Tuberculosis disease: Difference between revisions
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
===Description=== | ===Description=== | ||
[[Image:breakdownstructure.jpg|frame|left|'' Mycobacterium tuberculosis Stain'' [http://edoc.hu-berlin.de/dissertationen/roese-lars-2004-06-09/HTML/Roese_html_m7f300b77.png]]] | [[Image:breakdownstructure.jpg|frame|left|'' Mycobacterium tuberculosis Stain'' [http://edoc.hu-berlin.de/dissertationen/roese-lars-2004-06-09/HTML/Roese_html_m7f300b77.png]]] | ||
<i> Mycobacterium tuberculosis</i> is an acid fast, nonmotile, obligate anaerobe. These bacilli range in size from 2-4 µm and have an incredibly slow generation time of 15 to 20 hours. The genus of <i> Mycobacterium</i> is defined by the mycolic acids and waxes, which makes the bacterium resistant to many bactericidal agents. For this reason, the tuberculosis disease can be easily spread due to the difficulty in killing the bacteria. <i> Mycobacterium tuberculosis</i> is very diverse and provides different geographic areas with different disease symptoms. [[#References|[2]]] | |||
==Pathogenesis== | ==Pathogenesis== | ||
Revision as of 09:52, 22 July 2013

Etiology/Bacteriology
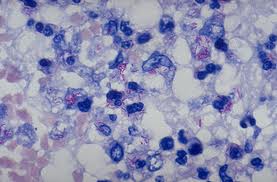
Taxonomy
Kingdom: Bacteria
Phylum: Actinobacteria
Class: Actinobacteria
Order: Actinomycetales
Family: Mycobacteriaceae
Genus: Mycobacterium
Species: tuberculosis
Description
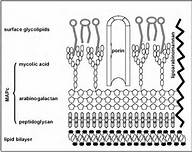
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is an acid fast, nonmotile, obligate anaerobe. These bacilli range in size from 2-4 µm and have an incredibly slow generation time of 15 to 20 hours. The genus of Mycobacterium is defined by the mycolic acids and waxes, which makes the bacterium resistant to many bactericidal agents. For this reason, the tuberculosis disease can be easily spread due to the difficulty in killing the bacteria. Mycobacterium tuberculosis is very diverse and provides different geographic areas with different disease symptoms. [2]
Pathogenesis
Transmission
Infectious Dose, Incubation, and Colonization
Epidemiology
Virulence Factors
Clinical Features and Symptoms
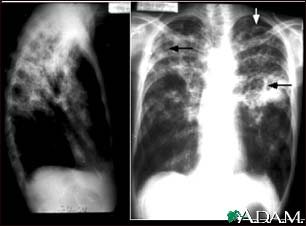
Diagnosis
Treatment
Prevention
Host Immune Response
References
1 Conway, Tyrrell. “Genus conway”. “Microbe Wiki” 2013. Volume 1. p. 1-2.
2 NHS General Information on Tuberculosis
3 Ozimek, Maleana Mycobacterium tuberculosis
4 CDC General Information on Tuberculosis
5 PPD skin test Medline Plus
6 Exposure to Tuberculosis Vanderbilt Occupational Health Clinic
Created by Jennifer Gallup, student of Tyrrell Conway at the University of Oklahoma.
