Ebola
Ebola virus (EBOV) is a highly pathogenic and deadly disease that has remained an enigma. Its high infection rate and mortality rate are extremely problematic since there is currently no vaccine or treatment for infection. We are currently experiencing the largest outbreak of EBOV in recorded human history. Extensive research on EBOV has shown that is largely effective because of how it induces massive immune system deregulation in infected humans.
Overview of Ebola Virus and Ebola Virus Infection
Ebola virus belongs to the Filoviridae viral family which has three identified genera that include Ebola virus, Marburg virus, and recently identified Cueva virus1. The Ebolavirus genus itself has five identified species which include Reston Ebolavirus, Bundibugyo Ebolavirus, Sudan ebolavirus, Taı¨ Forest Ebolavirus, and Zaire Ebolavirus1.
In 1976 an outbreak of hemorrhagic fever in both Zaire and Sudan infected 550 individuals and was fatal in 430 of them6,7. The virus responsible for the outbreak was isolated from the infected patients and was found to be morphologically similar to Marburg but it was also serologically distinct6. Even after multiple outbreaks of both Marburg and Ebola, and extensive research on the different strains that have caused those outbreaks, the origin of Filoviruses still remains a mystery6. Outbreaks of Filoviruses have usually been contained in remote areas of Central Africa7. However the world is currently experiencing the largest Ebolavirus outbreak in its history. The outbreak is affecting Guinea, Liberia, Sierra Leone and Nigeria7. Had no interventions taken place, it was estimated that 1.4 million cases could have occur in Liberia and Sierra Leone by the beginnings of 20157.
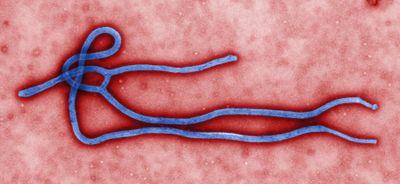
Morphology
Ebola can vary in length and observed optimal length as correlated to infectivity for is 970nm6. The individual virions can take many different shapes including long filaments, mace-shaped, ring, or U-shaped6,7. The virus has a diameter of 80nm and contain a nucleopcapsid, an envelope derived from host cell plasma membrane budding, and a surface layer of glycoprotein trimers6,7. EBOV is a linear negative-sense single stranded RNA virus6. EBOV is stable at room temperature, but can be inactivated by heating at 60˚C for thirty minutes, UV irradiation, commercial hypochlorite and phenolic disinfectants, and lipid solvents6.
Transmission and Host Invasion
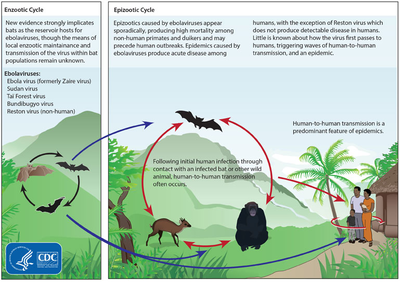
Ebola appears to be a zoonotic disease, yet the origin of the virus family still remains a mystery and no official reservoir has been identified6,7. Current speculation points to rodent or bat reservoirs6. Data analysis suggest that fruit bats, such as Hypsignathus monstrosus, Epomops franqueti, Rousettus aegyptiacus and Myonycteris torquata may be the reservoir7. Filoviruses are transmitted through direct contact with infected (living or dead) animals6,7. The viruses are also transmissible from person-to-person through direct or intimate contact with the infected individual or the individual’s bodily fluids6,7.
Ebola can infect its hosts through breaks or abrasions in the skin, accidental injection, or through mucosal surfaces7. The entry process is thought to go through three phases which include cellular attachment, endocytosis, and fusion1,7. It is strongly believed that Ebola enters the host cells by apoptotic mimicry and is consequently phagocytosed as part of micropinocytosis cellular response1,7. Accordingly, it is speculated that Ebola entry into host cells is enhanced by its lack of needing a surface receptor for entrance1,7.
Humans are able to transmit EBOV as soon as symptoms begin to manifest7. The human body continues to be infectious throughout the course of the infection and even after death7. In the current Ebola outbreak, the majority of infected individuals range from ages 15 to 44 years of age2. Incubation period of the infection is about 11.4 days, and the disease lasts about 15.3 days, and can end in either recovery or death2. It is estimated that the current case fatality rate is 70.8%2.
Symptoms of Ebola Infection
EBOV causes acute hemorrhagic fever and illness4,6. The virus usually incubates between 4-10 days6. Post incubation the infected individual becomes abruptly ill while displaying unspecific symptoms such as severe headache, myalgia, fever, bradycardia, malaise, and conjunctivitis6. The patient quickly deteriorates over the next 2-3 days while experiencing severe nausea, pharyngitis, hematemesis, melena, prostration, and obtundation6. Further deterioration includes uncontrolled bleeding from visceral hemorrhagic effusions, as well as venipuncture sites6. Usually a maculopapular rash appears at around day 5, and death usually occurs 6-9 days after onset of the disease6.
