Karst Springs: Difference between revisions
From MicrobeWiki, the student-edited microbiology resource
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
===Introduction=== | ===Introduction=== | ||
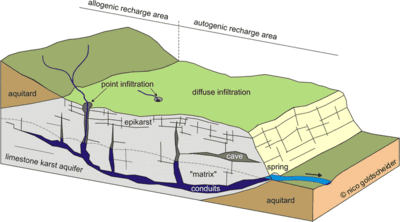
A Karst topography is formed when rock (often limestone) is dissolved, causing small fissures within the surface structure | A Karst topography is formed when rock (often limestone) is dissolved, causing small fissures within the surface structure. Karst springs are formed when water exits the subterranean matrix and forms surface pools. | ||
===Microbial Inhabitants=== | ===Microbial Inhabitants=== | ||
Revision as of 16:21, 27 March 2010
Introduction
A Karst topography is formed when rock (often limestone) is dissolved, causing small fissures within the surface structure. Karst springs are formed when water exits the subterranean matrix and forms surface pools.
Microbial Inhabitants
References
Picture references: 1. International Association of Hydrogeologists http://www.iah.org/karst/karst_hydrogeology.html