Tina Torres Bacillus thuringiensis
Classification
Domain: Bacteria, Phylum: Firmicutes, Class: Bacilli, Order: Bacillales, Family: Bacillaceae [Others may be used. Use NCBI link to find]
Species
|
NCBI: Taxonomy |
Bacillus thuringiensis
Habitat Information
This soil sample was collected at 289 Spring Lane, Dripping Springs, TX 78620 Temperature: 60 F Humidity: 40% Wind Speed: NE 14G 22 mph Dewpoint: 35 F GPS coordinates: Latitude - 30.29001624465091, Longitude - -97.7299631715784
Description and Significance
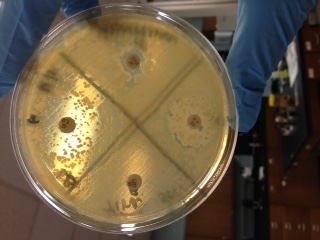
When streaked on an LB plate, the colonies that formed were opaque in appearance and flat. When tested for antimicrobial properties the one antibiotic that showed the most susceptibility was Sulfisoxazole, also a small zone of inhibition was seen with Ampicillin. Linezolid and Cefamandole showed no zone of inhibition.
Bacillus thuringiensis is a gram positive, soil dwelling bacterium that is commonly used as a biological pesticide.
Genome Structure
This is the forward sequence I used to determine that my soil sample was Bacillus thuringiensis:
GACGGAGCAACGCCGCGTGAGTGATGAAGGCTTTCGGGTCGTAAAACTCTGTTGTTAGGGAAGAACAAGTGCTAGTTGAATAAGCTGGCACCTTGACGGTACCTAACCAGAAAGCCACGGCTAACTACGTGCCAGCAGCCGCGGTAATACGTAGGTGGCAAGCGTTATCCGGAATTATTGGGCGTAAAGCGCGCGCAGGTGGTTTCTTAAGTCTGATGTGAAAGCCCACGGCTCAACCGTGGAGGGTCATTGGAAACTGGGAGACTTGAGTGCAGAAGAGGAAAGTGGAATTCCATGTGTAGCGGTGAAATGCGTAGAGATATGGAGGAACACCAGTGGCGAAGGCGACTTTCTGGTCTGTAACTGACACTGAGGCGCGAAAGCGTGGGGAGCAAACAGGATTAGATACCCTGGTAGTCCACGCCGTAAACGATGAGTGCTAAGTGTTAGAGGGTTTCCGCCCTTTANTGCTGAAGTTAACGCATTAAGCACTCCGCCTGGGGAGTACGGCCGCAAGGCTGAAACTCNNAGGAATTGACNGGGGCCCGCACAANCGGTGGANCATGTGGTTTAATT ACCAGGTNTTGAAATCCTCTGANAACCCTANAGATACGGCNTCTCNCNTCTNNAACATANTGAC
Consists of a 5.5-Mb chromosome and nine plasmids.
This organism is gram positive and forms endospores.
It is also found naturally in the gut of caterpillars, moths and butterflies.
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
This gram positive microorganism has a thick, cross linked peptidoglycan layer in the bacterial cell wall. It is harmful to many insects which is why it is commonly used as a pesticide.
During sporulation it produces crystal proteins or endotoxins. It is also closely related to Bacillus anthrasis, which is the cause of anthrax.
Physiology and Pathogenesis
Using various biochemical tests I was able to determine the following about this organism:
Citrate: test used to test an organism's ability to use carbon as it's only source
*soil sample - negative for citrate
SIM (Sulfar, Indole, Motility)
*soil sample - negative for sulfar, indole and motility
Nitrate
*soil sample - positive for nitrite reduction (nitrate --> nitrite)
Urea: tests an organism's ability to break down or convert urea to amonia
*soil sample - negative for urea
TSI (Triple Sugar Iron)
*soil sample - glucose fermentation with acid production
Decarboxylation: tests organism's ability to produce an enzyme called decarboxylase
*soil sample - Argine: positive for decarboxylase
Lysine: positive for fermentation
Ornithine: positive for decarboxylase
Phenylalanine Deaminase: tests organism's ability to produce enzyme deaminase
*soil sample - negative
Oxidase: identifies organisms that produce enzyme cytochrome oxidase, which participates in the electron transport chain
*soil sample - positive for cytochrome oxidase
Hektoen Enteric Agar: this media is selective and differential that is used to isolate Salmonella and Shigella species
*soil sample - negative and negative for fermentation
MacConkey Agar: selective and differential media that is used to isolate organisms based on their ability to ferment lactose
*soil sample - negative and negative for fermentation
Eosin Methylene Blue Agar: selective and differential media used to isolate fecal coliforms
*soil sample - positive for fermentation
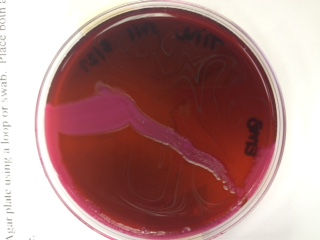
Blood Agar: helps to determine the hemolytic capabilities of an organism
*soil sample - alpha hemolysis (incomplete)
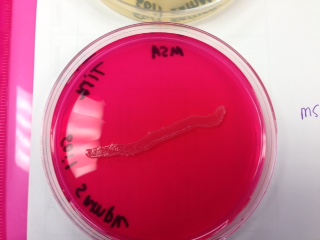
Mannitol Salt Agar: is selective for the genus Staphylococcus and differential for the fermentation of mannitol
*soil sample - negative for fermentation, positive for growth
Phenylethyl Alcohol Agar: selective media used to grow gram positive organisms
*soil sample - positive for growth
Catalase Test: enzyme (catalase) breaks down hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen
*soil sample - negative
6.5% Salt Tolerance: broth is made using tryptic soy broth and table salt to create high salt concentration, most organisms can't survive in high salt environments
*soil sample - positive (turbid)
Bile Esculin Test: used to identify enterococci and group D streptococci based on their ability to hydrolize esculin
*soil sample - positive for esculin hydrolysis
References
http://www.eol.org/pages/975750/overview
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bacillus_thuringiensis
Author
Page authored by Tina Torres, student of Prof. Kristine Hollingsworth at Austin Community College.