Nostoc: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Biorealm}} | {{Biorealm Genus}} | ||
[[Image:PJnost2.jpg|thumb|400px|right|''Nostoc'' colonies. Image from [http://www.microscopy-uk.org.uk/mag/indexmag.html?http://www.microscopy-uk.org.uk/mag/artoct01/pjnostoc.html Paul James, Microscopy-UK.]]] | [[Image:PJnost2.jpg|thumb|400px|right|''Nostoc'' colonies. Image from [http://www.microscopy-uk.org.uk/mag/indexmag.html?http://www.microscopy-uk.org.uk/mag/artoct01/pjnostoc.html Paul James, Microscopy-UK.]]] | ||
| Line 16: | Line 12: | ||
''Nostoc calcicola, N. commune, N. cycadae, N. desertorum, N. edaphicum, N. ellipsosporum, N. entophytum, N. flagelliforme, N. indistinguenda, N. lichenoides, N. linckia, N. muscorum, N. paludosum, N. piscinale, N. punctiforme, N. sphaericum, N. cf. trichormus 113.5, N. sp.'' | ''Nostoc calcicola, N. commune, N. cycadae, N. desertorum, N. edaphicum, N. ellipsosporum, N. entophytum, N. flagelliforme, N. indistinguenda, N. lichenoides, N. linckia, N. muscorum, N. paludosum, N. piscinale, N. punctiforme, N. sphaericum, N. cf. trichormus 113.5, N. sp.'' | ||
{| | |||
| height="10" bgcolor="#FFDF95" | | |||
'''NCBI: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&id=1177&lvl=3&lin=f&keep=1&srchmode=1&unlock Taxonomy] Genome''' | |||
|} | |||
==Description and Significance== | ==Description and Significance== | ||
Revision as of 14:40, 16 August 2006
A Microbial Biorealm page on the genus Nostoc

Classification
Higher order taxa:
Bacteria; Cyanobacteria]; Nostocales; Nostocaceae
Species:
Nostoc calcicola, N. commune, N. cycadae, N. desertorum, N. edaphicum, N. ellipsosporum, N. entophytum, N. flagelliforme, N. indistinguenda, N. lichenoides, N. linckia, N. muscorum, N. paludosum, N. piscinale, N. punctiforme, N. sphaericum, N. cf. trichormus 113.5, N. sp.
|
NCBI: Taxonomy Genome |
Description and Significance
Nostoc is a diverse genus of simple algae, belonging to the blue-green group. They are found in gelatinous colonies, composed of filaments called "trichomes" surrounded by a thin sheath. They are common in both aquatic and terrestrial habitats. These organisms are known for their unusual ability to lie dormant for long periods of time and abruptly recover metabolic activity when rehydrated with liquid water. The bacteria's ability to withstand freezing and thawing cycles make them well-adapted to living in extreme environments, such as the Arctic and Antarctica. They can fix atmospheric nitrogen, making them good candidates for environments with low nitrogen rates. Nostoc, first discovered in the 19th century, is one of the most widespread phototrophic bacteria in the world. As a nitrogen fixer, these bacteria may provide plants with important nutrients and therefore can be used agriculturally. In 1988 a terrestrial species, Nostoc commune, was found to harbor a previously unidentified UV-A/B absorbing pigment. This protective pigment has enabled them to survive not only while under hydration-related stress, but in areas of extreme UV radiation as well.
Genome Structure
Nostoc's genetics are worth studying because of the genus' unique adaptations which allow them to survive and even thrive in extreme environments. Also, a better understanding of soil-dwelling nitrogen fixers such as Nostoc may help advance fertilizer production and benefit agriculturalists.
Cell Structure and Metabolism
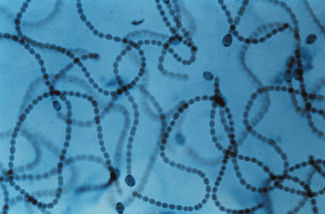
Nostocs are photosynthesizers which use cytoplasmic photosynthetic pigments rather than chloroplasts in their metabolic process. They are single-celled, and lack a nucleus or other internal membrane systems; their cytoplasm is composed 70%-85% of water. The cells do not possess flagella, but are motile by a swaying motion. Division is by binary fission; some branching may occur. The cells form filamentous structures known as trichomes, which in turn make up colonies encased by a thin sheath; these colonies may be mat-like or spherical and are either micro- or macroscopic--spherical colonies may reach sizes of up to 2.6 kg wet weight.
Ecology
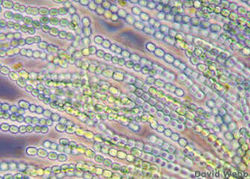
Nostoc environments are diverse and widespread over the globe; isolates have been found in fresh water, soils, and both extremely cold and extremely arid habitats. Their role as a nitrogen fixer in terrestrial ecosystems allow them to maintain symbiotic interactions with organisms including fungi, lichen, mosses, and ferns. They are largely protected from predation by their outer sheath covering and the large size of their colonies, which make them difficult for some algivores to ingest. Some types of Nostoc are edible, and are even considered delicacies in some regions; in China during holidays a black hairlike vegetative species, Nostoc flagelliforme or "fat choy", are consumed. However, these algae can also cause problems for humans by growth on sport turf and buildings, and can lead to unpleasant odors in drinking water. Some phenolic extracts from Nostoc are known as human pathogen inhibitors, and may in the future be valuable to scientists medicinally. Very rarely Nostoc have been found to be symbionts of terrestrial plants, such as species which colonize the root nodules of Hawaiian cycad Gunnera genus.

References
Dodds, Walter K. The Ecology of Nostoc. Journal of Phycology vol 33(1) February 1995. 2-18.
James, Paul. Nostoc. Microscopy-UK.
(Cyanobacteria). Nikon Microscopy.
Webb, David T. Cycad Root Nodules. Botany Department, University of Hawai'i at Manoa.
