Bacteriophages in Cancer Biology and Treatment: Difference between revisions
Shubitidze1 (talk | contribs) |
Shubitidze1 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
Tumors have become increasingly more clever in their ways of evading the immune system. | Tumors have become increasingly more clever in their ways of evading the immune system. | ||
<b>The Tumor Microenvironment</b> | ===<b>The Tumor Microenvironment</b>=== | ||
In both animal and human models, tumors have been discovered to actively suppress and manipulate immune responses. Usually our immune system's CD8+ cytotoxic T cells (CTL) and CD4 + helper T (Th)1 cells are capable of warding off cancer development by producing interferons (IFN) and cytotoxins (SCB).[1] Cytotoxic T cells are a type of white blood cell that kill cancer cells, or cells that are dysfunctional. Interferons are signaling proteins released by infected host cells that alert nearby cells to strengthen up their defenses. The continual production of these type of cells, however, leads to chronic inflammation, which has been tied to the spread of cancer. Inflammatory responses occur when damaged cells release chemicals that alert the immune system that something is wrong. White blood cells will flood to the scene, and start the process of creating new cells by diving existing ones in order to help with rebuilding the damaged tissue. The continual division of cells, leads to a higher likelihood of DNA damage, and subsequently cancer. <ref>[https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/chronic-inflammation National Cancer Institute "Chronic Inflammation" April 2015.</ref> | In both animal and human models, tumors have been discovered to actively suppress and manipulate immune responses. Usually our immune system's CD8+ cytotoxic T cells (CTL) and CD4 + helper T (Th)1 cells are capable of warding off cancer development by producing interferons (IFN) and cytotoxins (SCB).[1] Cytotoxic T cells are a type of white blood cell that kill cancer cells, or cells that are dysfunctional. Interferons are signaling proteins released by infected host cells that alert nearby cells to strengthen up their defenses. The continual production of these type of cells, however, leads to chronic inflammation, which has been tied to the spread of cancer. Inflammatory responses occur when damaged cells release chemicals that alert the immune system that something is wrong. White blood cells will flood to the scene, and start the process of creating new cells by diving existing ones in order to help with rebuilding the damaged tissue. The continual division of cells, leads to a higher likelihood of DNA damage, and subsequently cancer. <ref>[https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/chronic-inflammation National Cancer Institute "Chronic Inflammation" April 2015.</ref> | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
[[Image: phagesimmune.png|thumb|400px|right|Figure 2. Interaction of bacteriophages with mammalian immune cells <ref name=interactions/>]] | [[Image: phagesimmune.png|thumb|400px|right|Figure 2. Interaction of bacteriophages with mammalian immune cells <ref name=interactions/>]] | ||
<b>Manipulating the Tumor Microenvironment</b> | ===<b>Manipulating the Tumor Microenvironment</b>=== | ||
Recently, bacteriophages have been show to be capable of modifying the tumor environment. Phage coat proteins, and phage DNA tend to elicit strong responses from the innate immune system, prompting phagocytosis and cytokine release.<ref name=Eriksson/>There have been studies that show cytokine storms can be generated as a response to phage infiltration. <ref name=interactions>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6356784/pdf/viruses-11-00010.pdf Van Belleghem, J.D.; Dąbrowska, K.; Vaneechoutte, M.; Barr, J.J.; Bollyky, P.L. Interactions between Bacteriophage, Bacteria, and the Mammalian Immune System. Viruses 2019, 11, 10.]</ref> Tiwari et al. described the need for a neutrophil-phage cooperation in order for the immune system to get rid of <i>P. aeruginosa</i> infections. Therefore, the presence of neutrophils has been demonstrated to be necessary for the eradication of phages. <ref>[Tiwari, B.R.; Kim, S.; Rahman, M.; Kim, J. Antibacterial efficacy of lytic Pseudomonas bacteriophage in normal and neutropenic mice models. J. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 994–999]</ref> | Recently, bacteriophages have been show to be capable of modifying the tumor environment. Phage coat proteins, and phage DNA tend to elicit strong responses from the innate immune system, prompting phagocytosis and cytokine release.<ref name=Eriksson/>There have been studies that show cytokine storms can be generated as a response to phage infiltration. <ref name=interactions>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6356784/pdf/viruses-11-00010.pdf Van Belleghem, J.D.; Dąbrowska, K.; Vaneechoutte, M.; Barr, J.J.; Bollyky, P.L. Interactions between Bacteriophage, Bacteria, and the Mammalian Immune System. Viruses 2019, 11, 10.]</ref> Tiwari et al. described the need for a neutrophil-phage cooperation in order for the immune system to get rid of <i>P. aeruginosa</i> infections. Therefore, the presence of neutrophils has been demonstrated to be necessary for the eradication of phages. <ref>[Tiwari, B.R.; Kim, S.; Rahman, M.; Kim, J. Antibacterial efficacy of lytic Pseudomonas bacteriophage in normal and neutropenic mice models. J. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 994–999]</ref> | ||
Revision as of 06:19, 15 May 2020
Bacteriophages in Cancer Biology and Treatment
By Salome Shubitidze!