Treatment
Currently there is no designated treatment for Ebola hemorrhagic fever6. An anti-viral drug that has been used to treat other hemorrhagic fever, Ribavirin, has shown no in vitro effect on EBOV, and is thus of little clinical value6. Passive immunity for other viral diseases has been provided to individuals suffering from an infection using human convalescent plasma; however efficacy has not been confirmed when used on patients suffering from EBOV infection6. The best care available to patients infected with EBOV is intensive supportive care to prevent shock, bacterial superinfection, hypoxia, hypotension, renal failure and cerebral edema6.
Ebola Evades the Immune System
Ebola viral protein VP24
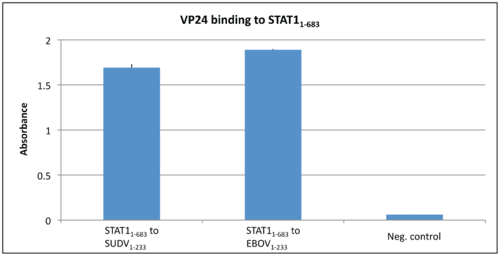
In a normal immune system response interferons (IFNs) trigger the protective defenses of the immune system to eliminate pathogens. IFNs activate Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcriptions (STAT) proteins, which in turn activate an immune response9. STAT1 is a crucial part of the Ebola viral infection pathway9. Normally STAT1 is phosphorylated when activated, and consequently is translocated to the nucleus via karyopherin-mediated nuclear trafficking9. Karyopherins, also known as importins, are responsible for the nuclear import of proteins that are too large for diffusion across the membrane, such as STAT110. Karyopherins have specific structural features that allow them to participate in binding. Karyopherin-α (Kapα) consists of ten helical repeats that are called armadillos (ARMs)11. ARMs 8-10 are important for Kapα binding to classical nuclear localization signal (cNLS)11. It had been shown in previous studies that Zaire Ebola virus protein VP24 has the ability to bind to karyopherin α1, α5, or α6. Thus Ebola protein VP24 selectively inhibits IFN-induced gene expression by sequestering nuclear accumulation of phosphorylated STAT1 since Kapα cannot bind to and translocate STAT112. More recent research has shown that VP24 can also bind directly to STAT1, consequently blocking STAT1 translocation to the nucleus through two inhibitory mechanisms13. Zhang et al preformed an ELISA test to determine if Ebola virus VP24 or Sudan Virus VP24 could bind to purified STAT113. It can be seen that there is a strong binding affinity between STAT1 and both versions of VP24 as compared to the negative control BSA 13.
Ebola uses apoptotic mimicry to invade cells
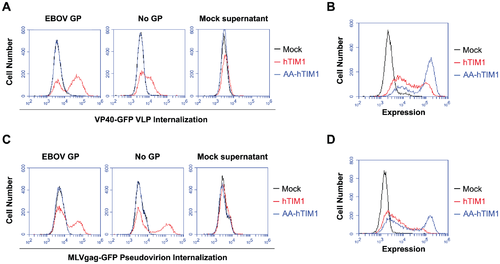
Ebola virus is very large, which can make it very difficult to enter using the classic clathrin endocytosis pathway1. It is suspected that because of its size, Ebola is taken up through cellular micropinocytosis1. Studies have shown that Ebola virus has an enriched amount of phosphatidylserine (PS) on its surface1. PS is a type of lipid that is normally present in the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane in healthy cells1. However PS is presented on the outer leaflet when the cell becomes unhealthy or is partaking in a programmed cell death mechanism15. PS on the outer leaflet signals neighboring cells to phagocytose the ‘marked’ cell15. This mechanism is mediated by TIM1 and does not produce an inflammatory or immune response14. Consequently this form of viral uptake has been termed ‘apoptotic mimicry’ and ensures that the virus will be taken into the cell without signaling the immune system1. T-cell Immunoglobulin and Mucin-domain containing proteins (TIM) selectively bind to PS14. Very recent research has demonstrated that when PS receptors on macrophages are inhibited, Ebola virus entry is blocked14. This data suggests that TIM is responsible in some part for the micropinocytosis of large enveloped viruses14. Jemielity S, et al tested this hypothesis by using GFP-fused matrix proteins as reporters that allow the detection of prefusion stages of viral entry14. The results of the figure provided indicate that virions bind to and internalize using TIM1 in a way that is not dependent on viral entry proteins but rather on the components of the viral membrane14.
Further Reading
Novel Nucleoside Ebola Treatement-Nature article presenting research on potential Ebola treatement.
Top Ebola Facts- CDC page on Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever.
Ebola Outbreak Updates- Doctors Without Borders latest updates on the outbreak in West Africa.
References
9. Reich, Ling. Tracking STAT nuclear traffic. Molecular Genetics and Microbiology. 2006, 602-612.
Edited by Constanza Jackson, a student of Nora Sullivan in BIOL168L (Microbiology) in The Keck Science Department of the Claremont Colleges Spring 2015.
