Fungal Endophytes: Drought Tolerance in Plants: Difference between revisions
SBarnes7151 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
SBarnes7151 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<!--[Sample reference] [http://ijs.sgmjournals.org/cgi/reprint/50/2/489 Takai, K., Sugai, A., Itoh, T., and Horikoshi, K. "''Palaeococcus ferrophilus'' gen. nov., sp. nov., a barophilic, hyperthermophilic archaeon from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent chimney". ''International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology''. 2000. Volume 50. p. 489-500.]--> | <!--[Sample reference] [http://ijs.sgmjournals.org/cgi/reprint/50/2/489 Takai, K., Sugai, A., Itoh, T., and Horikoshi, K. "''Palaeococcus ferrophilus'' gen. nov., sp. nov., a barophilic, hyperthermophilic archaeon from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent chimney". ''International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology''. 2000. Volume 50. p. 489-500.]--> | ||
|[1] [Smith, S., Read, D., 1997: Mycorrhizal symbiosis, 2nd edn., Academy Press, San Diego. ]<br> | |[1] [https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=qLciOJaG0C4C&oi=fnd&pg=PP2&dq=Smith,+S.,+Read,+D.,+1997:+Mycorrhizal+symbiosis&ots=zptZgTSFpO&sig=svsWG48yCBBJHTr3-Gtx2mSdnfY#v=onepage&q=Smith%2C%20S.%2C%20Read%2C%20D.%2C%201997%3A%20Mycorrhizal%20symbiosis&f=false Smith, S., Read, D., 1997: Mycorrhizal symbiosis, 2nd edn., Academy Press, San Diego. ]<br> | ||
|[2] [http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs00239-003-2564-9 Shu-Miaw C., Chien-Chang C., Hsin-Liang C., Wen-Hsiung L."Dating the Monocot–Dicot Divergence and the Origin of Core Eudicots Using Whole Chloroplast Genomes". "Journal of Molecular Evolution". 2004. Volume 58, p. 424-441]<br> | |[2] [http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs00239-003-2564-9 Shu-Miaw C., Chien-Chang C., Hsin-Liang C., Wen-Hsiung L."Dating the Monocot–Dicot Divergence and the Origin of Core Eudicots Using Whole Chloroplast Genomes". "Journal of Molecular Evolution". 2004. Volume 58, p. 424-441]<br> | ||
|[3] [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169534797012305 Selosse, M-A, and F. Le Tacon. "The Land Flora: A Phototroph-Fungus Partnership?" Trends in Ecology & Evolution 13.1 (1998): 15-20. Print.]<br> | |[3] [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169534797012305 Selosse, M-A, and F. Le Tacon. "The Land Flora: A Phototroph-Fungus Partnership?" Trends in Ecology & Evolution 13.1 (1998): 15-20. Print.]<br> | ||
Revision as of 15:48, 14 April 2015
It has been estimated that over 80% of terrestrial plants form a symbiotic association with fungi.[1] Species of fungi that reside within living plant tissue without causing symptoms of disease in their host are known as fungal endophytes.[4] Fungal endophytes colonize a variety of both monocot and eudicot plants which suggests that this symbiosis predated the monocot-dicot split that occurred 140-150 million years ago.[2] It is also hypothesized that it was phototroph-fungi associations that enabled plants to first colonize land.[3] This mutualistic association could have helped plants acclimate to new environmental stresses such as desiccation, increased exposure to solar radiation, and more extreme temperatures differences.[3]
Fungal endophytes remain an important component of today’s terrestrial ecosystems, and many enable their hosts to thrive in harsh environments. Studies show that fungal endophytes can enhance the drought, salt, and soil temperature tolerance of their host plant in addition to increasing resistance to parasitic fungi and herbivores.[4] With growing concerns about climate change and its effects on agriculture, learning about fungal endophyte conferred drought tolerance has become increasingly important. By influencing plant morphology, development, and physiological and biochemical responses to stress, fungal endophytes can induce mechanisms of drought avoidance, drought tolerance, and drought recovery in their hosts.[8]
Classes of Fungal Endophytes
Clavicipitaceous Endophytes
Class 1
Clavicipitaceous endophytes are associated with grasses.[4] They typically are found within the plant shoots and form systemic intercellular infections.[4] While they are often passed down in the seed through vertical transmission, they may also undergo horizontal transmission.[4] Many class 1 endophytes produce alkaloids to protect their host plant from herbivory by insects and mammals, and studies have shown some class 1 endophytes to confer drought and metal tolerance.[5][8] Neotyphodium coenophialum , for example, stimulates plants to develop more extensive root systems and longer and thinner root hairs. [8]
Nonclavicipitaceous Endophytes
Nonclavicipitaceous endophytes are highly diverse and have been isolated from every major lineage of land plant, which includes nonvascular plants, ferns, conifers, and angiosperms.
Class 2
Class 2 endophytes are usually found in the roots, stem, or leaves of their hosts.[4] Like class 1 endophytes, they can also be transmitted either vertically through the seed coat or horizontally. [4] They are unique in that they can confer habitat-specific stress tolerance to their hosts.[4] They often increase root and/or shoot biomass in their host, and they infect a higher percentage of plants in high-stress environments.[4]
Class 3 and 4
Class 3 colonizes the shoot of plants while Class 4 colonizes plant roots.[4] Both are horizontally transmitted.[4] Class 3 endophytes are highly localized when they colonize a plant, and a diverse number of species can colonize an individual plant.[4] Few studies have been performed on Classes 3 and 4 endophytes, and little is known about their ecological role or their ability to confer tolerance.
