Picrophilus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Curated}} | |||
{{Biorealm Genus}} | {{Biorealm Genus}} | ||
Latest revision as of 21:15, 6 August 2010
A Microbial Biorealm page on the genus Picrophilus

Classification
Higher order taxa:
Archaea; Euryarchaeota; Thermoplasmata; Thermoplasmatales; Picrophilaceae
Species:
Picrophilus oshimae, P. torridus
Description and Significance
Pircrophilus (acid-lover) is a moderately thermophilic (grows at temperatures between 45 and 65°C, optimum temperature at 60°C), irregular cocci-shaped archaeon around 1 to 1.5 µm in diameter. The archaeon lives in an extremely hostile environment and grows at the lowest pH values known among all organisms, including in conditions such as 1 M sulfuric acid. The studies show that the archaeon grows only below pH 3.5 (optimal pH = 0.7), and that significant growth has been observed even at a pH around 0.
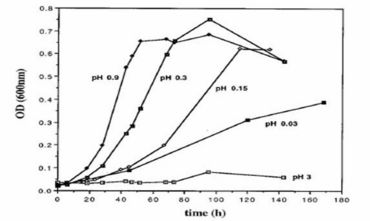
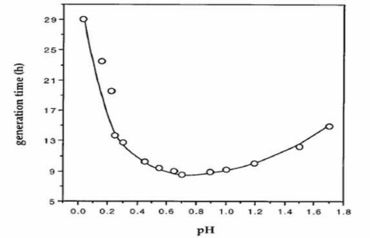
Therefore, studies are held to investigate about its unique properties and mechanisms which ensure viability under such conditions.
Genome Structure
The large single circular chromosome of Picrophilus torridus is 1,545,900 bp in length and contains 1,535 protein-encoding sequences (CDS). This is the smallest genome among nonparasitic aerobic microorganisms growing on organic susbstances. Also, 92% of its sequence is coding, which is the highest coding density in the genomes of the thermoacidophile group.
Cell Structure and Metabolism
One of the reasons for its vulnerability to higher pH is its membrane structure, which displays a very low proton permeability, a high acid stability, and which loses its integrity when incubated at pH 7. More specifically, the cells have an envelope in the form of an S-layer located on top of the cytoplasmic membrane, which consists of an outer dense and inner, empty stratum, with the latter structured by thin and widely spaced pillars anchoring the surface layer in the membrane.
Because it is a strict aerobic organism, P. torridus has some mechanisms to protect the cell against oxidative damage. They include genes coding for a superoxide dismutase, three putative peroxiredoxin-like proteins, and an alkyl hydroperoxide reductase present only in thermoacidophilic archaea and Pyrococcus furiosus.
The archaeon grows heterotrophically under aerobic conditions on yeast extract. It is unable to utilize starch, glucose, sucrose, and lactose alone, for growth. Further, no growth has been reported under aerobic conditions with CO2 as the only source of carbon and sulfur as the energy source. Biosynthetic pathways for all 20 amino acids have been found in the genome of P. torridus, which is different from the species of Thermoplasma, the genetically closest organism to Picrophilus. The archaeon also utilizes amino acids such as histidine, proline, glutamate, and serine for growth; however, only glutamate, proline, and leucine can be used to drive respiration. Further, genome analysis demonstrates that it has certain genes and pathways for the degradation of aspartate, glutamate, serine, arginine, histidine, glycine, threonine, and the aromatic amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine.
Ecology
The two species of Picrophilus were isolated from solfataric locations in nothern Japan. The habitats of the archaeon have moderate temperatures and strong acidity (pH < 0.5 to 2.2).
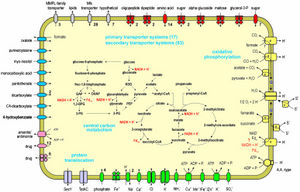
The unusual high ratio of secondary to primary solute transport systems in Picrophilus shows that the predominant use of proton-driven secondary transport represents a highly relevant strategy for the adaptation of this archaeon to its extremely acidic environment.
