Neorickettsia risticii: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
The interaction between N. risticii and the horse is a pathogenic one. Infection of a horse with N. risticii causes Potomac Horse Fever, an acute and potentially fatal disease. | The interaction between N. risticii and the horse is a pathogenic one. Infection of a horse with N. risticii causes Potomac Horse Fever, an acute and potentially fatal disease. | ||
N. risticii uses a trematode, otherwise known as a flukes, to survive and proliferate. Flukes tend to multiply within snails, and then lay larvae. Or N. risticii uses other aquatic vectors, such as the mayfly or caddisfly, to survive and proliferate. It is through ingestion of fluke larvae or one of these aquatic vectors that the horse becomes infected with N. risticii and contracts Potomac Horse Fever. | N. risticii is an obligate parasite, it uses a trematode, otherwise known as a flukes, to survive and proliferate. Flukes tend to multiply within snails, and then lay larvae. Or N. risticii uses other aquatic vectors, such as the mayfly or caddisfly, to survive and proliferate. It is through ingestion of fluke larvae or one of these aquatic vectors that the horse becomes infected with N. risticii and contracts Potomac Horse Fever. | ||
Once inside the horse,the bacteria colonizes in the epithelial cells of the horses intestines and causes many adverse symptoms such as anorexia, fever, depression, diarrhea, lethargy, and in some cases laminitis. N. risticii is also known to cause miscarriages in pregnant horses. | Once inside the horse,the bacteria colonizes in the epithelial cells of the horses intestines and causes many adverse symptoms such as anorexia, fever, depression, diarrhea, lethargy, and in some cases laminitis. N. risticii is also known to cause miscarriages in pregnant horses. | ||
Revision as of 01:36, 21 November 2011
WIKI IN PROGRESS
Ex. Potomac Horse Fever
Characteristics of the pathogen
Neorickettsia risticii is a member of the Erlichiaea family of bacteria. It is a gram-negative, coccus, and obligate bacterium.
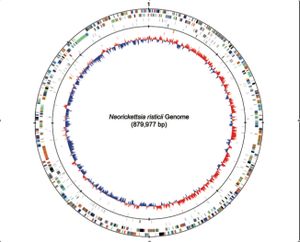
The genome for Neorickettsia risticii was fully sequenced in 2009. The Neorickettsia risticii strain sequenced was the Illinois strain, which consists of one circular chromosome that has 879,977 base pairs, with a GC content of 41.3%. This chromosome encodes for 38 different RNA species, including a 16s RNA, and 898 different proteins.
Characteristics of the host
What host/s is/are involved? Is there host specificity? Are there secondary reservoirs?
Host-Symbiont Interaction
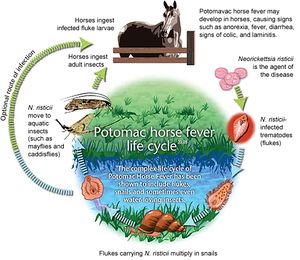
The interaction between N. risticii and the horse is a pathogenic one. Infection of a horse with N. risticii causes Potomac Horse Fever, an acute and potentially fatal disease.
N. risticii is an obligate parasite, it uses a trematode, otherwise known as a flukes, to survive and proliferate. Flukes tend to multiply within snails, and then lay larvae. Or N. risticii uses other aquatic vectors, such as the mayfly or caddisfly, to survive and proliferate. It is through ingestion of fluke larvae or one of these aquatic vectors that the horse becomes infected with N. risticii and contracts Potomac Horse Fever.
Once inside the horse,the bacteria colonizes in the epithelial cells of the horses intestines and causes many adverse symptoms such as anorexia, fever, depression, diarrhea, lethargy, and in some cases laminitis. N. risticii is also known to cause miscarriages in pregnant horses.
Molecular Insights into the Symbiosis
Describe molecular/genetic studies on the symbiosis.
Ecological and Evolutionary Aspects
What is the evolutionary history of the interaction? Do particular environmental factors play a role in regulating the symbiosis?
Recent Discoveries
Describe two findings on the symbiosis published within the last two years.
References
[Sample reference] [[3] Seemanapalli SV, Xu Q, McShan K, Liang FT. 2010. Outer surface protein C is a dissemination-facilitating factor of Borrelia burgdorferi during mammalian infection. PLoS One 5:e15830.]
Edited by [Sierra Wangensteen], student of Grace Lim-Fong
