Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi: Difference between revisions
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
==Clinical Features== | ==Clinical Features== | ||
Symptoms include a sustained fever of 103-104° F, weakness, abdominal pain, appetite loss, rose-colored spots, self-limiting diarrhea, weight loss, delirium, and malaise. In severe cases this disease can cause intestinal perforation and peritonitis, toxic encephalopathy associated with myocarditis and hemodynamic shock that can lead to death within one month of infection. | |||
<br> | |||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Revision as of 18:26, 16 July 2014

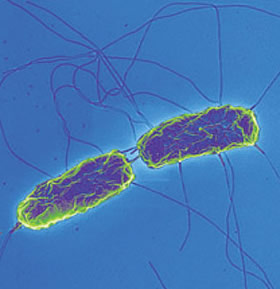
Etiology/Bacteriology
Taxonomy
| Domain = Bacteria | Phylum = Proteobacteria | Class = Gammaproteobacteria | Order = Enterobacteriales | Family = Enterobacteriaceae | Genus = Salmonella | species = S. enterica
Description
Salmonella enterica is a gram-negative facultative anaerobe with the ability of motility. This bacterium also lacks the ability to ferment lactose. Typhoid fever is caused by the specific serotype Salmonella tyhphi. [1]
Pathogenesis
Transmission
Fecal-oral transmission via contaminated water, vegetables, eggs, meat, poor hygiene Humans serve as only viable reservoir to Salmonella typhi. This bacterium resides primarily in the blood stream and intestinal tract. To gain access to the host, this bacterium first adheres to the mucosal lining and invades epithelial cells. Next, this pathogen encounters dendritic cells in the innate immune system and begins to compromise enterocytes, macrophages in the submucosa. The bacterium enters Peyer’s patches and messenterial lymph nodes in the reticulo-endothelial system and blood stream. Secondary infection occurs in the bone marrow, liver, spleen, and gall bladder. Severe symptoms associated with this infection include necrosis of Peyer’s patches along with peritonis, sepsis, toxic encephalopathy with myocarditis leading to haemodynamic shock.
Infectious dose, incubation, and colonization
ID50>100K bacteria Incubation period: 7-14 days To colonize, S. typhi adheres to the mucosal lining of the small intestine and penetrates the epithelial cells. The bacterium spreads to peripheral lymphoid organs during secondary infection. Mainly the gallbladder serves as the reservoir of a chronic infection. The formation of biofilms and on gallstones is a critical factor in the carriage and shedding of S. typhi.
Epidemiology
This disease is a major factor in countries that lack access to purified water; for example India, South America, Southeast Asia, and Africa, placing children at especially high risk that play in sewage water on the streets. There are more than twenty-seven million cases annually, and two-hundred seventeen thousand deaths world-wide each year.
Virulence Factors
This bacterium’s virulence factors include: endotoxin production by a gram-negative bacterium and the Vi antigen. The protein invasin is secreted to allow non-phagocytic cells to ingest the bacterium to give it intracellular access; this leads to the inhibition of oxidative leukocytes, rendering the innate immune response ineffective.
Clinical Features
Symptoms include a sustained fever of 103-104° F, weakness, abdominal pain, appetite loss, rose-colored spots, self-limiting diarrhea, weight loss, delirium, and malaise. In severe cases this disease can cause intestinal perforation and peritonitis, toxic encephalopathy associated with myocarditis and hemodynamic shock that can lead to death within one month of infection.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Prevention
References
1 University of Oklahoma Faculty and Staff.
2 Kenyan Waterborne Disease Center
3 de Jong, H.K., Parry, C.M., van der Pol, T. "Host-Pathogen Interaction in Invasive Salmonellosis" PLOS Pathogens.
4 "Typhoid Fever" Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
