Soil Unknown: P. aeruginosa: Difference between revisions
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
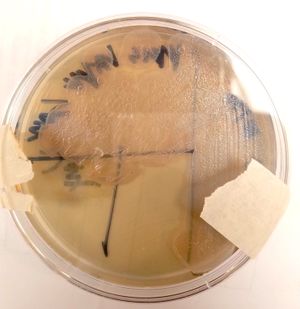
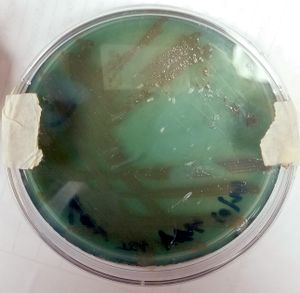
[[Image: P.aeruginosa30.jpg|thumb|left| 30 degree incubation of ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''.]] [[Image: P.aeruginosa37.jpg|thumb|center| 37 degree incubation of ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''.]] | [[Image: P.aeruginosa30.jpg|thumb|left| 30 degree incubation of ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''.]] [[Image: P.aeruginosa37.jpg|thumb|center| 37 degree incubation of ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''.]] | ||
'''Possible Antimicrobial Activity''' | '''Possible Antimicrobial Activity''' | ||
A study published in the ''Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials'' concluded that Pseudomonas aeruginosa-derived extracellular compounds such as phenazines have inhibitory effects against MRSA. A synergic effect was observed when combined with silver nanoparticles produced by Fusarium oxysporum (2). | |||
'''Significance of organism''' | '''Significance of organism''' | ||
Revision as of 18:52, 1 December 2017
Classification
Domain; Phylum; Class; Order; family [Others may be used. Use NCBI link to find]
Species
|
NCBI: Taxonomy |
Genus species: Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Habitat Information
The organism was isolated from 1 gram of a soil sample gathered from a park in the Barton Creek Landing complex in Travis County. In general, P. aeruginosa can be found in soil, decaying organic matter, and a variety of moist environments, including swimming pools, hot tubs, sponges, washcloths, and contact lens solutions (1).
Description and Significance
Describe the appearance (colonial and cellular), possible antimicrobial activity etc. of the organism, and why the organism might be significant.
Appearance P. aeruginosa colonies appear to be of small to moderate, irregular, pulvinate and smooth. When incubated at 30 degrees celsius, the colonies have a small amount of orange pigmentation. When incubated at 37 degrees celsius, the colonies have gray pigmentation, as well as blue-green extracellular pigmentation:
Possible Antimicrobial Activity
A study published in the Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials concluded that Pseudomonas aeruginosa-derived extracellular compounds such as phenazines have inhibitory effects against MRSA. A synergic effect was observed when combined with silver nanoparticles produced by Fusarium oxysporum (2).
Significance of organism
Genome Structure
Describe the size and content of the genome. How many chromosomes? Circular or linear? Other interesting features? What is known about its sequence? Include S Ribosomal sequence that you obtained from PCR and sequencing here.
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Interesting features of cell structure; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces.
Physiology and Pathogenesis
Biochemical characteristics, enzymes made, other characteristics that may be used to identify the organism; contributions to environment (if any).
If relevant, how does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.
References
1. Bauman, R. W. (2015) Microbiology with Diseases by Body System, pp. 567, 570. Glenview, IL: Pearson.
Author
Page authored by _____, student of Prof. Kristine Hollingsworth at Austin Community College.