunits to the cytoplasmic tails of envelope glycoproteins to secure the integrity of the virion. The first layer of tegument around the capsid is icosahedrally shaped and composed of UL36. A second layer is composed of UL37, while UL48 appears critical for tegument assembly [18]. After this protein coat is assembled, tegumented capsides bud into trans-Golgi vesicles to form a final envelope. Tegument protein UL49 interacts with the cytoplasmic tails of vesicle membrane glycoproteins gE/I and gM to help drive this last budding process [17].
Like many other herpes viruses, FPTHV can also persist as a latent infection. It expresses Latency Associated Transcript RNA that regulates the host genome and interferes with the natural cell death mechanism, ensuring that a reservoir of virus is ready for another lytic outbreak [17].
Viral Ecology & Pathology
Skin tumors in turtles affected by FP are characterized by a branching collagen matrix mixed with scattered fibroblasts covered by an epidermis that is abnormally thickened [11]. Cell dependent levels of FPTHV pol DNA suggest that lytic viral production occurs in keratinocytes, while the majority of FPTHV viral genomes are contained in fibroblasts either as an episome, a portion of genetic material that can exist independently of the main genome, or as part of host DNA [7]. This genome sequence has also been used to prove that FPTHV plays a dominant role in the maintenance of the tumor state, despite the fact that infection appears predominantly latent in fibropapilloma cells [8,19].
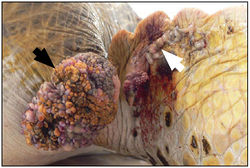
It has been suggested that FPTHV infection occurs when marine turtles return to their natal breeding grounds [27]. Recently, marine leeches of the genus Ozobranchus have been associated with FPTHV DNA, and thus considered candidate vectors. However, no viral pol transcripts were found in the leech RNA samples, showing that the leech vector role is most likely limited to mechanical transmission between turtles [8]. This does not rule out waterborne infection though, as the lung-eye-trachea virus, another herpesvirus of marine turtles, is incredibly stable in salt water [5].
References
Basler, C.F., Wang, X., Mühlberger, E., Volchkov, V., Paragas, J., Klenk, H.D., Garcia-Sastre, A. & Palese, P. (2000). The Ebola virus VP35 protein functions as a type I IFN antagonist. PNAS, 97, 12289-12294.
Basler, C.F., Mikulasova, A., Martinez-Sobrido, L., Paragas, J., Mühlberger, E., Bray, M., Klenk, H.D., Palese, P. & García-Sastre, A. (2003). The Ebola Virus VP35 Protein Inhibits Activation of Interferon Regulatory Factor 3. Journal of Virology, 77(14), 7945-7956.
Bavari, S., Bosio, C.M., Wiegand, E., Ruthel, G., Will, A.B., Geisbert, T.W., Hevey, M., Schmaljohn, C., Schmaljohn, A. & Aman, M.J. (2002). Lipid Raft Microdomains: A Gateway for Compartmentalized Trafficking of Ebola and Marburg Viruses. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 195(5), 593-602.
Bhattacharyya, S., Warfield, K.L., Ruthel, G., Bavari, S., Aman, M.J. & Hope, T.J. (2010). Ebola virus uses clathrin-mediated endocytosis as an entry pathway. Virology, 401, 18-28.
Borio, L., Inglesby, T., Peters, C.J., Schmaljohn, A.L., Hughes, J.M., Jahrling, P.B., Ksiazek, T., Johnson, K.M., Meyerhoff, A., O’Toole, T., Ascher, M.S., Bartlett, J., Breman, J.G., Eitzen, Jr., E.M., Hamburg, M., Hauer, J., Henderson, D.A., Johnson, R.T., Kwik, G., Layton, M., Lillibridge, S., Nabel, G.J., Osterholm, M.T., Perl, T.M., Russell, P. & Tonat, K. (2002). Hemorrhagic fever viruses as biological weapons: medical and public health management. Journal of the American Medical Association, 287, 2391-2405.
CDC Special Pathogens Branch. (2010). Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever Case Count and Location List. Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever Information Packet.
Cheng, P.C., Cherukuri, A., Dykstra, M., Malapati, S., Sproul, T., Chen, M.R. & Pierce, S.K. (2001). Floating the raft hypothesis: the roles of lipid rafts in B cell antigen receptor function. Semininars in Immunology, 13, 107-114.
Crary, S.M., Towner, J.S., Honig, J.E., Shoemaker, T.R. & Nichol, S.T. (2003). Analysis of the role of predicted RNA secondary structures in Ebola virus replication. Virology, 306(2), 210-218.
Emerson, S.U. (1982). Reconstitution studies detect a single polymerase entry site on the vesicular stomatitis virus genome. Cell, 31, 635-642.
Empig, C.J. & Goldsmith, M.A. (2002). Association of the caveola vesicular system with cellular entry by filoviruses. Journal of Virology, 76, 5266-5270.
Feldmann, H., Klenk, H.D. & Sanchez, A. (1993). Molecular biology and evolution of filoviruses. Archives of Virology, Supplementum, 7, 81-100.
Hoenen, T., Groseth, A., Kolesnikova, L., Theriault, S., Ebihara, H., Hartlieb, B., Bamberg, S., Feldmann, H., Ströher, U. & Becker, S. (2006). Infection of Naïve Target Cells with Virus-Like Particles: Implications for the Function of Ebola Virus VP24. Journal of Virology, 80(14), 7260-7264.
Huang, Y., Xu, L., Sun, Y. & Nabel, G.J. (2002). The assembly of Ebola virus nucleocapsid requires virion-associated proteins 35 and 24 and posttranslational modification of nucleoprotein. Molecular Cell, 10, 307-316.
