User:S4315109: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (71 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Lyman Ngiam | Lyman Ngiam 43151093 | ||
Bench D | Bench D | ||
23/9/16 | |||
<ref>MICR3004</ref> | <ref>MICR3004</ref> | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
===Higher order taxa=== | ===Higher order taxa=== | ||
The order taxa for Veillonella Parvula is listed as below: | The order taxa for ''Veillonella Parvula'' is listed as below: | ||
Kingdom – Domain – Phylum – Class – Order – Family – Genus | Kingdom – Domain – Phylum – Class – Order – Family – Genus | ||
[Bacteria]-[Terrabacteria group]-[Firmicutes]-[Negativicutes]-[Veillonellales]-[Veillonellacea]-[Veillonella] | [Bacteria] - [Terrabacteria group] - [Firmicutes] - [Negativicutes] - [Veillonellales] - [Veillonellacea] - [Veillonella] | ||
===Species=== | ===Species=== | ||
There are a total of | There are a total of 11 species <sup>[[#References|[1]]]</sup> have been reported under the genus Veillonella. ''Veillonella parvula'' is one of the species name. There are many different description terms for the strain of ''Veillonella Parvula'', as listed below: | ||
Type strain: strain ATCC10790 = CCUG 5123 = DSM 2008 = JCM 12972 = NCTC 11810 | Type strain: strain ATCC10790 = CCUG 5123 = DSM 2008 = JCM 12972 = NCTC 11810 | ||
==Description and significance== | ==Description and significance== | ||
Veillonella parvula is a gram negative, anaerobic, coccus bacteria that is part of the normal flora of the mouth, gastrointestinal tract and vagina in humans. The microorganism is first discovered by Veillon and Zuber in 1898. | ''Veillonella parvula'' is a gram negative, anaerobic, coccus bacteria that is part of the normal flora of the mouth, gastrointestinal tract and vagina in humans <sup>[[#References|[2]]]</sup>. The microorganism is first discovered by Veillon and Zuber in 1898. | ||
Generally, ''Veillonella parvula'' has been treated as normal commensal, however in rare cases, it can also cause infection as a pathogenic bacteria. Over the past years, reports has identified Veillonella species as a cause of endocarditis, obstructive pneumonitis, lung abscess, chronic sinusitis, chronic tonsillitis, liver abscess, and even meningitis <sup>[[#References|[2]]]</sup>. However,the most common reported infection caused by Veillonella parvula is osteomyelitis. | |||
One of the significant feature of this microoganism is the ability to confer multi antimicrobial resistance properties to ''Streptococcus mutans'' <sup>[[#References|[3]]]</sup>, a primary pathogen in dental caries and thrives in dental plague. The resistance is obtained via formation of a dual species biofilm between ''Veillonella parvula and Streptococcus mutans''. | |||
==Genome structure== | ==Genome structure== | ||
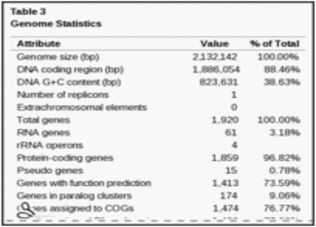
The genome of Veillonella parvula type strain DSM 2008 consist of a single circular chromosome that is 2,132,142 bp longs with 38.6% of GC contents | The genome of ''Veillonella parvula'' type strain DSM 2008 consist of a single circular chromosome that is 2,132,142 bp longs with 38.6% of GC contents <sup>[[#References|[4]]]</sup>. | ||
In terms of the gene identified, there are a total of 1920 genes that have been reported, however only 1859 of the genes are protein coding genes and 15 genes being identified as pseudogenes. The table below shows the genome statistics for ''Veillonella parvula''. | |||
[[File:t3 (1).png]] | |||
==Cell structure and metabolism== | ==Cell structure and metabolism== | ||
* Cell wall structure | * Cell wall structure | ||
[[File:sigs.png|thumb|right|alt=Electron micrograph of Veillonella Parvula.|Electron micrograph of ''Veillonella Parvula'']] | |||
''Veillonella parvula'' has a morphology of a coccus bacteria, with sizes of roughly 0.3 to 0.5 um <sup>[[#References|[5]]]</sup> in diameter, and grows in pairs or chains. Since it is a gram negative bacteria, the cell wall structure consist of an outer membrane, peptidoglycan layer and cytoplasmic membrane. The peptidoglycan layer consist of A1γ-type with glutamic acid in D configuration, diaminopimelic acid in meso configuration and covalently bound cadaverine or putrescine attached in α-linkage to glutamic acid <sup>[[#References|[5]]]</sup>. | |||