Introduce the topic of your paper. What is your research question? What experiments have addressed your question? Applications for medicine and/or environment?
The Use of Bacteriophages for Drug Delivery
Chemotherapy drugs, while shown to have anti-tumor effects, tend to result in severe toxicity and widespread distribution throughout the body: notably damaging healthy and malignant cells. New research has started to focus on using bacteriophages as an individualized drug-carrying anti-cancer therapy. The therapy would be targeted, based on genetically-modifying and chemically manipulating filamentous bacteriophages. In Bar et al. 2008, the phages were modified to display a host-specificity-conferring ligand, and carry a cytotoxic drug by chemical conjugation
Antibodies anti ErbB2 and anti ERGR were used to direct bacteriophages to cancer cells. ErbB2 is a a well known protein that is found to be over expressed in approximately 20% of invasive breast cancers. ERGR is a receptor protein that is found on the surface of cells that causes some cells to duplicate if an epidermal growth factor binds to it. They both belong to the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family (19). They are both common proteins that tend to be associated with the growth of cancers. The cell lines used in Bar et al. 2008 were SKBR3 and MDA-MB23 (human breast carcinoma cell lines), A431 (human epidermoid carcinoma), and HEK293 (human kidney). Phages were engineered to be linked to respective antibodies.
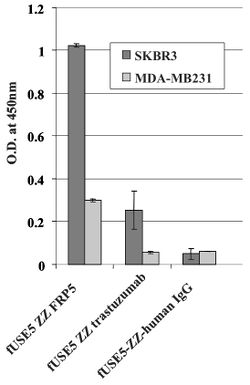
Assessing The Ability of the Engineered Antibody-Phages to go to Their Respective Receptors
A whole cell ELISA was performed in order to assess the binding of phage-attached antibodies (see figure 1.) MDA-MB231 cells express a low level of ErbB2 proteins, while SKBR3 express a much higher level of ErbB2 proteins. As shown, one can see that the antibody-complexed phages showed cell-specific binding. The engineered fUSE5-ZZ-chFRP5 phage had higher rates of binding to receptors on SKBR3 and even MDA-MB231 than the control phage fUSE5-ZZ-human IgG. This shows that the engineered phages are capable of attaching to their respective receptors through the use of antibodies.
Assessing Engineered Antibody-Phages as Drug Carriers
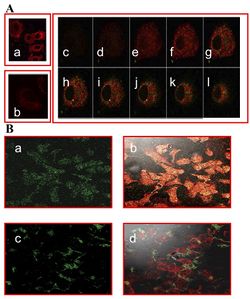
In order to check if phages could effectively deliver drugs, researchers had to verify that they could enter into host cells. One way this was done was by visualizing phage internalization using confocal microscopy and immunofluorescence staining (See Figure 2). Bar et al. 2008 engineered its phages to carry hygromycin inside cancer cells. Hygromycin is an antibiotic produced by the bacterium Streptomyces hygroscopicus. It kills bacteria, fungi, and interestingly inhibits the growth of some eukaryotic cells. Therefore, by engineering phages to carry the this drug into cancer cells, it is possible further growth can be stopped. The assay was done at 2, 12, and 24 hours in order to track the rate at which phages entered malignant cells. Surprisingly, internalization of hygromycin was the greatest at 2 hours, and diminished over time. Figure 2, images "c" and "d" show the attempt of internalization of hygromycin conjugated phages complexed with with human IgG. They were unsuccessful, filling their role as controls. Therefore, data supports that engineered antibody carrying phages are capable of transporting large amounts of shipments of a drug into a compromised cell.
Activating the Innate Immune System and Changing the Tumor Microenvironment
Tumors have become increasingly more clever in their ways of evading the immune system.
