Rhodococcus equi: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Classification== | ==Classification== | ||
Bacteria/Actinobacteria/Actinobacteria; Actinobacteridae; Actinomycetales; Corynebacterineae; Nocardiaceae | Bacteria/Actinobacteria/Actinobacteria; Actinobacteridae; Actinomycetales; Corynebacterineae; Nocardiaceae | ||
==='''''Genus Species'''''=== | ==='''''Genus Species'''''=== | ||
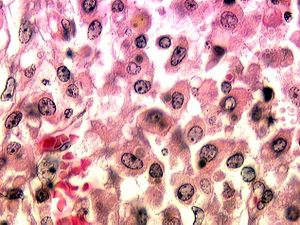
[[File: micro19.jpg|thumb|right|These are stained, cytoplasmic bodies of "R. equi" within lung tissue.]] | Rhodococcus; Rhodococcus equi | ||
[[File: micro19.jpg|thumb|right|These are stained, cytoplasmic bodies of ""R. equi" within lung tissue.]] | |||
==Description and Significance== | ==Description and Significance== | ||
Revision as of 17:47, 21 July 2013
Classification
Bacteria/Actinobacteria/Actinobacteria; Actinobacteridae; Actinomycetales; Corynebacterineae; Nocardiaceae
Genus Species
Rhodococcus; Rhodococcus equi
Description and Significance
Give a brief description of the microorganism and explain why you think it is important. How does it relate to the other organisms in its phylum (bacteria and fungi) or group (archaea, virus, protist). Use the following for each reference in text (change number accordingly)--> [1]
Structure, Metabolism, and Life Cycle
Interesting features of its structure; how it gains energy (how it replicates, if virus); what important molecules it produces (if any), does it have an interesting life cycle?
Ecology and Pathogenesis
Natural habitat (soil, water, commensal of humans or animals?)
If relevant, how does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, or plant hosts? Important virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.
References
[1] Prescott, John F. 1991. "Rhodococcus Equi": an Animal and Human Pathogen". '"'Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 4 (1)": 20-34. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC358176/pdf/cmr00042-0036.pdf
Author
Page authored by Mattie Hogg, student of Mandy Brosnahan, Instructor at the University of Minnesota-Twin Cities, MICB 3301/3303: Biology of Microorganisms.