Apart from that, in the presence of plasmalogens such as plasmenylethanolamine and plasmenylserine, these ether lipids are able to replace the phospholipids found in ''Veillonella parvula'' membrane and aid in regulation of membrane fluidity. | |||
* Metabolic functions | * Metabolic functions | ||
Since the bacteria is an anaerobic bacteria, the main energy are produced via fermentative pathway, however it has been reported that Veillonellae are unable to use glucose or other carbohydrates for fermentation, instead it uses other organic acids such as pyruvate, malate or fumarate for fermentation. These molecules are usually end product of other carbohydrate-fermenting bacteria, therefore, Veillonella Parvula co-exist with carbohydrate-fermenting bacteria as a way to obtain required precursor molecules for its survival. | Since the bacteria is an anaerobic bacteria, the main energy are produced via fermentative pathway, however it has been reported that Veillonellae are unable to use glucose or other carbohydrates for fermentation, instead it uses other organic acids such as pyruvate, malate or fumarate for fermentation <sup>[[#References|[6]]]</sup>. These molecules are usually end product of other carbohydrate-fermenting bacteria, therefore, ''Veillonella Parvula'' co-exist with carbohydrate-fermenting bacteria as a way to obtain required precursor molecules for its survival. | ||
Besides that, another unique metabolic characteristic of the bacteria is the utilisation of methyl-CoA decarboxylase for the conversion of free energy derived from decarboxylation reactions into an electrochemical gradient of sodium ions. Oxaloacetate decarboxylase plays important role in citrate fermentation pathway and has additional function to conserve free energy from decarboxylation via generation of sodium ion gradient. Sodium ion bioenergetics play important roles in link between exergonic and endogenic reactions in the membrane. | Besides that, another unique metabolic characteristic of the bacteria is the utilisation of methyl-CoA decarboxylase <sup>[[#References|[7]]]</sup> for the conversion of free energy derived from decarboxylation reactions into an electrochemical gradient of sodium ions. Oxaloacetate decarboxylase plays important role in citrate fermentation pathway and has additional function to conserve free energy from decarboxylation via generation of sodium ion gradient <sup>[[#References|[7]]]</sup>. Sodium ion bioenergetics play important roles in link between exergonic and endogenic reactions in the membrane. | ||
* Cell characterisitc | * Cell characterisitc | ||
Another structural characteristic trait of veillonellae is their ability to form intergeneric coaggregates with other bacteria in the same niche. Besides that, the bacteria are unable to adhere itself to the surfac, instead it relies on specific attachment to certain surface structure on other bacterium via lectin-carbohydrate interactions. | Another structural characteristic trait of veillonellae is their ability to form intergeneric coaggregates with other bacteria in the same niche. Besides that, the bacteria are unable to adhere itself to the surfac, instead it relies on specific attachment to certain surface structure on other bacterium via lectin-carbohydrate interactions <sup>[[#References|[8]]]</sup>. | ||
==Ecology== | |||
The natural habitat of this bacteria is human dental plague and majority of it resides in the subgingival sites <sup>[[#References|[9]]]</sup>. The bacteria can also be found in gastrointestinal tract. | |||
==Pathology== | |||
''Veillonella parvula'' is generally regarded as normal commensal in both human oral cavity or gastrointestinal tract. However, in rare cases, the bacteria can also be a pathogen, that causes infection such as osteomyelitis, meningitis and oral diseases. However, most of the disease arises as a consequence of polymicrobial interaction. During the interaction, ''Veillonella parvula'' are able to adhere to specific cell structure of the microbe and form biofilm. As a result from this, a dual-species biofilm is formed, providing more protection for the microbe community within the biofilm, allowing better survival of other pathogenic bacteria. a good example of this is ''Streptococcus mutans'' and ''Veillonella parvula'' <sup>[[#References|[3]]]</sup>. | |||