The Tumor Microenvironment
In both animal and human models, tumors have been discovered to actively suppress and manipulate immune responses. Usually our immune system's CD8+ cytotoxic T cells (CTL) and CD4 + helper T (Th)1 cells are capable of warding off cancer development by producing interferons (IFN) and cytotoxins (SCB).[1] Cytotoxic T cells are a type of white blood cell that kill cancer cells, or cells that are dysfunctional. Interferons are signaling proteins released by infected host cells that alert nearby cells to strengthen up their defenses. The continual production of these type of cells, however, leads to chronic inflammation, which has been tied to the spread of cancer. Inflammatory responses occur when damaged cells release chemicals that alert the immune system that something is wrong. White blood cells will flood to the scene, and start the process of creating new cells by diving existing ones in order to help with rebuilding the damaged tissue. The continual division of cells, leads to a higher likelihood of DNA damage, and subsequently cancer. [1] In fact, there are many protein factors released by tumor cells that may recruit tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). TAMs are M2- polarized.[2] M2- polarized macrophages function to repair damaged tissues, and aid the final phase of inflammation repair. The recruitment of TAMS has been found to suppress tumor-specific T cell activation and proliferation. By flooding the the tumor area with TAMS, the tumor is able to trick the body into thinking that repair is needed due to the inflammatory response, instead of actively seeking out the destruction of the cancer cells. Presence of TAMS in and around a tumor microenvironment is correlated with a poor prognosis for those suffering from melanoma or breast cancer specifically. [2] Figure 1. shows more examples of the relationship between tumor growth and the immune system.
Therefore, evidence shows that if our immune system's initial response fails to eradicate tumor cells, the flood of immunoregulatory cells leads to the resurgence of a "smarter" cancer.
Manipulating the Tumor Microenvironment
Recently, bacteriophages have been show to be capable of modifying the tumor environment. Phage coat proteins, and phage DNA tend to elicit strong responses from the innate immune system, prompting phagocytosis and cytokine release.[2]There have been studies that show cytokine storms can be generated as a response to phage infiltration. [3] Tiwari et al. described the need for a neutrophil-phage cooperation in order for the immune system to get rid of P. aeruginosa infections. Therefore, the presence of neutrophils has been demonstrated to be necessary for the eradication of phages. [4]
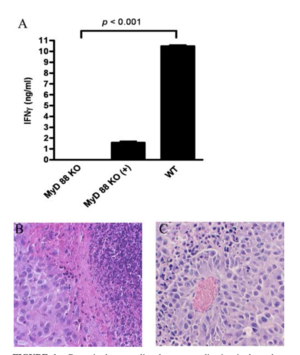
Delivering phages into the tumor microenvironment has been demonstrated to initiate infiltration of tumor-associated macrophages. Eriksson et al. 2009 found that the microenvironment of bacteriophage-treated tumors switched from M2-polarized to a more M1-polarized environment post phage treatment. The study found the administration of bacteriophages lead to an increase of neutrophilic granulocytes around the site of cancer.[2] Evidence from Gambashidze et al. 2012 has shown that combining E.coli phagelysate and chemotherapy inhibits the rate of cancer growth three fold compared to tumors left untreated. The combined cancer therapy was more potent than chemotherapy and phagelysate administered alone. The study showed that injected doses of phagelysates did not lead to malignant growth, and was accepted in mice [5]
Conclusion
References
- ↑ [https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/chronic-inflammation National Cancer Institute "Chronic Inflammation" April 2015.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19234207 Eriksson, Fredrik & Tsagozis, Panagiotis & Lundberg, Kajsa & Parsa, Roham & Mangsbo, Sara & Persson, Mats & Harris, Robert & Pisa, Pavel. (2009). Tumor-Specific Bacteriophages Induce Tumor Destruction through Activation of Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950). 182. 3105-11. 10.4049/ jimmunol.0800224.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Van Belleghem, J.D.; Dąbrowska, K.; Vaneechoutte, M.; Barr, J.J.; Bollyky, P.L. Interactions between Bacteriophage, Bacteria, and the Mammalian Immune System. Viruses 2019, 11, 10.
- ↑ [Tiwari, B.R.; Kim, S.; Rahman, M.; Kim, J. Antibacterial efficacy of lytic Pseudomonas bacteriophage in normal and neutropenic mice models. J. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 994–999]
- ↑ [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19234207 Gambashidze, Ketevan & Khorava, P. & Azaladze, T. & Azaladze, A. & Lasareishvili, Besarion & Jaiani, Ekaterine & Tediashvili, Marina. (2012). ANTI-TUMOR EFFECTS OF PHAGELYSATES OF E.COLI. 16-16.
Authored for BIOL 238 Microbiology, taught by Joan Slonczewski, 2018, Kenyon College.