Co-Evolution of Microbes and the Mammalian Gut: Difference between revisions
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
<br>Research question(s): How specialized are the microbe lineages associated with mammalian guts? When a mammal adopts a diffferent diet, how much does its gut microbiome resemble the microbiomes of its close relatives?<br> | <br>Research question(s): How specialized are the microbe lineages associated with mammalian guts? When a mammal adopts a diffferent diet, how much does its gut microbiome resemble the microbiomes of its close relatives?<br> | ||
<br> Microbes likely had commensal relationships with the ancestors of mammals, long before they evolved to give birth to live young or obtained many of the traits that charcterize the class of vertabrates today. <ref name=Ley2008a>Ley, Ruth E et al. “Worlds within worlds: evolution of the vertebrate gut microbiota.” Nature reviews. Microbiology vol. 6,10 (2008): 776-88. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1978 </ref> Today, the microbiota of mammalian guts show similarities between species from similar ancestry, but also between those that have similar diets. <ref name=Ley2008a>Ley, Ruth E et al. “Worlds within worlds: evolution of the vertebrate gut microbiota.” Nature reviews. Microbiology vol. 6,10 (2008): 776-88. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1978 </ref> The earliest mammals were carnivorous, and without microbes, they would have not been able take advantage of the diverse array of nutrients offered by the plant kingdom, allowing them to fill many of the ecological niches left when the dinosaurs became extinct 65 million years ago. | <br> Microbes likely had commensal relationships with the ancestors of mammals, long before they evolved to give birth to live young or obtained many of the traits that charcterize the class of vertabrates today. <ref name=Ley2008a>Ley, Ruth E et al. “Worlds within worlds: evolution of the vertebrate gut microbiota.” Nature reviews. Microbiology vol. 6,10 (2008): 776-88. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1978 </ref> Today, the microbiota of mammalian guts show similarities between species from similar ancestry, but also between those that have similar diets. <ref name=Ley2008a>Ley, Ruth E et al. “Worlds within worlds: evolution of the vertebrate gut microbiota.” Nature reviews. Microbiology vol. 6,10 (2008): 776-88. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1978 </ref> The earliest mammals were carnivorous, and without microbes, they would have not been able take advantage of the diverse array of nutrients offered by the plant kingdom, allowing them to fill many of the ecological niches left when the dinosaurs became extinct 65 million years ago.<ref name=Yong2016>Yong, Ed. I contain multitudes: The microbes within us and a grander view of life. Random House, 2016.</ref> | ||
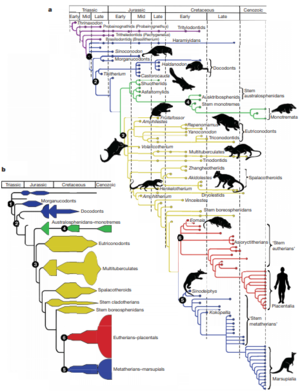
[[Image:mammalphylogeny.png|thumb|300px|right| Phylogeny and diversification of major mammal groups <ref name=Luo2007>Luo, Zhe-Xi. "Transformation and diversification in early mammal evolution." Nature 450.7172 (2007): 1011-1019.</ref>]] | [[Image:mammalphylogeny.png|thumb|300px|right| Phylogeny and diversification of major mammal groups <ref name=Luo2007>Luo, Zhe-Xi. "Transformation and diversification in early mammal evolution." Nature 450.7172 (2007): 1011-1019.</ref>]] | ||
Revision as of 20:39, 21 April 2020
Introduction
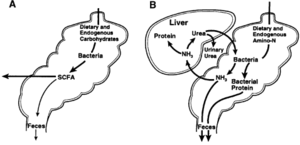
By Joanna van Dyk
Research question(s): How specialized are the microbe lineages associated with mammalian guts? When a mammal adopts a diffferent diet, how much does its gut microbiome resemble the microbiomes of its close relatives?
Microbes likely had commensal relationships with the ancestors of mammals, long before they evolved to give birth to live young or obtained many of the traits that charcterize the class of vertabrates today. [3] Today, the microbiota of mammalian guts show similarities between species from similar ancestry, but also between those that have similar diets. [3] The earliest mammals were carnivorous, and without microbes, they would have not been able take advantage of the diverse array of nutrients offered by the plant kingdom, allowing them to fill many of the ecological niches left when the dinosaurs became extinct 65 million years ago.[4]
Other examples:
Bold
Italic
Subscript: H2O
Superscript: Fe3+
A citation code consists of a hyperlinked reference within "ref" begin and end codes.
The repeated citation works like this, with a back slash.[1]
Hindgut Fermentation
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Foregut Fermentation
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Section 3
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Section 4
Conclusion
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Grajal, A., and S. D. Strahl. "A bird with the guts to eat leaves." Natural History 8 (1991): 48.
- ↑ Stevens, C. Edward, and Ian D. Hume. "Contributions of microbes in vertebrate gastrointestinal tract to production and conservation of nutrients." Physiological reviews 78.2 (1998): 393-427.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Ley, Ruth E et al. “Worlds within worlds: evolution of the vertebrate gut microbiota.” Nature reviews. Microbiology vol. 6,10 (2008): 776-88. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1978
- ↑ Yong, Ed. I contain multitudes: The microbes within us and a grander view of life. Random House, 2016.
- ↑ Luo, Zhe-Xi. "Transformation and diversification in early mammal evolution." Nature 450.7172 (2007): 1011-1019.
Authored for BIOL 238 Microbiology, taught by Joan Slonczewski, 2018, Kenyon College.
