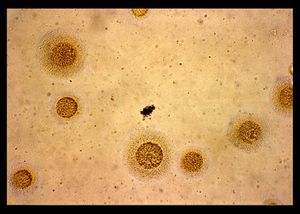
Mycoplasma hominis
Introduction
By [Jimmy Chapman 2013]
Classification
Higher Order Taxa:
Bacteria; Firmicutes; Mollicutes; Mycoplasmatales; Mycoplasmataceae; Mycoplasma
Species:
M. hominis
Cluster: M. bovis; M. pulmonis; M. hominis
Description and Significance:
M. hominis is a pathogen in humans commonly found as part of urogenital tract flora especially of women and sexually active adult males [14]. This bacteria cause a variety of infections which may lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, post-abortal fever, post-partum fever and extragenital infections for immunodepressed humans [14]. It also can cause meningitis, pneumonia and abcesseses in newborn children [20]. M. hominis lives parasitically and saphrophytically with hosts [25].
Section 1
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Section 2
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Section 3
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Conclusion
Overall text length at least 3,000 words, with at least 3 figures.
References
Edited by student of Joan Slonczewski for BIOL 238 Microbiology, 2011, Kenyon College.