Ebola Transmission: Difference between revisions
Vgawlik6782 (talk | contribs) |
Vgawlik6782 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
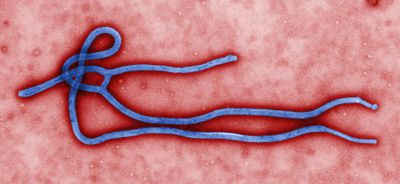
The Ebola virus is a severe disease-causing pathogen that poses a huge threat to human health mostly within central Africa. Ebola is considered a Biosafety level 4 (BSL-4) agent; classifying it among the most threatening | The Ebola virus is a severe disease-causing pathogen that poses a huge threat to human health mostly within central Africa due to its high mortality<sup>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1579243/ 4]</sup>. Ebola is considered a Biosafety level 4 (BSL-4) agent; classifying it among the most threatening pathogens that exist in the world today. Agents within this category pose severe threats to human health and can be fatal due to the lack of treatments and/or available vaccines. There are five known Ebola species within the family <i>Filoviridae</i> and all of the species within the family cause varying degrees of viral hemorrhagic fever illnesses. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
==Virus Structure== | ==Virus Structure== | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
The Ebola virus has an RNA genome that codes for <sup>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1579243/ Feldmann, Heinz, Steven Jones, Hans-Joachim Schnittler. "Ebola virus: from discovery to vaccine 3]</sup> | |||
[[Image:Viron.jpg|thumb|400px|left|A closeup photo of the Ebola virus.]] | [[Image:Viron.jpg|thumb|400px|left|A closeup photo of the Ebola virus.]] | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
==Conclusion== | ==Conclusion== | ||
In today's world Ebola is still a huge problem that faces many developing nations within Africa. In 2012 alone there were 5 outbreaks of Hemorrhagic Fevers around the world and 3 of them were due to the Ebola virus.<sup>[http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/dvrd/spb/outbreaks/index.htm#lcmv-2012 | In today's world Ebola is still a huge problem that faces many developing nations within Africa. In 2012 alone there were 5 outbreaks of Hemorrhagic Fevers around the world and 3 of them were due to the Ebola virus.<sup>[http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/dvrd/spb/outbreaks/index.htm#lcmv-2012 7]</sup> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3189988/ Aleksandrowicz, P., A. Marzi, N. Biedenkopf, N. Beimforde, S. Becker et al. "Ebola Virus Enters Host Cells by Macropinocytosis and Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis". ''The Journal of Infectious Diseases''. 2011. Volume 204. Suppl 3S957-967.] | 1. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3189988/ Aleksandrowicz, P., A. Marzi, N. Biedenkopf, N. Beimforde, S. Becker et al. "Ebola Virus Enters Host Cells by Macropinocytosis and Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis". ''The Journal of Infectious Diseases''. 2011. Volume 204. Suppl 3S957-967.] | ||
2. [http://www.pnas.org/content/early/2012/02/22/1120453109 Bharat T., et al. "Structural dissection of Ebola virus and its assembly determinants using cryo-electron tomography". '' Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America''. 2012. p. 4275-4280.] | |||
[http://www. | 3. [http://www.nature.com/nri/journal/v3/n8/full/nri1154.html "Ebola virus: from discovery to vaccine". ''Nature Reviews Immunology 3''. 2003. p. 667- 85.] | ||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1579243/ Noda, T., H. Ebihara, Y. Muramoto, K. Fujii, A. Takada, et al. "Assembly and Budding of Ebolavirus". ''PLoS Pathogens''. 2006. Volume 2(9).] | 4. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1579243/ Noda, T., H. Ebihara, Y. Muramoto, K. Fujii, A. Takada, et al. "Assembly and Budding of Ebolavirus". ''PLoS Pathogens''. 2006. Volume 2(9).] | ||
[http://www.pnas.org/content/early/2011/11/29/1117715108 Phoolcharoen, Waranyoo, John M. Dye, et al. "A nonreplicating subunit vaccine protects mice against lethal Ebola virus challenge". ''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America''. 2011. Volume 180.51. p. 20695-0700.] | 5. [http://www.pnas.org/content/early/2011/11/29/1117715108 Phoolcharoen, Waranyoo, John M. Dye, et al. "A nonreplicating subunit vaccine protects mice against lethal Ebola virus challenge". ''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America''. 2011. Volume 180.51. p. 20695-0700.] | ||
[http://www.nature.com/srep/2012/121115/srep00811/full/srep00811.html Weingartl, Hana M., Carissa Embury-Hyatt, Charles Nfon, Anders Leung, Greg Smith, and gary Kobinger. "Transmission of Ebola virus from pigs to non-human primates". ''Scientific Reports 2''. 2012.] | 6. [http://www.nature.com/srep/2012/121115/srep00811/full/srep00811.html Weingartl, Hana M., Carissa Embury-Hyatt, Charles Nfon, Anders Leung, Greg Smith, and gary Kobinger. "Transmission of Ebola virus from pigs to non-human primates". ''Scientific Reports 2''. 2012.] | ||
Revision as of 12:38, 26 March 2013
Introduction
The Ebola virus is a severe disease-causing pathogen that poses a huge threat to human health mostly within central Africa due to its high mortality4. Ebola is considered a Biosafety level 4 (BSL-4) agent; classifying it among the most threatening pathogens that exist in the world today. Agents within this category pose severe threats to human health and can be fatal due to the lack of treatments and/or available vaccines. There are five known Ebola species within the family Filoviridae and all of the species within the family cause varying degrees of viral hemorrhagic fever illnesses.
Virus Structure
The Ebola virus has an RNA genome that codes for Feldmann, Heinz, Steven Jones, Hans-Joachim Schnittler. "Ebola virus: from discovery to vaccine 3
Containment and Transmission
Include some current research in each topic, with at least one figure showing data.
Possible Treatments
Include some current research in each topic, with at least one figure showing data.
Conclusion
In today's world Ebola is still a huge problem that faces many developing nations within Africa. In 2012 alone there were 5 outbreaks of Hemorrhagic Fevers around the world and 3 of them were due to the Ebola virus.7
References
3. "Ebola virus: from discovery to vaccine". Nature Reviews Immunology 3. 2003. p. 667- 85.
Edited by (Victoria Rose Gawlik), a student of Nora Sullivan in BIOL187S (Microbial Life) in The Keck Science Department of the Claremont Colleges Spring 2013.