In terms treatment availability, due to lack of reports on Veillonella infection, antibiotic treatment has been prescribed to treat ''Veillonella parvula'' infections. However, ''Veillonella parvula'' are resistant to certain antibiotic such as tetracycline, vancomycin, aminoglycosides, and ciprofloxacin and have intermediate susceptibility to erythromycin <sup>[[#References|[10]]]</sup>. Till date, the most effective choice of antibiotic treatment is Penicillin. | |||
==Application to biotechnology== | |||
Currently, the properties of ''Veillonella parvula'' biofilm and antibiotic resistance <sup>[[#References|[11]]]</sup> has been studied due to the colonisation of the bacteria in majority of the oral cavity. Apart from that, researchers have also explored that fermenting abilities of ''Veillonella parvula'', as a probiotic control against ''Salmonella'' <sup>[[#References|[12]]]</sup>. | |||
==Current research== | |||
The characterisitc of Veillonellae biofilm interaction has been studied in order to understand its mutualistic relationship with early, middle and late colonizers of the oral cavity and it's association with dental plague. In this case, the resistance properties of ''Veillonella parvula'' to certain antibiotic has been studied, via identifying resistant gene. From the studies, it is found that Veillonella species might be a reservoir for transferable Tetracyline resistance in oral cavity, and the gene tet(M)-positive is the causative gene <sup>[[#References|[11]]]</sup>. Through the gene transfer activity, the gene are able to provide additional resistance properties to nearby microbe. | |||
"Veillonella parvula" lactate fermenting abilities has also been explored and used as a pro-biotic control for ''Salmonella''<sup>[[#References|[12]]]</sup>, a bacterium that can cause food poisoning. From the studies, the growth of "Salmonella" is inhibited by production of volatile fatty acids by Veillonella that is grown on lactate or succinate agar medium. Apart from the volatile compounds, the presence of succinate in the media and final pH of the media also contribute to the inhibition of "Salmonella" growth. | |||
==References== | |||
References examples | |||
Veillonella | 1. [http://ijs.microbiologyresearch.org/content/journal/ijsem/10.1099/ijs.0.2008/001032-0#tab2.x/full Kraatz M, Taras D. 2008. Veillonella magna sp. nov., isolated from the jejunal mucosa of a healthy pig, and emended description of Veillonella ratti. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology <b>58<b>:2755-2761.] | ||
2. [http://standardsingenomics.org/content/9/2/431/.x/full Vesth T, Ozen A, Andersen SC, Kaas RS, Lukjancenko O, Bohlin J, Nookaew I, Wassenaar TM, Ussery DW. 2013. Veillonella , Firmicutes : Microbes disguised as Gram negatives. Standards in Genomic Sciences <b>9<b>:431-448.] | |||
3. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2593232/ Chalmers NI, Palmer RJ, Cisar JO, Kolenbrander PE. 2008. Characterization of a Streptococcus sp.-Veillonella sp. Community Micromanipulated from Dental Plaque. Journal of Bacteriology <b>190<b>:8145-8154. doi:10.1128/JB.00983-08.] | |||
4. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3035260/ Gronow S, Welnitz S, Lapidus A. 2010. Complete genome sequence of Veillonella parvula type strain (Te3T). Standards in Genomic Sciences.<b>2<b>:57-65. doi:10.4056/sigs.521107.] | |||
5. [http://ijs.microbiologyresearch.org/content/journal/ijsem/10.1099/ijs.0.02952-0#tab2 Jumas-Bilak E, Carlier J-P, Jean-Pierre H, Teyssier C, Gay B, Campos J, Marchandin H. 2004. Veillonella montpellierensis sp. nov., a novel, anaerobic, Gram-negative coccus isolated from human clinical samples. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology <b>54<b>:1311-1316.] | |||
6. [http://mic.microbiologyresearch.org.ezproxy.library.uq.edu.au/content/journal/micro/10.1099/00221287-138-5-967 Denger K, Schink B. 1992. Energy conservation by succinate decarboxylation in Veillonella parvula. Microbiology <b>138<b>:967-971.] | |||
7. [http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com.ezproxy.library.uq.edu.au/doi/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb18426.x/abstract DIMROTH, P. (1985), Biotin-dependent Decarboxylases As Energy Transducing Systems. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, <b>447<b>: 72–85. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb18426.] | |||
8. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC202786/ Hughes, C. V., Kolenbrander, P. E., Andersen, R. N., & Moore, L. V. 1988. Coaggregation properties of human oral Veillonella spp.: relationship to colonization site and oral ecology. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, <b>54<b>: 1957–1963.] | |||
9. [http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com.ezproxy.library.uq.edu.au/doi/10.1111/j.1600-0463.2009.02584.x/full LEUCKFELD, I., PASTER, B. J., KRISTOFFERSEN, A. K. and OLSEN, I. (2010), Diversity of Veillonella spp. from subgingival plaque by polyphasic approach. APMIS, <b>118<b>: 230–242. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0463.2009.02584.x] | |||
10. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC444184/ Martin, W. J., Gardner, M., & Washington, J. A. 1972. In Vitro Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Anaerobic Bacteria Isolated from Clinical Specimens. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, <b>1<b>:148–158.] | |||
11. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1538667/ Ready, D., Pratten, J., Roberts, A. P., Bedi, R., Mullany, P., & Wilson, M. 2006. Potential Role of Veillonella spp. as a Reservoir of Transferable Tetracycline Resistance in the Oral Cavity. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, <b>50<b>:2866–2868. http://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00217-06] | |||
12. [http://www.jstor.org.ezproxy.library.uq.edu.au/stable/1591872?sid=primo&origin=crossref&seq=1#page_scan_tab_contents Hinton A, Hume ME. 1995. Synergism of Lactate and Succinate as Metabolites Utilized by Veillonella to Inhibit the Growth of Salmonella typhimurium and Salmonella enteritidis in vitro. Avian Diseases <b>39<b>:309-316.] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:03, 22 September 2016
Lyman Ngiam 43151093 Bench D 23/9/16 [1]
Classification
Higher order taxa
The order taxa for Veillonella Parvula is listed as below:
Kingdom – Domain – Phylum – Class – Order – Family – Genus
[Bacteria] - [Terrabacteria group] - [Firmicutes] - [Negativicutes] - [Veillonellales] - [Veillonellacea] - [Veillonella]
Species
There are a total of 11 species [1] have been reported under the genus Veillonella. Veillonella parvula is one of the species name. There are many different description terms for the strain of Veillonella Parvula, as listed below:
Type strain: strain ATCC10790 = CCUG 5123 = DSM 2008 = JCM 12972 = NCTC 11810
Description and significance
Veillonella parvula is a gram negative, anaerobic, coccus bacteria that is part of the normal flora of the mouth, gastrointestinal tract and vagina in humans [2]. The microorganism is first discovered by Veillon and Zuber in 1898.
Generally, Veillonella parvula has been treated as normal commensal, however in rare cases, it can also cause infection as a pathogenic bacteria. Over the past years, reports has identified Veillonella species as a cause of endocarditis, obstructive pneumonitis, lung abscess, chronic sinusitis, chronic tonsillitis, liver abscess, and even meningitis [2]. However,the most common reported infection caused by Veillonella parvula is osteomyelitis.
One of the significant feature of this microoganism is the ability to confer multi antimicrobial resistance properties to Streptococcus mutans [3], a primary pathogen in dental caries and thrives in dental plague. The resistance is obtained via formation of a dual species biofilm between Veillonella parvula and Streptococcus mutans.
Genome structure
The genome of Veillonella parvula type strain DSM 2008 consist of a single circular chromosome that is 2,132,142 bp longs with 38.6% of GC contents [4].
In terms of the gene identified, there are a total of 1920 genes that have been reported, however only 1859 of the genes are protein coding genes and 15 genes being identified as pseudogenes. The table below shows the genome statistics for Veillonella parvula.
Cell structure and metabolism
- Cell wall structure
Veillonella parvula has a morphology of a coccus bacteria, with sizes of roughly 0.3 to 0.5 um [5] in diameter, and grows in pairs or chains. Since it is a gram negative bacteria, the cell wall structure consist of an outer membrane, peptidoglycan layer and cytoplasmic membrane. The peptidoglycan layer consist of A1γ-type with glutamic acid in D configuration, diaminopimelic acid in meso configuration and covalently bound cadaverine or putrescine attached in α-linkage to glutamic acid [5].
