User:Newman5: Difference between revisions
From MicrobeWiki, the student-edited microbiology resource
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<b>By Alexis Newman</b> | <b>By Alexis Newman</b> | ||
[[Image:Gutmicrobiome.webp|thumb|300px|left|The gut microbiome contains millions of microbes essential to the health of humans. Photo credit: [https://news.harvard.edu/gazette/story/2021/05/study-links-genetic-makeup-of-bacteria-in-the-human-gut-to-several-diseases/]]] | [[Image:Gutmicrobiome.webp|thumb|300px|left|The gut microbiome contains millions of microbes essential to the health of humans. Photo credit: [https://news.harvard.edu/gazette/story/2021/05/study-links-genetic-makeup-of-bacteria-in-the-human-gut-to-several-diseases/]]] | ||
The human gut microbiome is a critical indicator of a person's health because of its profound influence on physiological processes. The number of bacterial cells outnumbers the number of human cells in the gut microbiota, and these microbes play large roles in metabolism and immune function to keep the body alive. | The human gut microbiome is a critical indicator of a person's health because of its profound influence on physiological processes. The number of bacterial cells outnumbers the number of human cells in the gut microbiota, and these microbes play large roles in metabolism and immune function to keep the body alive.<ref>Bull MJ. (2014). Part 1: The Human Gut Microbiome in Health and Disease. <i>Integr Med (Encinitas)<i>, 13(6):17-22. From PMC4566439<ref> | ||
The gut microbiome also serves as a barrier against pathogens, preventing their colonization and mitigating the risk of infections. However, disruption in the gut microbiota composition or function can weaken this barrier, increasing the susceptibility to pathogen invasion and potentially leading to gastrointestinal infections.[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4566439/#:~:text=In%20a%20healthy%20state%2C%20the,modulation%20of%20the%20immune%20system.] | The gut microbiome also serves as a barrier against pathogens, preventing their colonization and mitigating the risk of infections. However, disruption in the gut microbiota composition or function can weaken this barrier, increasing the susceptibility to pathogen invasion and potentially leading to gastrointestinal infections.[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4566439/#:~:text=In%20a%20healthy%20state%2C%20the,modulation%20of%20the%20immune%20system.] | ||
Revision as of 16:07, 14 April 2024
Human Gut Microbiome and Helicobacter pylori's presence
By Alexis Newman
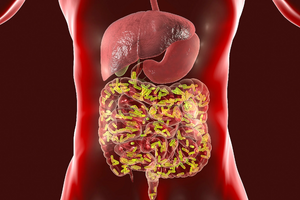
The gut microbiome contains millions of microbes essential to the health of humans. Photo credit: [1]
The human gut microbiome is a critical indicator of a person's health because of its profound influence on physiological processes. The number of bacterial cells outnumbers the number of human cells in the gut microbiota, and these microbes play large roles in metabolism and immune function to keep the body alive.Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag
[1]
A citation code consists of a hyperlinked reference within "ref" begin and end codes.
To repeat the citation for other statements, the reference needs to have a names: "<ref name=aa>"
The repeated citation works like this, with a forward slash.[2]
- ↑ Bartlett et al.: Oncolytic viruses as therapeutic cancer vaccines. Molecular Cancer 2013 12:103.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedaa
