Thiothrix nivea
A Microbial Biorealm page on the genus Thiothrix nivea
Classification
Higher order taxa
Bacteria; Proteobacteria; Gammaproteobacteria; Thiotrichales; Thiotrichaceae; Thiothrix 2
Species
Thiothrix nivea
Description and significance
Thiothrix nivea is the type species for the Thiothrix genera. It was first described in 1888 by the Russian microbiologist, Sergey Nikolayevich Winogradsky. He had been doing research on various sulfur bacteria.5 It is found in sulfur containing flowing water such as sulfur springs, deep sea vents, and waste water treatment plants. It is not known to be pathogenic, due to its metabolic needs of constant sulfur flow, and the fact that it has been found to exist in temperatures of no more than 32-34 °C. None of which are found within the human body.
Genome structure
Thiothrix nivea's genome was completely mapped by the US Department of Energy's DOE Joint Genome Institute. The genome was found to contain about 4.7 mega-base pairs. The genome contains 4,594 total genes with 4,542 of those coding for proteins.4
Cell and colony structure
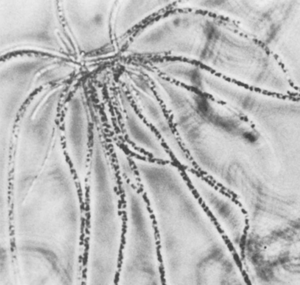
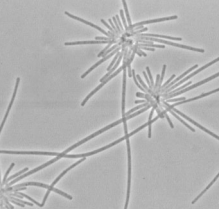
Thiothrix nivea is a 1-1.5 µm rod-shaped gram negative bacteria. When in the presence of sulfate or thiosulfate sulfur granules are deposited, external to the cytoplasm, in invaginations of the cytoplasmic membrane. Each cell has a tuft of fimbriae which anchors it to the cell beside it. Cells do not exhibit flagella. Cells grow and divide in a gliding motion enclosed within sheaths producing filamentous structures. When cells are clumped together, their division produces rosettes.3
Metabolism
Ecology
T. nivea is found free living in sulfide containing flowing waters such as sulfur springs, deep sea hydrothermal vents and is most well known for its populations in sewage waste water.4 T. nivea has been found to thrive within an optimal pH of 7.5 and temperatures ranging from 25-30 °C. 1 Cells have been found to withstand temperatures of minimally 6-8 °C and maximally 32-34 °C.2
References
1) Rossetti, Simona, Linda Blackall, et al. (2003) "Phylogenetic and physiological characterization of a heterotrophic, chemolithoautotrophic Thiothrix strain isolated from activated sludge." International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. Journal. DOI 10.1099/ijs.0.02647-0
2) Gerrity, George. (2005) Bergey's Manual of Sytematic Bacteriology: Volume 2 - The Proteobacteria Part B The Gammaproteobacteria. 2nd Ed. Volume 2. New York: Springer. pp 134-141. Ebook
3)Larkin, John, and Dean Sinabarger. (1983) "Characterization of Thiothrix nivea." International Journal ofSystematic Bacteriology. Volume 33. Issue 4. : pp 841-846. Journal
4) "Thiothrix nivea JP2, DSM 5205 ." Integrated Microbial Genomes (2011): n.pag. DOE Joint Genome Institute. Integrated Microbial Genome.
Edited by Brittany N King, student of Dr. Lisa R. Moore, University of Southern Maine, Department of Biological Sciences, University of Southern Maine Biology Department Website