Candidatus Mellornella promiscua
Classification
Prokaryota; Proteobacteria; Alphaproteobacteria; Rickettsiales; Anaplasmataceae.
Description and Significance
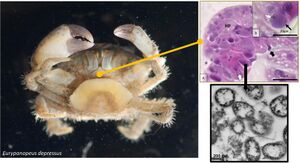
Bacterial pathogens such as Candidatus Mellornella promiscua threaten the survival and fitness of crustaceans. This is threatening the shellfish stock which is a major part of the economy. The cost estimating at $11.5 billion. This shows the importance of studying this economically significant species. Candidatus Mellornella promiscua inhabits brackish marine environments on the coastline of the eastern United States, specifically North Carolina is where it was found and studied at East Carolina University. It is the first identified hepatopancreatic rickettsia-like organism in the crab species which is important to study it further and its effect on the crustacean species.
Bojko J. et al. 2022
Genome Structure
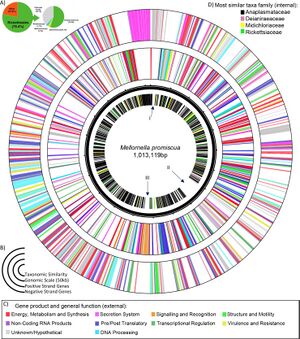
Candidatus Mellornella promiscua has a circular genome about 1,013,119 base pair in length. It encodes 899 protein coding genes, 1 pseudo gene, 3 ncRNA genes, 3 rRNA genes, and 33 tRNA genes. This encodes functional proteins that help with metabolism, synthesis, energy, DNA processing, secretion, translation, signaling, recognition, regulation, structure, motility, resistance, and others. Region I is composed of mix of metabolic and structural proteins. Region II is the largest region, and is composed of two protein groups: nitrogen processing and biosynthesis. Region III is signaling functions. Importantly, the bacterium has virulence genes that ensure antimicrobial drug resistance and it has multiple secondary metabolite clusters within.
Bojko J. et al. 2022
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Identification during a transmission electron micrograph showed multiple bacterial vacuoles expanding in the cell cytoplasm. The bacterium typically had a vacuolar membrane but in advanced infections they didn't have the vacuolar membrane and directly interacted with the host cell cytoplasm. Most bacterium presented a pili-like structure expanding around the bacteria cell as well as a fibrous inclusion body. Their life cycle consist of binary fission. Region 1 of the genome contains 12 protein coding genes which also consist of metabolic proteins. The bacterium also has multiple semi-conserved biosynthetic secondary metabolite clusters.
Bojko J. et al. 2022
Since there was not a lot of information on Candidatus Mellornella promiscua metabolic network, Zymomonas mobilis is broadly related to Region I of Ca. Mellornella which is the part of the genome that encodes metabolic genes. Zymomonas mobilis is a gram negative bacteria that is different from others in the fact that it is only known to metabolize glucose, fructose, and sucrose through the ED pathway. It is unable to use the glycolytic pathway, unable to use pentose sugars, and is a facultative anaerobic bacterium.
Bojko J. et al. 2022
Lee K. et al. 2010
Ecology and Pathogenesis
Candidatus Mellornella promiscua is a bacterial pathogen that is found in the fatback mud crab, Eurypanopeus depressus. The mud crab is native to estuaries in the Western Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico; particularly on the North Carolina coastline with a prevalence of 10.8%. It co-infects with rhizocephalan barnacle, Loxothylacus panopaei. It causes cytoplasmic hypertrophy, tubule necrosis, hepatopancreatic degradation, large plaques, and an abundance of sex-pili. It also contains bacterial symbionts that cause disease in different hosts; however, since it is a relatively new identified species it is unknown if it causes mortality in the crab host. It is predicted that it may have a way of altering the host microbiome to benefit its reproduction and growth and utilize the resources supplied by the host.
Bojko J. et al. 2022
References
Bojko J., McCoy K., Blakeslee A."Candidatus Mellornella promiscua n.gen.n.sp.(Alphaproteobacteria: Rickettsiales: Anaplasmataceae): An intracytoplasmic, hepatopancreatic, pathogen of the flatback mud crab, Eurypanopeus depressus".Journal of Invertebrate Pathology.2022. Volume 190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jip.2022.107737
Lee K., Park J., Kim T., Yun H., Lee S. The genome-scale metabolic network analysis of Zymomonas mobilis ZM4 explains the physiological features and suggests ethanol and succinic acid production strategies.Microbial Cell Factories 9. 2010. Volume 94. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-9-94
Author
Page authored by Maggie West, student of Prof. Bradley Tolar at UNC Wilmington.