Iverson, L.E. & Rose, J.K. (1982). Sequential synthesis of 5’-proximal vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA sequences. Journal of Virology, 44, 356-365.
Jasenosky, L.D., Neumann, G., Lukashevich, I. & Kawaoka, Y. (2001). Ebola Virus VP40-Induced Particle Formatin and Association with the Lipid BIlayer. Journal of Virology, 75(11), 5205-5214.
John, S.P., Wang, T., Steffen, S., Longhi, S., Schmaljohn, C.S. & Jonsson, C.B. (2007). Ebola Virus VP30 Is an RNA Binding Protein. Journal of Virology, 81(17), 8967-8976.
Johnson, K.M. & Breman, J.G. (1978) Ebola haemorrhagic fever in Zaire, 1976. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 56(2), 271-293.
Klenk, H.-D. & Feldmann, H. (2004). Ebola and Marburg Viruses: Molecular and Cellular Biology. Wymondham: Horizon Bioscience.
Martínez, M.J., Biedenkopf, N., Volchkova, V., Hartlieb, B., Alazard-Dany, N., Reynard, O., Becker, S. & Volchkov, V. (2008). Role of Ebola Virus VP30 in Transcription Reinitiation. Journal of Virology, 82(24), 12569-12573.
Modrof, J., Becker, S. & Muhlberger, E. (2003). Ebola virus transcription activator VP30 is a zinc-binding protein. Journal of Virology, 77, 3334-3338.
Moran, M. & Miceli, M.C. (1998). Engagement of GPI-linked CD48 contributes to TCR signals and cytoskeletal reorganization: a role for lipid rafts in T cell activation. Immunity, 9, 787-796.
Mühlberger, E.,Weik, M., Volchkov, V.E., Klenk, H.D. & Becker, S. (1999). Comparison of the transcription and replication strategies of Marburg virus and Ebola virus by using artificial replication systems. Journal of Virology, 73, 2333-2342.
Pratt, W.D., Wang, D., Nichols, D.K., Luo, M., Woraratanadharm, J., Dye, J.M., Holman, D.H. & Dong, J.Y. (2010). Protection of Nonhuman Primates against Two Species of Ebola Virus Infection with a Single Complex Adenovirus Vector. Clinical and Vaccine Immunology, 17(4), 572-581.
Quinn, K., Brindley, M.A., Weller, M.L., Kaludov, N., Kondratowicz, A., Hunt, C.L., Sinn, P.L., McCray, P.B., Stein, C.S., Davidson, B.L., Flick, R., Mandell, R., Staplin, W., Maury, W. & Chiorini, J.A. (2009). Rho GTPases Modulate Entry of Ebola Virus and Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Pseudotyped Vectors. Journal of Virology, 83(19), 10176-10186.
Reid, S.P., Leung, L.W., Hartman, A.L., Martinez, O., Shaw, M.L., Carbonnelle, C., Volchkov, V.E., Nichol, S.T. & Basler, C.F. (2006). Ebola Virus VP24 Binds Karyopherin α1 and Blocks STAT1 Nuclear Accumulation. Journal of Virology, 80(11), 5156-5167.
Saeed, M.F., Kolokoltsov, A.A., Albrecht, T. & Davey, R.A. (2010). Cellular Entry of Ebola Virus Involves Uptake by a Macropinocytosis-Like Mechanism and Subsequent Trafficking through Early and Late Endosomes. PLOS Pathogens, 6(9).
Saifuddin, M., Hedayati, T., Atkinson, J.P., Holguin, M.H., Parker, C.J. & Spear, G.T. (1997). Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 incorporates both glycosyl phosphatidylinositol-anchored CD55 and CD59 and integral membrane CD46 at levels that protect from complement-mediated destruction. Journal of General Virology, 78, 1907-1911.
Sanchez, A., Kiley, M.P., Holloway, B.P. & Auperin, D.D. (1993). Sequence analysis of the Ebola virus genome: organization, genetic elements, and comparison with the genome of Marburg virus. Virus Research, 29, 215-240.
Schümann, M., Gantke, T. & Mühlberger, E. (2009). Ebola Virus VP35 Antagonizes PKR Activity through Its C-Terminal Interferon Inhibitory Domain. Journal of Virology, 83(17), 8993-8997.
Schornberg, K., Matsuyama, S., Kabsch, K., Delos, S., Bouton, A. & White, J. (2006). Role of endosomal cathepsins in entry mediated by the Ebola virus glycoprotein. Journal of Virology, 80(8), 4174-4178.
Volchkov, V.E., Becker, S., Vochkova, V.A., Ternovoj, V.A., Kotov, A.N., Netesov, S.V. & Klenk, H.D. (1995). GP mRNA of Ebola virus is edited by the Ebola virus polymerase and by T7 and vaccinia virus polymerases. Virology, 214, 421-430.
Watanabe, S., Noda, T., Halfmann, P., Jasenosky, L. & Kawaoka, Y. (2007). Ebola Virus (EBOV) VP24 Inhibits Transcription and Replication of the EBOV Genome. The Journal of Infectious Diseases, 196, S284-290.
Weik, M., Modrof, J., Klenk, H.D., Becker, S. & Mühlberger, E. (2002). Ebola Virus VP30-Mediated Transcription Is Regulated by RNA Secondary Structure Formation. Journal of Virology, 76(17), 8532-8539.
World Health Organization. (2010). Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever. Epidemic and Pandemic Alert and Response (EPR).
Yonezawa, A., Cavrois, M. & Greene, W.C. (2005). Studies of Ebola Virus Glycoprotein-Mediated Entry and Fusion by Using Pseudotyped Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Virions: Involvement of Cytoskeletal Proteins and Enhancement by Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha. Journal of Virology, 79(2), 918-926.
Page authored for BIOL 375 Virology, September 2010