Apart from that, in the presence of plasmalogens such as plasmenylethanolamine and plasmenylserine, these ether lipids are able to replace the phospholipids found in Veillonella parvula membrane and aid in regulation of membrane fluidity.
- Metabolic functions
Since the bacteria is an anaerobic bacteria, the main energy are produced via fermentative pathway, however it has been reported that Veillonellae are unable to use glucose or other carbohydrates for fermentation, instead it uses other organic acids such as pyruvate, malate or fumarate for fermentation [6]. These molecules are usually end product of other carbohydrate-fermenting bacteria, therefore, Veillonella Parvula co-exist with carbohydrate-fermenting bacteria as a way to obtain required precursor molecules for its survival.
Besides that, another unique metabolic characteristic of the bacteria is the utilisation of methyl-CoA decarboxylase [7] for the conversion of free energy derived from decarboxylation reactions into an electrochemical gradient of sodium ions. Oxaloacetate decarboxylase plays important role in citrate fermentation pathway and has additional function to conserve free energy from decarboxylation via generation of sodium ion gradient [7]. Sodium ion bioenergetics play important roles in link between exergonic and endogenic reactions in the membrane.
- Cell characterisitc
Another structural characteristic trait of veillonellae is their ability to form intergeneric coaggregates with other bacteria in the same niche. Besides that, the bacteria are unable to adhere itself to the surfac, instead it relies on specific attachment to certain surface structure on other bacterium via lectin-carbohydrate interactions [8].
Ecology
The natural habitat of this bacteria is human dental plague and majority of it resides in the subgingival sites [9]. The bacteria can also be found in gastrointestinal tract.
Pathology
Veillonella parvula is generally regarded as normal commensal in both human oral cavity or gastrointestinal tract. However, in rare cases, the bacteria can also be a pathogen, that causes infection such as osteomyelitis, meningitis and oral diseases. However, most of the disease arises as a consequence of polymicrobial interaction. During the interaction, Veillonella parvula are able to adhere to specific cell structure of the microbe and form biofilm. As a result from this, a dual-species biofilm is formed, providing more protection for the microbe community within the biofilm, allowing better survival of other pathogenic bacteria. a good example of this is Streptococcus mutans and Veillonella parvula [3].
In terms treatment availability, due to lack of reports on Veillonella infection, antibiotic treatment has been prescribed to treat Veillonella parvula infections. However, Veillonella parvula are resistant to certain antibiotic such as tetracycline, vancomycin, aminoglycosides, and ciprofloxacin and have intermediate susceptibility to erythromycin [10]. Till date, the most effective choice of antibiotic treatment is Penicillin.
Application to biotechnology
Currently, the properties of Veillonella parvula biofilm and antibiotic resistance [11] has been studied due to the colonisation of the bacteria in majority of the oral cavity. Apart from that, researchers have also explored that fermenting abilities of Veillonella parvula, as a probiotic control against Salmonella [12].
Current research
The characterisitc of Veillonellae biofilm interaction has been studied in order to understand its mutualistic relationship with early, middle and late colonizers of the oral cavity and it's association with dental plague. In this case, the resistance properties of Veillonella parvula to certain antibiotic has been studied, via identifying resistant gene. From the studies, it is found that Veillonella species might be a reservoir for transferable Tetracyline resistance in oral cavity, and the gene tet(M)-positive is the causative gene [11]. Through the gene transfer activity, the gene are able to provide additional resistance properties to nearby microbe.
"Veillonella parvula" lactate fermenting abilities has also been explored and used as a pro-biotic control for Salmonella[12], a bacterium that can cause food poisoning. From the studies, the growth of "Salmonella" is inhibited by production of volatile fatty acids by Veillonella that is grown on lactate or succinate agar medium. Apart from the volatile compounds, the presence of succinate in the media and final pH of the media also contribute to the inhibition of "Salmonella" growth.
References
References examples
- ↑ MICR3004
This page is written by Lyman Ngiam Tze Kin for the MICR3004 course, Semester 2, 2016