User:S4355889: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<ref>MICR3004</ref> | <ref>MICR3004</ref> | ||
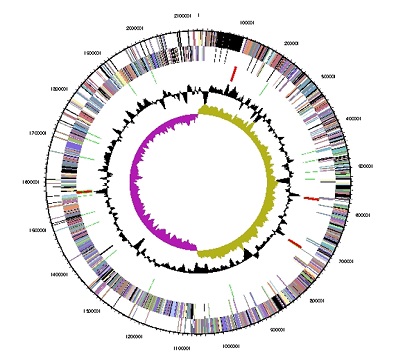
[[File:V parvula genome map C Le Lay.jpeg|500px|right|border|Graphical circular map of the genome. From outside to the center: Genes on forward strand (color by COG categories), Genes on reverse strand (color by COG categories), RNA genes (tRNAs green, rRNAs red, other RNAs black), GC content, GC skew.]] | |||
==Classification== | ==Classification== | ||
===Higher order taxa=== | ===Higher order taxa=== | ||
Bacteria - Terrabacteria group - Firmicutes - Negativicutes - Veillonellales - Veillonellaceae - Veillonella | Bacteria - Terrabacteria group - Firmicutes - Negativicutes - Veillonellales - Veillonellaceae - Veillonella | ||
===Species=== | ===Species=== | ||
Revision as of 12:41, 2 September 2016
Name: Callum Le Lay
Bench ID: C
Date: 31/08/2016
[1]
Classification
Higher order taxa
Bacteria - Terrabacteria group - Firmicutes - Negativicutes - Veillonellales - Veillonellaceae - Veillonella
Species
Type strain: ATCC 10790, ATCC 17742, CCUG 5123, DSM 2008, JCM 12972, KCTC 5019, NCTC 11810, Prevot Te 3, Prévot Te3, ATCC 10790, Te 3, VTT E-001737
Species name and type strain (consult LPSN http://www.bacterio.net/index.html for this information)
Description and significance
Give a general description of the species (e.g. where/when was it first discovered, where is it commonly found, has it been cultured, functional role, type of bacterium [Gram+/-], morphology, etc.) and explain why it is important to study this microorganism. Examples of citations [1], [2]
Genome structure
Select a strain for which genome information (e.g. size, plasmids, distinct genes, etc.) is available.
Cell structure and metabolism
Cell wall, biofilm formation, motility, metabolic functions.
Ecology
Aerobe/anaerobe, habitat (location in the oral cavity, potential other environments) and microbe/host interactions.
Pathology
Do these microorganisms cause disease in the oral cavity or elsewhere?
- Periodontitis and dental caries
- Bacterial vaginosis
- Osteomyelitus
- Endocarditis
Application to biotechnology
Bioengineering, biotechnologically relevant enzyme/compound production, drug targets,…
Current research
Summarise some of the most recent discoveries regarding this species.
References
References examples
- ↑ MICR3004
Notes
TEMPORARY: TO BE DELETED AFTER FINISH
This page was written by Callum Le Lay for the MICR3004 course, Semester 2, 2016