Introduction
Caitlin Barker.
Infamous throughout history as one of the most unpleasant, harmful, and silent of sexually transmitted diseases, Syphilis remains a major health issue in the world's most neglected and troubled regions. Although now relatively rare in the United States, with approximately 36,000 cases reported a year and only around 30 fatalities, an estimated 492,000 infants in Sub-Saharan Africa die each year from congenital syphilis [2].
Syphilis presents a severe diagnostic challenge to healthcare workers around the world, due to the broad and inconclusive nature of its symptoms. Furthermore, this “great imitator” of a disease can also remain unnoticed in infected people for years, thus helping it spread from person to person through sexual contact. Because of this, effective and cheap syphilis screening is essential to its erradication.
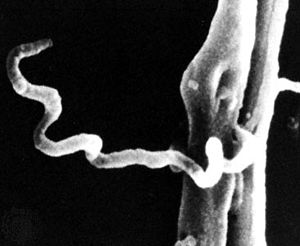
Fig. 1 The syphilis bacterium,
treponema pallidum attaching to a testicular cell. Source: The Encyclopedia Britannica, online.
Treponema Pallidum and Transmission
Stages, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Syphilis and HIV
Congenital Syphilis

Fig. 2 Symptoms of congenital syphilis in a newborn baby. Source: The New Zealand Medical Journal, online.
Current Issues
Conclusion
References
1. "Congenital Syphilis: Infections in Neonates: Merck Manual Professional." The Merck Manuals Online Medical Library. Merck and Co., n.d. Web. 7 Dec. 2009.
2. Peeling, Rosanna, David Mabey, Dan Fitzgerald, and Deborah Watson-Jones. "Avoiding HIV and Dying of Syphilis." The Lancet 364 (2004): 1561-1563. The Lancet. Web. 2 Dec. 2009.
3. "Prevention of Mother-to-Child Transmission of Syphilis." World Health Organization. N.p., n.d. Web. 6 Dec. 2009.
4."STD Facts - Syphilis." Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC, n.d. Web. 7 Dec. 2009.
5. "Syphilis: eMedicine Infectious Diseases." eMedicine - Medical Reference. N.p., n.d. Web. 7 Dec. 2009.
6. Terris-Prestholt, F, D Watson-Jones, K Mugeye, and L Kumaranayake. "Is Antenatal Syphilis Screening Still Cost Effective in Sub-Saharan Africa." Sexually Transmited Infections 375.79 (2003): 375-381. Sexually Transmited Infections. Web. 4 Dec. 2009.
7. Watson-Jones, Deborah, Monique Oliff, Fern Terris-Prestholt, and John Changalucha. "Antenatal Syphilis Screening in Sub-Saharan Africa: Lessons Learned from Tanzania." Tropical Medicine and International Health 10 (2005): 934-943. Tropical Medicine and International Health. Web. 7 Dec. 2009.
Edited by student of Joan Slonczewski for BIOL 191 Microbiology, 2009, Kenyon College.


