Sphingomonas sp., agents: Difference between revisions
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Curated}} | {{Curated}} | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
The Genus <i>Sphingomonas<i | The Genus <i>Sphingomonas</i> includes a range of bacterium that are remarkable for their ability to break down polycyclic hydrocarbons. Bacteria in this genus have been detected in a variety of environments, both marine and terrestrial. In recent years, these bacteria have been a focus of study because of their possible applications for bioremediation (one of the major components of oil being stable aromatic hydrocarbons). | ||
==Genome== | ==Genome== | ||
Revision as of 22:21, 24 April 2011
Introduction
The Genus Sphingomonas includes a range of bacterium that are remarkable for their ability to break down polycyclic hydrocarbons. Bacteria in this genus have been detected in a variety of environments, both marine and terrestrial. In recent years, these bacteria have been a focus of study because of their possible applications for bioremediation (one of the major components of oil being stable aromatic hydrocarbons).
Genome
123
Soil contamination
.;l
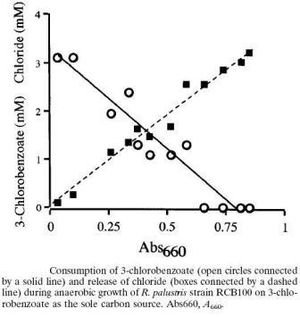
Degradation of Aromatic compounds
lkjk;
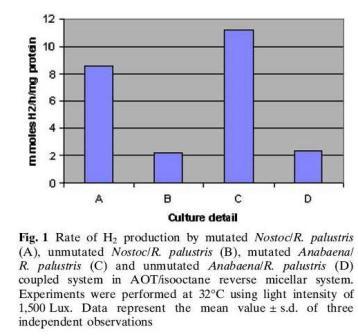
Hydrogen Production
kjhklkj
Nanoparticle synthesis
khjkh
Conclusion
R.palustris is truly a versatile bacterium and its different metabolic capabilities have very important applications in this present day and age with problems of environmental contamination and non-renewable energy sources. It provides us a way for dealing with these problems by just optimizing some of these metabolic capabilites. It has a lot of potential in bio-remediation, hydrogen fuel production and nanoparticle synthesis and thus more research in these areas would of immense value.
References
Edited by student of Joan Slonczewski for BIOL 238 Microbiology, 2010, Kenyon College.