Tuberculosis disease

Etiology/Bacteriology
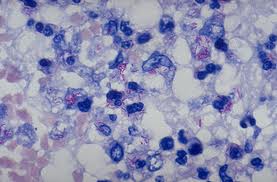
Taxonomy
Kingdom: Bacteria
Phylum: Actinobacteria
Class: Actinobacteria
Order: Actinomycetales
Family: Mycobacteriaceae
Genus: Mycobacterium
Species: tuberculosis
Description
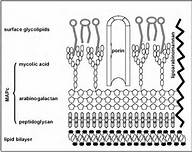
Pathogenesis
Transmission
Much too contrary belief, the only method by which tuberculosis (TB) is spread, is through airborne particles from person to person. If a healthy human were to breathe in the bacteria that escaped the lungs of an infected individual who coughed, sneezed, or even spoke, they will contract the disease. With Mycobacterium tuberculosis being able to colonize and affect many different parts of the body, the only contagious form of the disease is pulmonary tuberculosis. [3]
Infectious Dose, Incubation, and Colonization
Epidemiology
Virulence Factors
Clinical Features and Symptoms
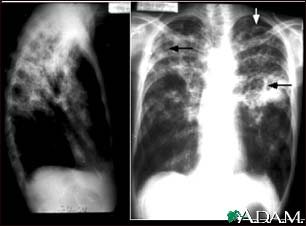
Diagnosis
Treatment
Prevention
Host Immune Response
References
1 Conway, Tyrrell. “Genus conway”. “Microbe Wiki” 2013. Volume 1. p. 1-2.
2 NHS General Information on Tuberculosis
3 Ozimek, Maleana Mycobacterium tuberculosis
4 CDC General Information on Tuberculosis
5 PPD skin test Medline Plus
6 Exposure to Tuberculosis Vanderbilt Occupational Health Clinic
Created by Jennifer Gallup, student of Tyrrell Conway at the University of Oklahoma.
