Alcaligenes ammonioxydans: Difference between revisions
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
=Genome Structure= | =Genome Structure= | ||
Strain HO-1's genome is completed and consists of one chromosome and is composed of 3.77Mbp with a DNA G+C content of 57.17%. The genome contained 3,320 predicted proteins with 57 tRNA sequences and 9 rRNA operons. Some genes were acquired horizontally as evident by 6 prophage sequences and 6 genomic islands. 80 tandem repeats and 63 interspersed repeats are found. Average nucleotide identity (ANI) analysis of related ''Alcaligenes'' genomes indicate that strain HO-1 belongs to a new, | Strain HO-1's genome is completed and consists of one chromosome and is composed of 3.77Mbp with a DNA G+C content of 57.17%. The genome contained 3,320 predicted proteins with 57 tRNA sequences and 9 rRNA operons. Some genes were acquired horizontally as evident by 6 prophage sequences and 6 genomic islands. 80 tandem repeats and 63 interspersed repeats are found. Average nucleotide identity (ANI) analysis of related ''Alcaligenes'' genomes indicate that strain HO-1 belongs to a new, undescribed species (Wu et al. 2021) | ||
=Cell structure and metabolism= | =Cell structure and metabolism= | ||
Revision as of 15:18, 18 April 2023
Classification
Higher order taxa
- Domain: Bacteria
- Phylum: Proteobacteria
- Class: Beta Proteobacteria
- Order: Burkholderiales
- Family: Alcaligenaceae
- Order: Burkholderiales
- Class: Beta Proteobacteria
- Phylum: Proteobacteria
Species
Species
- Genus: Alcaligenes
- Species: ammonioxydans
Alcaligenes ammonioxydans sp. nov. strain HO-1
Description and significance
The Genus Alcaligenes is composed of Gram negative, typically aerobic species that have a wide range of metabolic capabilities, which included heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification (Hendrie et al. 1974; Wu et al. 2021). Alcaligenes ammonioxydans sp. nov. HO-1 was first isolated from the active sludge of a SHARON bioreactor of a combined system which was used to treat wastewater from pig husbandry (Wu et al. 2021) This species is capable of high amounts of ammonia removal, and without optimization was capable of removing 195.59 mg/L NH4 per day on 28mM NH4.. A. ammonioxydans grew aerobically and achieved ammonia removal on a range of carbon substrates which include acetate, ethanol, propionate, malate, succinate, and citrate and on C/N ratios ranging from 2-20. Optimal pH is 7 but growth is observed at range from 6-10, and optimal temperature is 30°C with growth seen at 23-37°C and growth halts at 45°C (Wu et al. 2021).
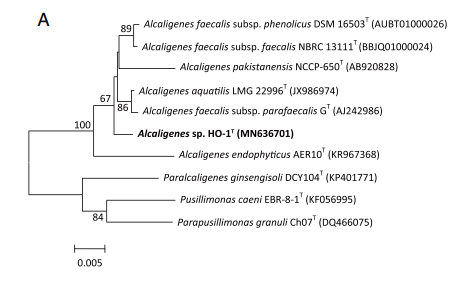
16S Ribosomal RNA Gene Information
Alcaligenes ammonioxydans forms a cluster with other Alcaligenes isolates that is clearly separate from Alcaligenes faecalis but is still closely related (Wu et al. 2021)
Genome Structure
Strain HO-1's genome is completed and consists of one chromosome and is composed of 3.77Mbp with a DNA G+C content of 57.17%. The genome contained 3,320 predicted proteins with 57 tRNA sequences and 9 rRNA operons. Some genes were acquired horizontally as evident by 6 prophage sequences and 6 genomic islands. 80 tandem repeats and 63 interspersed repeats are found. Average nucleotide identity (ANI) analysis of related Alcaligenes genomes indicate that strain HO-1 belongs to a new, undescribed species (Wu et al. 2021)
Cell structure and metabolism
Cells are stained Gram negative and are short rods with an average size of 0.8 µm in width and 1.0-1.5 µm in length. Strain HO-1 was isolated for its heterotrophic ammonia oxidation capabilities, and a novel metabolic pathway which involves the direct oxidation of ammonia to dinitrogen gas through a hydroxylamine intermediate was found. This novel pathway was called direct ammonia oxidation (Dirammox) and is translated from the novel gene cluster dnf. Genes dnfA, dnfB, and dnfC are all upregulated when ammonia is added to culture and is hypothesized to play an important role in this pathway. Alcaligenes have a wide range of nitrogen metabolism capabilities. In addition to the dnf cluser, strain HO-1 contains genes that encode a complete denitrification pathway from nitrite (nirk, norBC, nosZ) as nitrite, but not nitrate, was shown to be reduced in anerobic conditions. In aerobic conditions, neither nitrite nor nitrate is utilized as a sole nitrogen source. Thus, ammonia appears to be its main nitrogen source as the genome contains ammonia transportation and assimilation genes. However, no genes encoding protein homologs of ammonia monooxygenase and hydroxylamine oxidoreductase were found (Wu et al. 2021)