Streptococcus mutans- Tooth Decay
Etiology/Bacteriology
Taxonomy
Kingdom: Bacteria | Phylum: Firmicutes | Class: Bacilli | Order: Lactobacillales | Family: Streptococcaceae | Genus: Streptococcus | Species: S. mutans
Description
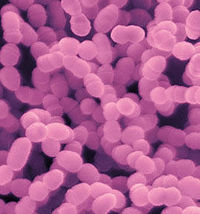
Streptococcus mutans are gram-positive coccus shaped bacteria. These facultative anaerobes are commonly found in the human oral cavity and is a significant contributor to tooth decay. The result of decay can greatly effect the overall health of the individual. (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Streptococcus_mutans) S. mutans are mesophilic and grow at temperatures between 18-40 degrees Celsius. Streptococcus mutans is a cariogenic microorganism that breaks down sugar for energy and produces an acidic environment, which demineralizes the superficial structure of the tooth. The result of the conversion disintegrates the coating of the tooth then later dissolves the Calcium molecule creating a hole. (http://www.whatarebacteria.com/streptococcus-mutans/) The transfer of genotypes are responsible for the transmission of S. mutans from mothers to their children, although there is a genotypic variation from one population to the next.
Pathogenesis
Transmission
Dental caries is an infectious and communicable dental disease that effects people of all ages. Streptococcus mutans can be passed from one person to the next via horizontal or vertical transmission. The transmission route of Streptococcus mutans is to colonize itself among human hosts. Children and infants are more prone to the diagnosis of Streptococcus mutans and studies show that many receive it from their primary caregivers. (http://www.podj.com.pk/Dec_2012/p-28.pdf) S. mutans favors hard non shedding surfaces to establish permanent colonies, which implies that levels of S. mutans are undetected in infants until the primary teeth extravasate. Although, recent studies have shown that S. mutans is able to colonize the furrows of the tongue in pre-denate infants. Typically between the ages of one and two, teeth erupt, which allows S. mutans to establish flourishing colonies on teeth, which lead to cavities. The indication of cavity formation is the appearance of detectable levels of bacteria on teeth. When S. mutans is detected in the furrows of the tongue it is concluded that the vertical transmission route for the bacteria from mother to child arises shortly after birth. To prove this, saliva samples of two to five year old children were taken, which revealed a high fidelity in genetic make-up of each host's S. mutans population. These experiments also concluded that plasmid DNA correlates to different rates, which primarily implys vertical transmission. Mothers with large amounts of bacteria or those who have suffered from many dental caries themselves are likely to transmit the same virulence factors to their children. When the mothers salivary S. mutans levels exceed 105 Colony Forming Units are nine times more likely to pass bacteria on to their children. (http://www.jyi.org/issue/the-role-of-streptococcus-mutans-and-oral-ecology-in-the-formation-of-dental-caries/)
Clinical features
Diagnosis
Treatment
Prevention
Host Immune Response
References
References
Created by {insert your names here}, students of Tyrrell Conway at the University of Oklahoma.
This template is just a general guideline of how to design your site. You are not restricted to this format, so feel free to make changes to the headings and subheadings and to add or remove sections as appropriate.