Reactions to Drought Stress
Osmotic Ajustment
Redman et al (2015) examined the osmotic concentrations in non symbiotic and heat-stress tolerant symbiotic plants. The pattern was different between the two groups, leading them to conclude that symbiotic plants do not only rely on increasing their osmolyte concentrations.[6] Endophyte known to promote drought tolerance have high levels of loline alkaloids. [7] Future experiments could test if these are present in sufficient concentration to prevent the denaturation of macromolecules or reduce the number of reactive oxygen species. [7
Reactive Oxygen Species
Abiotic stresses such as drought result in the overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [10] These highly reactive metabolic products act as signaling molecules; however, when their levels are too high, they cause oxidative stress and damage proteins, lipids, and DNA. [10] [11] ROS control many plant processes such as growth, abiotic stress response, cell cycle, and programmed cell death because they influence the expression of genes. [10]
Testing Endophyte Conferred Tolerances
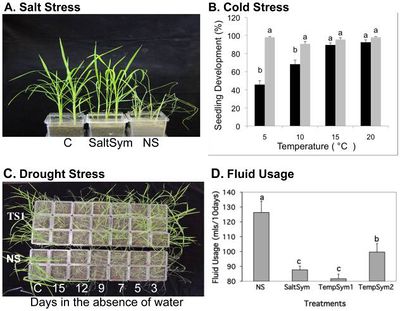
Redman et al (2015) tested how well the class 2 fungal endophytes Fusarium culmorum (SaltSym) and Curvularia protuberant (TempSym) would confer tolerance to salt, drought and cold to rice plants. SaltSym was isolated from the coastal plant Leymus mollis which is exposed to high salt stress, while TempSym 1 and 2 were isolated from Dichanthelium lanuginosum which grows in geothermal soils.
The study found that plants inoculated with the endophytes (S) showed no cost when grown in non-stressful conditions, but the number of colonized plants decreased from 100% to 65%.[6] When infected plants were grown in stressful environments, their water consumption decreased by 20–30% while their growth rate, reproductive yield, and biomass increased (Figure 1). [6] Non-infected plants (NS), on the other hand, lost shoot and root biomass when exposed to stress. All three endophytes treatments took 2-3 times longer to wilt than the non-infected; however, the mechanism of the conferred drought tolerance remains unknown. An interesting observation was that the endophytes changed the development of the plants to increase root biomass before shoot growth.
All plant species used in this experiment are members of the family Poacea but belong to different subfamilies. [6] The isolated fungal endophytes successfully conferred drought tolerance to the rice plants which supports the idea that the symbiotic communication needed to communicate between the fungi and the plant was conserved within the family. [6] While many fungal endophytes show habitat-adapted symbiosis, the fact that there is still lower biodiversity in high stress environments indicates that having the endophyte itself is not enough. [6]
Further Reading
References
|[1] Smith, S., Read, D., 1997: Mycorrhizal symbiosis, 2nd edn., Academy Press, San Diego.
|[2] Shu-Miaw C., Chien-Chang C., Hsin-Liang C., Wen-Hsiung L."Dating the Monocot–Dicot Divergence and the Origin of Core Eudicots Using Whole Chloroplast Genomes". "Journal of Molecular Evolution". 2004. Volume 58, p. 424-441
|[3] Selosse, M-A, and F. Le Tacon. "The Land Flora: A Phototroph-Fungus Partnership?" Trends in Ecology & Evolution 13.1 (1998): 15-20. Print.
|[4] Rodriguez, R. J., et al. "Fungal Endophytes: Diversity and Functional Roles." New Phytologist 182.2 (2009): 314-30. Print.
|[5] Koulman, Albert, et al. "Peramine and Other Fungal Alkaloids are Exuded in the Guttation Fluid of Endophyte-Infected Grasses." Phytochemistry 68.3 (2007): 355-60. Print.
|[6] Redman, Regina S. et al. “Increased Fitness of Rice Plants to Abiotic Stress Via Habitat Adapted Symbiosis: A Strategy for Mitigating Impacts of Climate Change.” Ed. Hany A. El-Shemy. PLoS ONE 6.7 (2011): e14823. PMC. Web. 24 Mar. 2015.
|[7] Schardl, C. L., Leuchtmann, A. & Spiering, M. J. (2004) Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 55, 315-340.
|[8] Malinowski DP, Belesky DP. 2000. Adaptations of endophtye-infected cool-season grasses to environmental stresses: mechanisms of drought and mineral stress tolerance. Crop Science 40: 923–940.
|[9] Cheplick GP. 2006. Costs of fungal endophyte infection in Lolium perenne genotypes from eurasia and north africa under extreme resource limitation. Environmental and Experimental Botany 60: 202–210.
|[10] Gill, S, Tuteja N. 2010. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 48: 909-930
|[11] Gechev, T. S., Van Breusegem, F., Stone, J. M., Denev, I. and Laloi, C. (2006), Reactive oxygen species as signals that modulate plant stress responses and programmed cell death. Bioessays, 28: 1091–1101.
|[12] Jacobs, S., Zechmann, B., Molitor, A., Trujillo, M., Petutschnig, E., Likpa, V., Kogel, K-H., Schaefer, P. (2011). Broad-spectrum suppression of innate immunity is required for colonization of arabidopsis roots by the fungus piriformospora indica. Plant Physiology, 156(2), 726-740. doi:10.1104/pp.111.176446
|[13] Kissoudis, C., van de Wiel, C., Visser, R. G. F., & van der Linden, G. (2014). Enhancing crop resilience to combined abiotic and biotic stress through the dissection of physiological and molecular crosstalk. Frontiers in Plant Science, 5, 207. doi:10.3389/fpls.2014.00207
Edited by Sarah Barnes, a student of Nora Sullivan in BIOL168L (Microbiology) in The Keck Science Department of the Claremont Colleges Spring 2014.
